Current Electricity · Physics · JEE Main
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
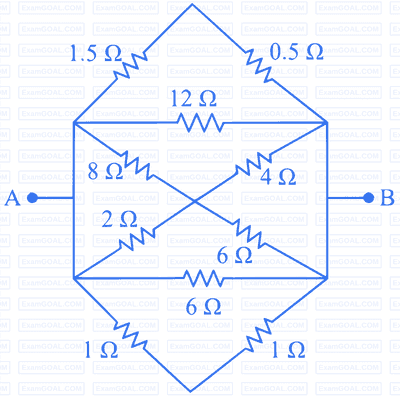
A wire of resistance $R$ is bent into a triangular pyramid as shown in figure with each segment having same length. The resistance between points $A$ and $B$ is $R / n$. The value of $n$ is :

There are ' $n$ ' number of identical electric bulbs, each is designed to draw a power $p$ independently from the mains supply. They are now joined in series across the mains supply. The total power drawn by the combination is :
From the combination of resistors with resistances values $R_1=R_2=R_3=5 \Omega$ and $R_4=10 \Omega$, which of the following combination is the best circuit to get an equivalent resistance of $6 \Omega$ ?
Current passing through a wire as function of time is given as $I(t)=0.02 t+0.01 \mathrm{~A}$. The charge that will flow through the wire from $t=1 \mathrm{~s}$ to $t=2 \mathrm{~s}$ is
The battery of a mobile phone is rated as $4.2 \mathrm{~V}, 5800 \mathrm{~mAh}$. How much energy is stored ir it when fully charged?
Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : Choke coil is simply a coil having a large inductance but a small resistance. Choke coils are used with fluorescent mercury-tube fittings. If household electric power is directly connected to a mercury tube, the tube will be damaged.
Reason (R): By using the choke coil, the voltage across the tube is reduced by a factor $\left(R / \sqrt{R^2+\omega^2 L^2}\right)$, where $\omega$ is frequency of the supply across resistor $R$ and inductor $L$. If the choke coil were not used, the voltage across the resistor would be the same as the applied voltage.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :

In the circuit shown here, assuming threshold voltage of diode is negligibly small, then voltage $ V_{AB} $ is correctly represented by:
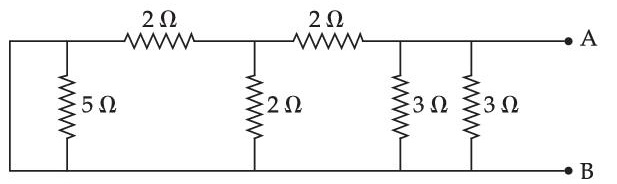
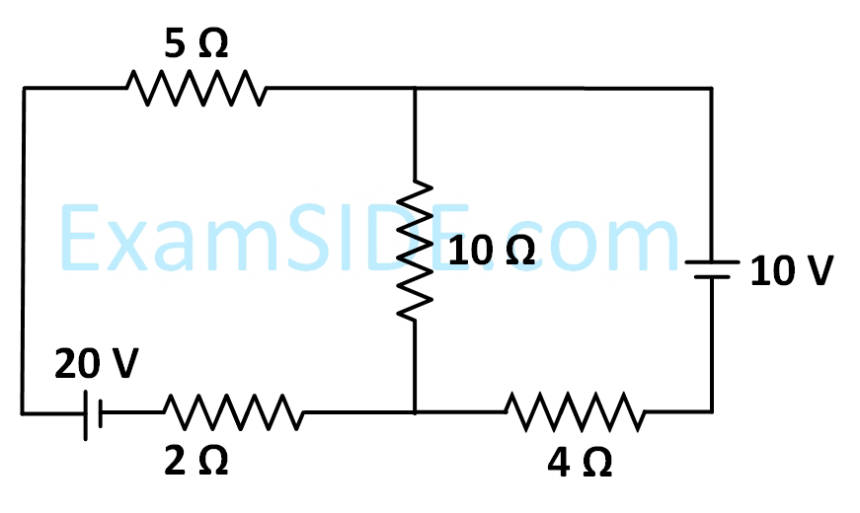
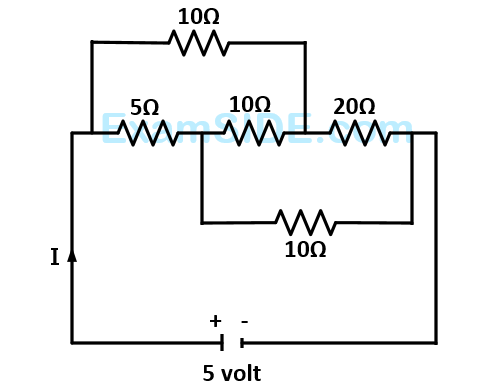
Find the equivalent resistance between two ends of the following circuit

