Chemistry
2NO(g) + O2 (g) $$\leftrightharpoons$$ 2NO2 (g)
The standard free energy of formation of NO(g) is 86.6 kJ/mol at 298 K. What is the standard free energy of formation of NO2(g) at 298 K? (KP = 1.6 × 1012)
| Catalyst | Process | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | TiCl3 | (i) | Wacker process |
| (B) | PdCl2 | (ii) | Ziegler - Natta polymerization |
| (C) | CuCl2 | (iii) | Contact process |
| (D) | V2O5 | (iv) | Deacon's process |

The product $$E$$ is :

The product C is
Reason : The reaction between nitrogen and oxygen requires high temperature.
Mathematics
$$g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {k\sqrt {x + 1} ,} & {0 \le x \le 3} \cr {m\,x + 2,} & {3 < x \le 5} \cr } } \right.$$
is differentiable, then the value of $$k+m$$ is :
$$\left( {x\,\log x} \right){{dy} \over {dx}} + y = 2x\,\log x,\left( {x \ge 1} \right).$$ Then $$y(e)$$ is equal to :
$$\left\{ {\left( {x,y} \right):{y^2} \le 2x} \right.$$ and $$\left. {y \ge 4x - 1} \right\}$$ is :
$$\int\limits_2^4 {{{\log \,{x^2}} \over {\log {x^2} + \log \left( {36 - 12x + {x^2}} \right)}}dx} $$ is equal to :
$$A{A^T} = 9\text{I},$$ where $$I$$ is $$3 \times 3$$ identity matrix, then the ordered
pair $$(a, b)$$ is equal to :
$$\matrix{ {2{x_1} - 2{x_2} + {x_3} = \lambda {x_1}} \cr {2{x_1} - 3{x_2} + 2{x_3} = \lambda {x_2}} \cr { - {x_1} + 2{x_2} = \lambda {x_3}} \cr } $$
has a non-trivial solution
at $$x=1$$ and $$x=2$$. If $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \left[ {1 + {{f\left( x \right)} \over {{x^2}}}} \right] = 3$$, then f$$(2)$$ is equal to :
where $$\left| x \right| < {1 \over {\sqrt 3 }}.$$ Then a value of $$y$$ is :
Physics


An $$LCR$$ circuit is equivalent to a damped pendulum. In an $$LCR$$ circuit the capacitor is charged to $${Q_0}$$ and then connected to the $$L$$ and $$R$$ as shown below :

If a student plots graphs of the square of maximum charge $$\left( {Q_{Max}^2} \right)$$ on the capacitor with time$$(t)$$ for two different values $${L_1}$$ and $${L_2}$$ $$\left( {{L_1} > {L_2}} \right)$$ of $$L$$ then which of the following represents this graph correctly ?
$$\left( {plots\,\,are\,\,schematic\,\,and\,\,niot\,\,drawn\,\,to\,\,scale} \right)$$
A rectangular loop of sides $$10$$ $$cm$$ and $$5$$ $$cm$$ carrying a current $$1$$ of $$12A$$ is placed in different orientations as shown in the figures below :
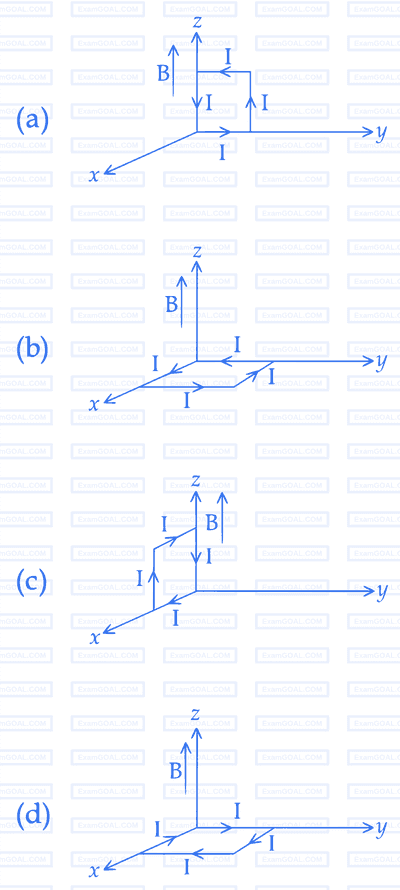
If there is a uniform magnetic field of $$0.3$$ $$T$$ in the positive $$z$$ direction, in which orientations the loop would be in $$(i)$$ stable equilibrium and $$(ii)$$ unstable equilibrium ?
(Assume stones do not rebound after hitting the ground and neglect air resistance, take $$g = 10m/{s^2}$$)
(The figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)

In the circuit shown, the current in the $$1\Omega $$ resistor is :
($$g=$$ $$gravitational$$ $$acceleration$$ )
(figures are schematic and not drawn to scale)
$$\left( {figures\,\,are\,\,drawn\,\,schematically\,\,and\,\,are\,\,not\,\,to\,\,scale} \right)$$

$$(graphs$$ $$are$$ $$schematic$$ $$and$$ $$not$$ $$drawn$$ $$to$$ $$scale)$$
($$g=$$ $$gravitational$$ $$acceleration$$)
($$G=gravitational $$ $$constant$$)
$$(i)$$ Sequentially keeping in contact with $$2$$ reservoirs such that each reservoir
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$supplies same amount of heat.
$$(ii)$$ Sequentially keeping in contact with $$8$$ reservoirs such that each reservoir
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$supplies same amount of heat.
In both the cases body is brought from initial temperature $${100^ \circ }C$$ to final temperature $${200^ \circ }C$$. Entropy change of the body in the two cases respectively is :
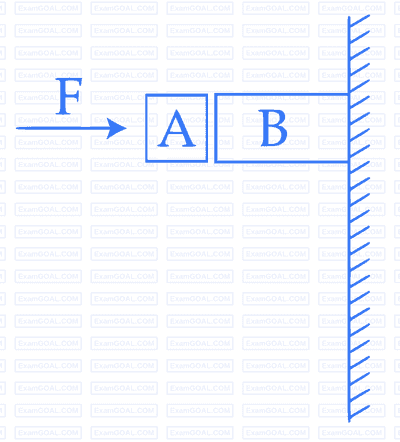
Given in the figure are two blocks $$A$$ and $$B$$ of weight 20 N and 100 N, respectively. These are being pressed against a wall by a force $$F$$ as shown. If the coefficient of friction between the blocks is 0.1 and between block $$B$$ and the wall is 0.15, the frictional force applied by the wall on block $$B$$ is :