Chemistry
(R = 8.314 J/mol K) ( l n 7.5 = 2.01)


$$E_{C{r^{2 + }}/Cr}^o$$ = -0.74 V; $$E_{MnO_4^ - /M{n^{2 + }}}^o$$ = 1.51 V
$$E_{C{r_2}O_7^{2 - }/C{r^{3 + }}}^o$$ = 1.33 V; $$E_{Cl/C{l^ - }}^o$$ = 1.36 V
Based on the data given above, strongest oxidising agent will be :
(h = 6.62 × 10−34 Js and c = 3.0 × 108 ms−1)
$$xMnO_4^- + yC_2O_4^{2-}$$ + zH+ $$\to$$ xMn2+ + 2yCO2 + $${z \over 2}{H_2}O$$
The value's of x, y and z in the reaction are, respectively :
Mathematics
$$\int\limits_{\pi /6}^{\pi /3} {{{dx} \over {1 + \sqrt {\tan \,x} }}} $$ is equal to $$\pi /6$$
Statement-2 : $$\int\limits_a^b {f\left( x \right)} dx = \int\limits_a^b {f\left( {a + b - x} \right)} dx.$$
$${\left( {{{x + 1} \over {{x^{2/3}} - {x^{1/3}} + 1}} - {{x - 1} \over {x - {x^{1/2}}}}} \right)^{10}}$$ is
has no solution, is
Physics



Statement - $${\rm I}$$ : Higher the range, greater is the resistance of ammeter.
Statement - $${\rm I}$$$${\rm I}$$ : To increase the range of ammeter, additional shunt needs to be used across it.

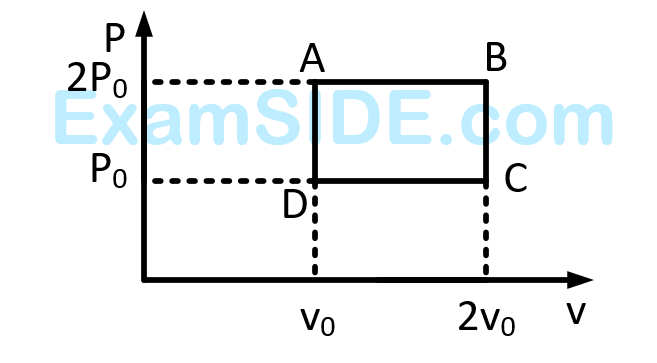
The above $$p$$-$$v$$ diagram represents the thermodynamic cycle of an engine, operating with an ideal monatomic gas. The amount of heat, extracted from the source in a single cycle is
Statement - $${\rm I}$$: A point particle of mass $$m$$ moving with speed $$\upsilon $$ collides with stationary point particle of mass $$M.$$ If the maximum energy loss possible is given as $$f\left( {{1 \over 2}m{v^2}} \right)$$, then $$f = \left( {{m \over {M + m}}} \right).$$
Statement - $${\rm II}$$: Maximum energy loss occurs when the particles get stuck together as a result of the collision.