A wire of resistance R is bent into an equilateral triangle and an identical wire is bent into $a$ square. The ratio of resistance between the two end points of an edge of the triangle to that of the square is
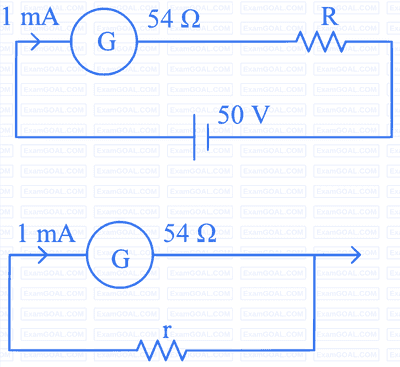
A galvanometer having a coil of resistance $30 \Omega$ need 20 mA of current for full-scale deflection. If a maximum current of 3 A is to be measured using this galvanometer, the resistance of the shunt to be added to the galvanometer should be $\frac{30}{X} \Omega$, where $X$ is
Consider a moving coil galvanomenter (MCG):
A. The torsional constant in moving coil galvanometer has dimensions $\left[\mathrm{ML}^2 \mathrm{~T}^{-2}\right]$
B. Increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage sensitivity.
C. If we increase number of turns $(\mathrm{N})$ to its double $(2 \mathrm{~N})$, then the voltage sensitivity doubles.
D. MCG can be converted into an ammeter by introducing a shunt resistance of large value in parallel with galvanometer.
E. Current sensitivity of MCG depends inversely on number of turns of coil.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Given below are two statements :
Statement-I : The equivalent emf of two nonideal batteries connected in parallel is smaller than either of the two emfs.
Statement-II : The equivalent internal resistance of two nonideal batteries connected in parallel is smaller than the internal resistance of either of the two batteries.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
Which of the following resistivity ( $\rho$ ) $\mathrm{v} / \mathrm{s}$ temperature ( T ) curves is most suitable to be used in wire bound standard resistors?

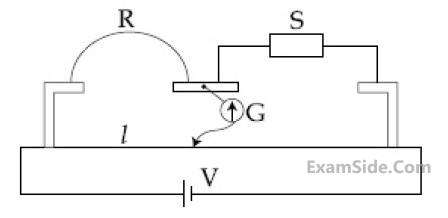
Sliding contact of a potentiometer is in the middle of the potentiometer wire having resistance $R_p=1 \Omega$ as shown in the figure. An external resistance of $R_e=2 \Omega$ is connected via the sliding contact. The electric current in the circuit is :
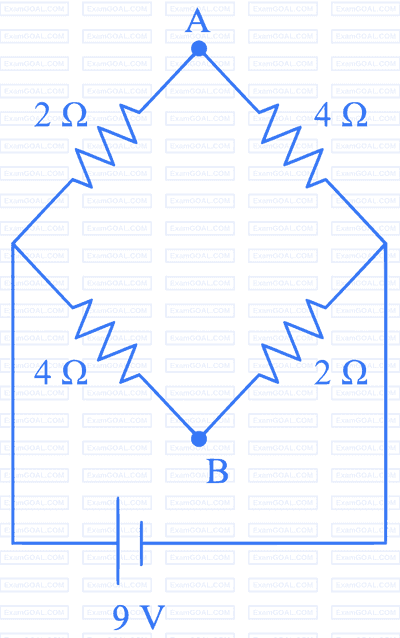
The effective resistance between $$A$$ and $$B$$, if resistance of each resistor is $$R$$, will be :

A galvanometer has a coil of resistance $$200 \Omega$$ with a full scale deflection at $$20 \mu \mathrm{A}$$. The value of resistance to be added to use it as an ammeter of range $$(0-20) \mathrm{mA}$$ is :
The equivalent resistance between A and B is :

Water boils in an electric kettle in 20 minutes after being switched on. Using the same main supply, the length of the heating element should be _________ to __________ times of its initial length if the water is to be boiled in 15 minutes.
In the given circuit, the terminal potential difference of the cell is :

The number of electrons flowing per second in the filament of a $$110 \mathrm{~W}$$ bulb operating at $$220 \mathrm{~V}$$ is : (Given $$\mathrm{e}=1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}$$)
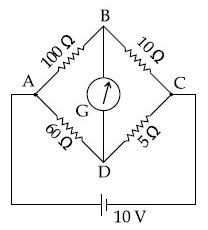
The value of unknown resistance $$(x)$$ for which the potential difference between $$B$$ and $$D$$ will be zero in the arrangement shown, is :

The ratio of heat dissipated per second through the resistance $$5 \Omega$$ and $$10 \Omega$$ in the circuit given below is:

A galvanometer of resistance $$100 \Omega$$ when connected in series with $$400 \Omega$$ measures a voltage of upto $$10 \mathrm{~V}$$. The value of resistance required to convert the galvanometer into ammeter to read upto $$10 \mathrm{~A}$$ is $$x \times 10^{-2} \Omega$$. The value of $$x$$ is :
In the given figure $$\mathrm{R}_1=10 \Omega, \mathrm{R}_2=8 \Omega, \mathrm{R}_3=4 \Omega$$ and $$\mathrm{R}_4=8 \Omega$$. Battery is ideal with emf $$12 \mathrm{~V}$$. Equivalent resistant of the circuit and current supplied by battery are respectively :

An electric bulb rated $$50 \mathrm{~W}-200 \mathrm{~V}$$ is connected across a $$100 \mathrm{~V}$$ supply. The power dissipation of the bulb is:
To measure the internal resistance of a battery, potentiometer is used. For $$R=10 \Omega$$, the balance point is observed at $$l=500 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and for $$\mathrm{R}=1 \Omega$$ the balance point is observed at $$l=400 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The internal resistance of the battery is approximately :

