1
AIEEE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
Rate of a reaction can be expressed by Arrhenius equation as:
$$$k = A\,{e^{ - E/RT}}$$$ In this equation, E represents
$$$k = A\,{e^{ - E/RT}}$$$ In this equation, E represents
2
AIEEE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
The following mechanism has been proposed for the reaction of NO with Br2 to form NOBr:
NO(g) + Br2 (g) $$\leftrightharpoons$$ NOBr2 (g)
NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) $$\to$$ 2NOBr (g)
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to NO(g) is
NO(g) + Br2 (g) $$\leftrightharpoons$$ NOBr2 (g)
NOBr2 (g) + NO (g) $$\to$$ 2NOBr (g)
If the second step is the rate determining step, the order of the reaction with respect to NO(g) is
3
AIEEE 2005
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
A schematic plot of $$ln$$ $${K_{eq}}$$ versus inverse of temperature for a reaction is shown below
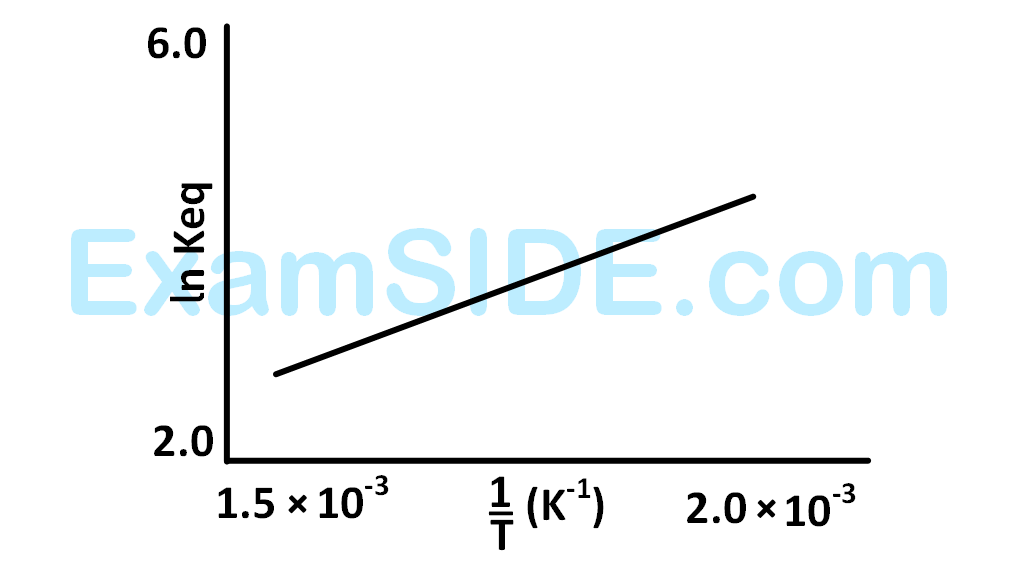
The reaction must be

The reaction must be
4
AIEEE 2005
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
t1/4 can be taken as the time taken for the concentration of a reactant to drop to $$3 \over 4$$ of its initial value. If the rate constant for a first order reaction is K, the t1/4 can be written as
Questions Asked from Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry (MCQ (Single Correct Answer))
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 8th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 7th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 7th April Morning Shift (2)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 4th April Evening Shift (2)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 4th April Morning Shift (2)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 3rd April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 3rd April Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 2nd April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 29th January Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 29th January Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 28th January Evening Shift (2)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 28th January Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 24th January Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 24th January Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 23rd January Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 22nd January Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2025 (Online) 22nd January Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2024 (Online) 8th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2024 (Online) 31st January Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2023 (Online) 11th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2023 (Online) 8th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2023 (Online) 6th April Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2023 (Online) 24th January Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2022 (Online) 28th July Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2022 (Online) 26th July Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2022 (Online) 24th June Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2021 (Online) 1st September Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2021 (Online) 27th July Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2021 (Online) 25th July Morning Shift (1)
JEE Main 2021 (Online) 22th July Evening Shift (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 6th September Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 5th September Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 5th September Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 3rd September Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 3rd September Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 2nd September Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 9th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 8th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 8th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2020 (Online) 7th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 12th April Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 12th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 10th April Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 10th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 9th April Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 9th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 8th April Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 8th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 12th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 12th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 11th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 11th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 10th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 10th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 9th January Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2019 (Online) 9th January Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2018 (Online) 16th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2018 (Offline) (1)
JEE Main 2018 (Online) 15th April Evening Slot (1)
JEE Main 2018 (Online) 15th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2017 (Online) 9th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2017 (Online) 8th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2017 (Offline) (1)
JEE Main 2016 (Online) 10th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2016 (Online) 9th April Morning Slot (1)
JEE Main 2016 (Offline) (1)
JEE Main 2015 (Offline) (1)
JEE Main 2014 (Offline) (1)
JEE Main 2013 (Offline) (1)
AIEEE 2012 (1)
AIEEE 2011 (1)
AIEEE 2010 (2)
AIEEE 2009 (1)
AIEEE 2008 (1)
AIEEE 2007 (4)
AIEEE 2006 (4)
AIEEE 2005 (5)
AIEEE 2004 (4)
AIEEE 2003 (5)
AIEEE 2002 (6)
JEE Main Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Units & Measurements Vector Algebra Motion in a Straight Line Motion in a Plane Circular Motion Laws of Motion Work Power & Energy Center of Mass and Collision Rotational Motion Properties of Matter Heat and Thermodynamics Simple Harmonic Motion Waves Gravitation
Electricity
Electrostatics Current Electricity Capacitor Magnetic Effect of Current Magnetic Properties of Matter Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Current Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Modern Physics
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Structure of Atom Redox Reactions Gaseous State Chemical Equilibrium Ionic Equilibrium Solutions Thermodynamics Electrochemistry Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry Solid State Surface Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Periodic Table & Periodicity Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Isolation of Elements Hydrogen s-Block Elements p-Block Elements d and f Block Elements Coordination Compounds Salt Analysis Environmental Chemistry
Organic Chemistry
Mathematics
Algebra
Sets and Relations Logarithm Quadratic Equation and Inequalities Sequences and Series Mathematical Induction Binomial Theorem Matrices and Determinants Permutations and Combinations Probability Vector Algebra 3D Geometry Complex Numbers Statistics Mathematical Reasoning
Trigonometry
Trigonometric Ratio and Identites Trigonometric Equations Inverse Trigonometric Functions Properties of Triangle Height and Distance
Coordinate Geometry
Calculus