By what percentage will the illumination of the lamp decrease if the current drops by 20%?
The resistance per centimeter of a meter bridge wire is $$r$$, with $$X \Omega$$ resistance in left gap. Balancing length from left end is at $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$ with $$25 \Omega$$ resistance in right gap. Now the wire is replaced by another wire of $$2 r$$ resistance per centimeter. The new balancing length for same settings will be at
Two conductors have the same resistances at $$0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ but their temperature coefficients of resistance are $$\alpha_1$$ and $$\alpha_2$$. The respective temperature coefficients for their series and parallel combinations are :
When a potential difference $$V$$ is applied across a wire of resistance $$R$$, it dissipates energy at a rate $$W$$. If the wire is cut into two halves and these halves are connected mutually parallel across the same supply, the energy dissipation rate will become:
A potential divider circuit is shown in figure. The output voltage V$$_0$$ is :

An electric toaster has resistance of $$60 \Omega$$ at room temperature $$\left(27^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right)$$. The toaster is connected to a $$220 \mathrm{~V}$$ supply. If the current flowing through it reaches $$2.75 \mathrm{~A}$$, the temperature attained by toaster is around : ( if $$\alpha=2 \times 10^{-4}$$/$$^\circ \mathrm{C}$$)
In the given circuit, the current in resistance R$$_3$$ is :

The deflection in moving coil galvanometer falls from 25 divisions to 5 division when a shunt of $$24 \Omega$$ is applied. The resistance of galvanometer coil will be :
A galvanometer having coil resistance $$10 \Omega$$ shows a full scale deflection for a current of $$3 \mathrm{~mA}$$. For it to measure a current of $$8 \mathrm{~A}$$, the value of the shunt should be:
The electric current through a wire varies with time as $$I=I_0+\beta t$$, where $$I_0=20 \mathrm{~A}$$ and $$\beta=3 \mathrm{~A} / \mathrm{s}$$. The amount of electric charge crossed through a section of the wire in $$20 \mathrm{~s}$$ is :
Three voltmeters, all having different internal resistances are joined as shown in figure. When some potential difference is applied across $$A$$ and $$B$$, their readings are $$V_1, V_2$$ and $$V_3$$. Choose the correct option.

A current of $$200 \mu \mathrm{A}$$ deflects the coil of a moving coil galvanometer through $$60^{\circ}$$. The current to cause deflection through $$\frac{\pi}{10}$$ radian is :
Wheatstone bridge principle is used to measure the specific resistance $$\left(S_1\right)$$ of given wire, having length $$L$$, radius $$r$$. If $$X$$ is the resistance of wire, then specific resistance is ; $$S_1=X\left(\frac{\pi r^2}{L}\right)$$. If the length of the wire gets doubled then the value of specific resistance will be :
A wire of length $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and radius $$\sqrt{7} \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}$$ connected across the right gap of a meter bridge. When a resistance of $$4.5 \Omega$$ is connected on the left gap by using a resistance box, the balance length is found to be at $$60 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the left end. If the resistivity of the wire is $$\mathrm{R} \times 10^{-7} \Omega \mathrm{m}$$, then value of $$\mathrm{R}$$ is :
A wire of resistance $$\mathrm{R}$$ and length $$\mathrm{L}$$ is cut into 5 equal parts. If these parts are joined parallely, then resultant resistance will be :
(A) for voltmeter $R \approx 50 \mathrm{k} \Omega$
(B) for ammeter $\mathrm{r} \approx 0.2 \Omega$
(C) for ammeter $\mathrm{r}=6 \Omega$
(D) for voltmeter $R \approx 5 \mathrm{k} \Omega$
(E) for voltmeter $R \approx 500 \Omega$
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
Statement I : The equivalent resistance of resistors in a series combination is smaller than least resistance used in the combination.
Statement II : The resistivity of the material is independent of temperature.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Different combination of 3 resistors of equal resistance $$\mathrm{R}$$ are shown in the figures. The increasing order for power dissipation is:

A wire of resistance $$160 ~\Omega$$ is melted and drawn in a wire of one-fourth of its length. The new resistance of the wire will be

The current flowing through R$$_2$$ is :
Two identical heater filaments are connected first in parallel and then in series. At the same applied voltage, the ratio of heat produced in same time for parallel to series will be:
The current sensitivity of moving coil galvanometer is increased by $$25 \%$$. This increase is achieved only by changing in the number of turns of coils and area of cross section of the wire while keeping the resistance of galvanometer coil constant. The percentage change in the voltage sensitivity will be:
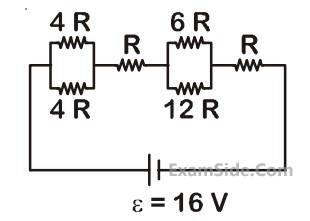
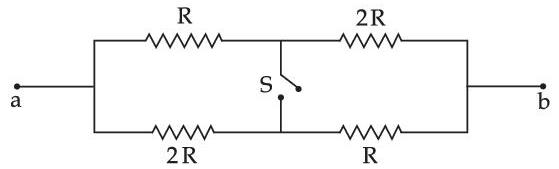
The equivalent resistance of the circuit shown below between points a and b is :

The equivalent resistance between A and B as shown in figure is:

Figure shows a part of an electric circuit. The potentials at points $$a, b$$ and $$c$$ are $$30 \mathrm{~V}, 12 \mathrm{~V}$$ and $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$ respectively. The current through the $$20 ~\Omega$$ resistor will be,

A student is provided with a variable voltage source $$\mathrm{V}$$, a test resistor $$R_{T}=10 ~\Omega$$, two identical galvanometers $$G_{1}$$ and $$G_{2}$$ and two additional resistors, $$R_{1}=10 ~M \Omega$$ and $$R_{2}=0.001 ~\Omega$$. For conducting an experiment to verify ohm's law, the most suitable circuit is:
Given below are two statements : One is labelled as Assertion $$\mathbf{A}$$ and the other is labelled as Reason $$\mathbf{R}$$.
Assertion A : For measuring the potential difference across a resistance of $$600 \Omega$$, the voltmeter with resistance $$1000 \Omega$$ will be preferred over voltmeter with resistance $$4000 \Omega$$.
Reason R : Voltmeter with higher resistance will draw smaller current than voltmeter with lower resistance.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below.
Equivalent resistance between the adjacent corners of a regular n-sided polygon of uniform wire of resistance R would be :
The equivalent resistance between $$A$$ and $$B$$ of the network shown in figure;

The drift velocity of electrons for a conductor connected in an electrical circuit is $$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{d}}$$. The conductor in now replaced by another conductor with same material and same length but double the area of cross section. The applied voltage remains same. The new drift velocity of electrons will be
The charge flowing in a conductor changes with time as $$\mathrm{Q}(\mathrm{t})=\alpha \mathrm{t}-\beta \mathrm{t}^{2}+\gamma \mathrm{t}^{3}$$. Where $$\alpha, \beta$$ and $$\gamma$$ are constants. Minimum value of current is :
With the help of potentiometer, we can determine the value of emf of a given cell. The sensitivity of the potentiometer is
(A) directly proportional to the length of the potentiometer wire
(B) directly proportional to the potential gradient of the wire
(C) inversely proportional to the potential gradient of the wire
(D) inversely proportional to the length of the potentiometer wire
Choose the correct option for the above statements :
Ratio of thermal energy released in two resistors R and 3R connected in parallel in an electric circuit is :
The resistance of a wire is 5 $$\Omega$$. It's new resistance in ohm if stretched to 5 times of it's original length will be :
A uniform metallic wire carries a current 2 A, when 3.4 V battery is connected across it. The mass of uniform metallic wire is 8.92 $$\times$$ 10$$^{-3}$$ kg, density is 8.92 $$\times$$ 10$$^{3}$$ kg/m$$^3$$ and resistivity is 1.7 $$\times$$ 10$$^{-8}~\Omega$$-$$\mathrm{m}$$. The length of wire is :
A cell of emf 90 V is connected across series combination of two resistors each of 100$$\Omega$$ resistance. A voltmeter of resistance 400$$\Omega$$ is used to measure the potential difference across each resistor. The reading of the voltmeter will be :
As shown in the figure, a network of resistors is connected to a battery of 24V with an internal resistance of 3 $$\Omega$$. The currents through the resistors R$$_4$$ and R$$_5$$ are I$$_4$$ and I$$_5$$ respectively. The values of I$$_4$$ and I$$_5$$ are :

Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R.
Assertion A: Alloys such as constantan and manganin are used in making standard resistance coils.
Reason R: Constantan and manganin have very small value of temperature coefficient of resistance.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ long wire is broken into two unequal parts $$\mathrm{X}$$ and $$\mathrm{Y}$$. The $$\mathrm{X}$$ part of the wire is streched into another wire W. Length of $$W$$ is twice the length of $$X$$ and the resistance of $$\mathrm{W}$$ is twice that of $$\mathrm{Y}$$. Find the ratio of length of $$\mathrm{X}$$ and $$\mathrm{Y}$$.
Two metallic wires of identical dimensions are connected in series. If $$\sigma_{1}$$ and $$\sigma_{2}$$ are the conductivities of the these wires respectively, the effective conductivity of the combination is :
Given below are two statements :
Statement I : A uniform wire of resistance $$80 \,\Omega$$ is cut into four equal parts. These parts are now connected in parallel. The equivalent resistance of the combination will be $$5 \,\Omega$$.
Statement II: Two resistances 2R and 3R are connected in parallel in a electric circuit. The value of thermal energy developed in 3R and 2R will be in the ratio $$3: 2$$.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the option given below
A wire of resistance R1 is drawn out so that its length is increased by twice of its original length. The ratio of new resistance to original resistance is :
(A) The drift velocity of electrons decreases with the increase in the temperature of conductor.
(B) The drift velocity is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of given conductor.
(C) The drift velocity does not depend on the applied potential difference to the conductor.
(D) The drift velocity of electron is inversely proportional to the length of the conductor.
(E) The drift velocity increases with the increase in the temperature of conductor.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Two sources of equal emfs are connected in series. This combination is connected to an external resistance R. The internal resistances of the two sources are $$r_{1}$$ and $$r_{2}$$ $$\left(r_{1}>r_{2}\right)$$. If the potential difference across the source of internal resistance $$r_{1}$$ is zero, then the value of R will be :
A battery of $$6 \mathrm{~V}$$ is connected to the circuit as shown below. The current I drawn from the battery is :

The current I in the given circuit will be :

A current of 15 mA flows in the circuit as shown in figure. The value of potential difference between the points A and B will be:

Which of the following physical quantities have the same dimensions?
An electric cable of copper has just one wire of radius 9 mm. Its resistance is 14 $$\Omega$$. If this single copper wire of the cable is replaced by seven identical well insulated copper wires each of radius 3 mm connected in parallel, then the new resistance of the combination will be :
The combination of two identical cells, whether connected in series or parallel combination provides the same current through an external resistance of 2$$\Omega$$. The value of internal resistance of each cell is
Resistance of the wire is measured as 2 $$\Omega$$ and 3 $$\Omega$$ at 10$$^\circ$$C and 30$$^\circ$$C respectively. Temperature co-efficient of resistance of the material of the wire is :
A 72 $$\Omega$$ galvanometer is shunted by a resistance of 8 $$\Omega$$. The percentage of the total current which passes through the galvanometer is :
The equivalent resistance between points A and B in the given network is :

An aluminium wire is stretched to make its length, 0.4% larger. The percentage change in resistance is :
Two cells of same emf but different internal resistances r1 and r2 are connected in series with a resistance R. The value of resistance R, for which the potential difference across second cell is zero, is :
If n represents the actual number of deflections in a converted galvanometer of resistance G and shunt resistance S. Then the total current I when its figure of merit is K will be:
A teacher in his physics laboratory allotted an experiment to determine the resistance (G) of a galvanometer. Students took the observations for $${1 \over 3}$$ deflection in the galvanometer. Which of the below is true for measuring value of G?
What will be the most suitable combination of three resistors A = 2$$\Omega$$, B = 4$$\Omega$$, C = 6$$\Omega$$ so that $$\left( {{{22} \over 3}} \right)$$$$\Omega$$ is equivalent resistance of combination?
Two identical cells each of emf 1.5 V are connected in parallel across a parallel combination of two resistors each of resistance 20 $$\Omega$$. A voltmeter connected in the circuit measures 1.2 V. The internal resistance of each cell is :


(Given resistivities of iron and copper-nickel alloy wire are 12 $$\mu$$$$\Omega$$ and 51 $$\mu$$$$\Omega$$ cm respectively)
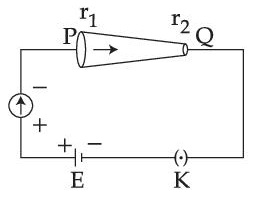
Choose the correct option as one moves from P to Q :



(Take Resistivity of Copper = 1.7 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$8 $$\Omega$$m and Resistivity of Aluminium = 2.6 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$8 $$\Omega$$m)

(Resistivity of magnesium $$\rho$$ = 44 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$8 $$\Omega$$m)
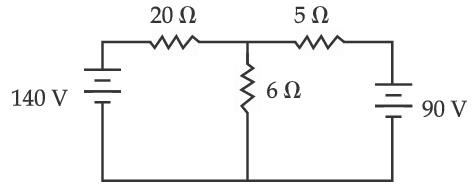
The value of current in the 6 $$\Omega$$ resistance is :
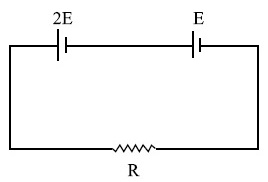
If the length of the wire of the same material is doubled and the area of cross-section is halved, the resultant current would be :

i = $$\alpha$$0t + $$\beta$$t2
where $$\alpha$$0 = 20 A/s and $$\beta$$ = 8 As$$-$$2. Find the charge crossed through a section of the wire in 15 s.

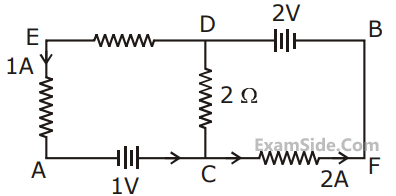




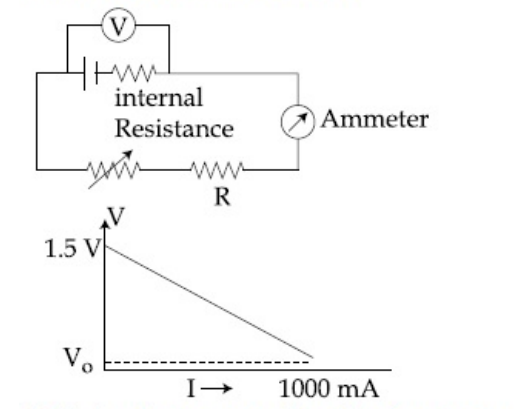
If V0 is almost zero, identify the correct statement :

| SI. No. | R($$\Omega $$) | l(cm) |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1000 | 60 |
| 2. | 100 | 13 |
| 3. | 10 | 1.5 |
| 4. | 1 | 1.0 |


(me = 9.1 × 10–31 kg)


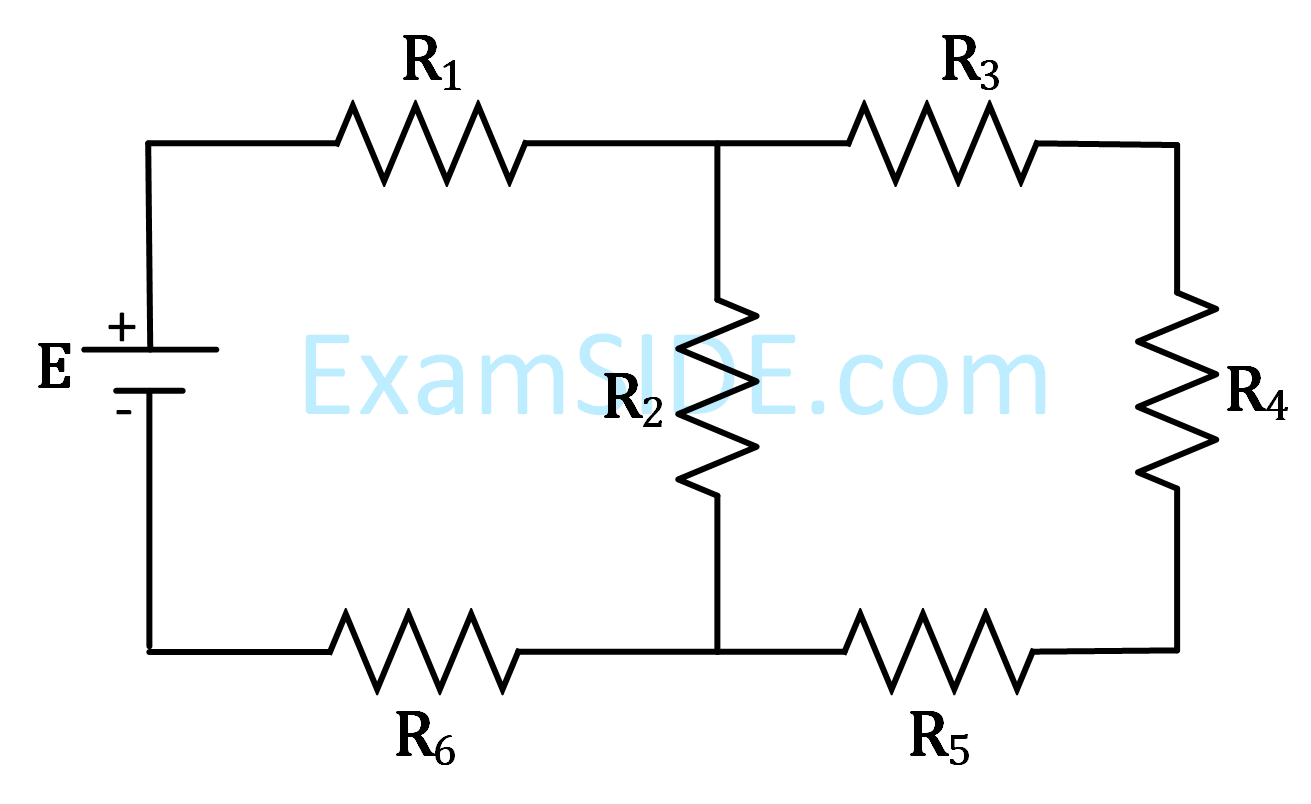
You are given: R1 = 15$$\Omega $$, R2 = 10 $$\Omega $$, R3 = 20 $$\Omega $$, R4 = 5$$\Omega $$, R5 = 25$$\Omega $$, R6 = 30 $$\Omega $$, E = 15 V



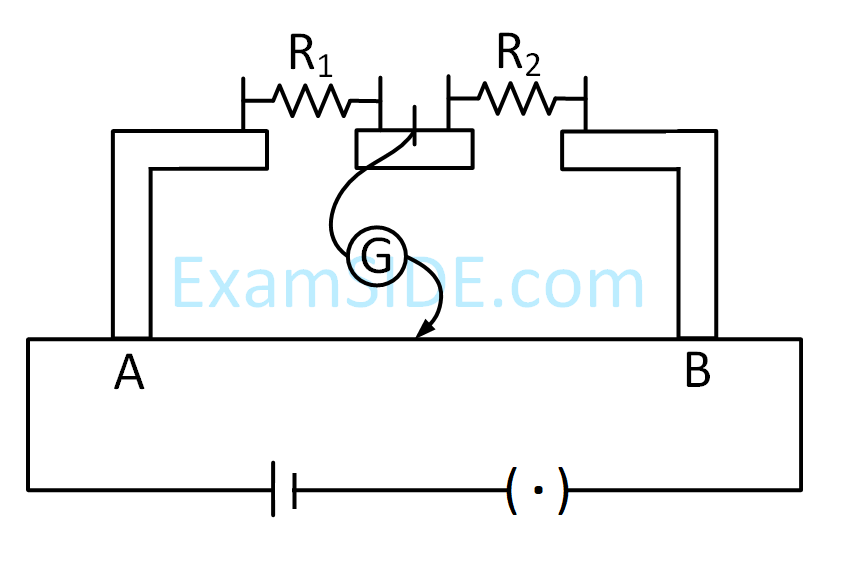




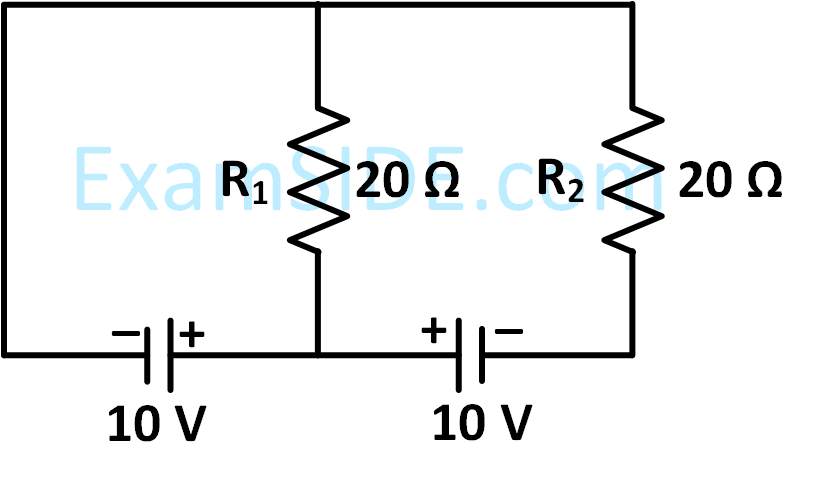






In a meter bridge, as shown in the figure, it is given that resistance $$Y = 12.5\,\,\Omega $$ and that the balance is obtained at a distance $$39.5$$ $$cm$$ from end $$A$$ (by Jockey J). After interchanging the resistances $$X$$ and $$Y$$, a new balance point is found at a distance $${l_2}$$ from end $$A.$$ What are the value of $$X$$ and $${l_2}$$ ?




A 9 V battery with internal resistance of 0.5 $$\Omega $$ is connected across an infinite network as shown in the figure. All ammeters A1, A2, 3 and voltmeter V are ideal.
Choose correct statement.


In the given circuit, the current in each resistance is:


In the circuit shown, the resistance r is a variable resistance. If for r = fR, the heat generation in r is maximum then the value of f is :

In the circuit shown, the current in the $$1\Omega $$ resistor is :
Statement - $${\rm I}$$ : Higher the range, greater is the resistance of ammeter.
Statement - $${\rm I}$$$${\rm I}$$ : To increase the range of ammeter, additional shunt needs to be used across it.
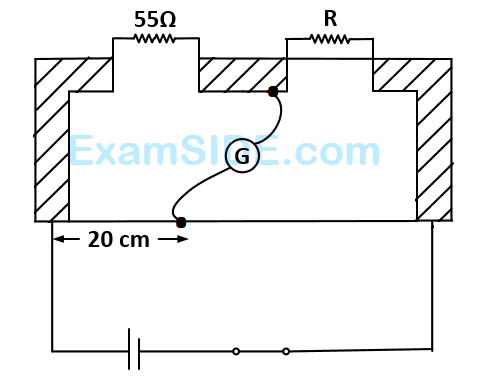
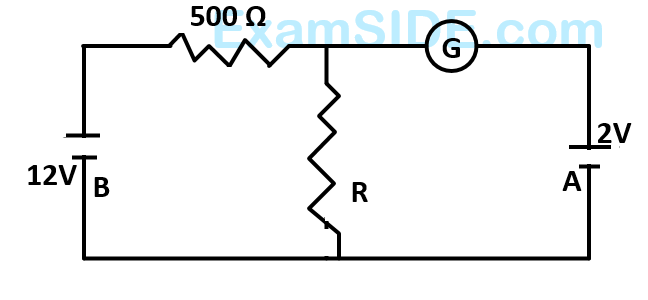
The value of the unknown resister $$R$$ is
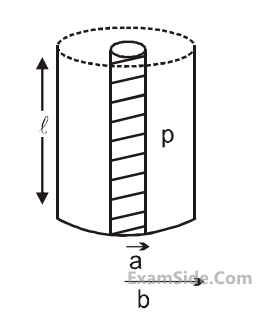
(i) Take current $$'I'$$ entering from $$'A'$$ and assume it to spread over a hemispherical surface in the block.
(ii) Calculate field $$E(r)$$ at distance $$'r'$$ from A by using Ohm's law $$E = \rho j,$$ where $$j$$ is the current per unit area at $$'r'$$.
(iii) From the $$'r'$$ dependence of $$E(r)$$, obtain the potential $$V(r)$$ at $$r$$.
(iv) Repeat (i), (ii) and (iii) for current $$'I'$$ leaving $$'D'$$ and superpose results for $$'A'$$ and $$'D'.$$
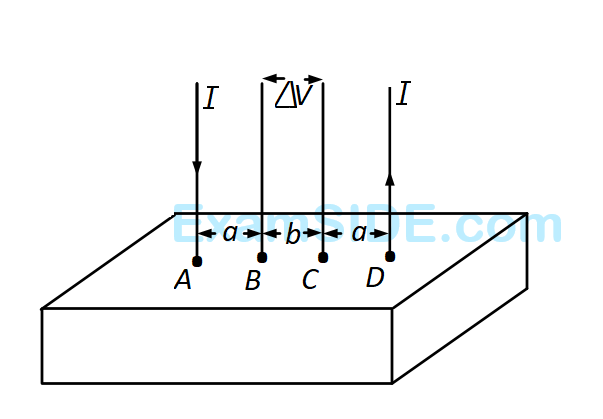
For current entering at $$A,$$ the electric field at a distance $$'r'$$ from $$A$$ is
(i) Take current $$'I'$$ entering from $$'A'$$ and assume it to spread over a hemispherical surface in the block.
(ii) Calculate field $$E(r)$$ at distance $$'r'$$ from A by using Ohm's law $$E = \rho j,$$ where $$j$$ is the current per unit area at $$'r'$$.
(iii) From the $$'r'$$ dependence of $$E(r)$$, obtain the potential $$V(r)$$ at $$r$$.
(iv) Repeat (i), (ii) and (iii) for current $$'I'$$ leaving $$'D'$$ and superpose results for $$'A'$$ and $$'D'.$$

$$\Delta V$$ measured between $$B$$ and $$C$$ is
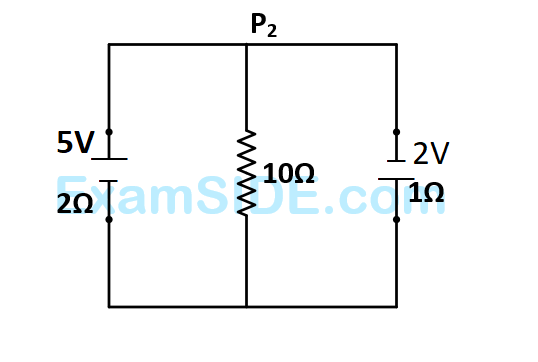
The current in the $$10\Omega $$ resistor is
where $$i$$ is the current in the potentiometer wire.

Numerical
Two cells of emfs 1 V and 2 V and internal resistances $2 \Omega$ and $1 \Omega$, respectively, are connected in series with an external resistance of $6 \Omega$. The total current in the circuit is $I_1$. Now the same two cells in parallel configuration are connected to same external resistance. In this case, the total current drawn is $\mathrm{I}_2$. The value of $\left(\frac{\mathrm{I}_1}{\mathrm{I}_2}\right)$ is $\frac{x}{3}$. The value of $x$ is___________.
In the figure shown below, a resistance of $150.4 \Omega$ is connected in series to an ammeter A of resistance $240 \Omega$. A shunt resistance of $10 \Omega$ is connected in parallel with the ammeter. The reading of the ammeter is___________mA .

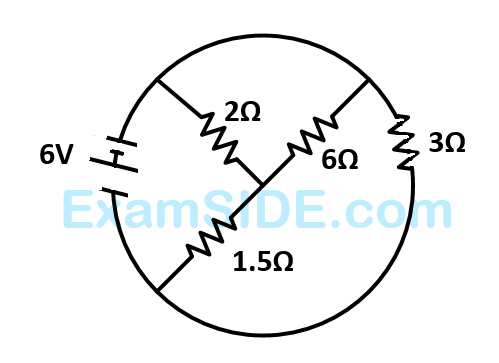
The value of current I in the electrical circuit as given below, when potential at A is equal to the potential at B, will be _______ A.

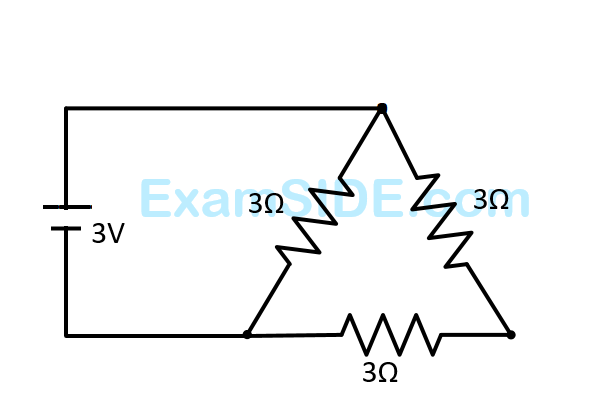
A wire of resistance $9 \Omega$ is bent to form an equilateral triangle. Then the equivalent resistance across any two vertices will be _________ ohm.
The net current flowing in the given circuit is __________ A.

To determine the resistance (R) of a wire, a circuit is designed below. The $$V$$-$$I$$ characteristic curve for this circuit is plotted for the voltmeter and the ammeter readings as shown in figure. The value of $R$ is _________ $$\Omega$$.

At room temperature $$(27^{\circ} \mathrm{C})$$, the resistance of a heating element is $$50 \Omega$$. The temperature coefficient of the material is $$2.4 \times 10^{-4}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}^{-1}$$. The temperature of the element, when its resistance is $$62 \Omega$$, is __________$${ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$.
The current flowing through the $$1 \Omega$$ resistor is $$\frac{n}{10}$$ A. The value of $$n$$ is _______.

A heater is designed to operate with a power of $$1000 \mathrm{~W}$$ in a $$100 \mathrm{~V}$$ line. It is connected in combination with a resistance of $$10 \Omega$$ and a resistance $$R$$, to a $$100 \mathrm{~V}$$ mains as shown in figure. For the heater to operate at $$62.5 \mathrm{~W}$$, the value of $$\mathrm{R}$$ should be _______ $$\Omega$$.

Resistance of a wire at $$0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}, 100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ and $$t^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ is found to be $$10 \Omega, 10.2 \Omega$$ and $$10.95 \Omega$$ respectively. The temperature $$t$$ in Kelvin scale is _________.
In the given figure an ammeter A consists of a $$240 \Omega$$ coil connected in parallel to a $$10 \Omega$$ shunt. The reading of the ammeter is ________ $$\mathrm{mA}$$.

A wire of resistance $$R$$ and radius $$r$$ is stretched till its radius became $$r / 2$$. If new resistance of the stretched wire is $$x ~R$$, then value of $$x$$ is ________.
A wire of resistance $$20 \Omega$$ is divided into 10 equal parts, resulting pairs. A combination of two parts are connected in parallel and so on. Now resulting pairs of parallel combination are connected in series. The equivalent resistance of final combination is _________ $$\Omega$$.
In the experiment to determine the galvanometer resistance by half-deflection method, the plot of $$1 / \theta$$ vs the resistance (R) of the resistance box is shown in the figure. The figure of merit of the galvanometer is _________ $$\times 10^{-1} \mathrm{~A} /$$ division. [The source has emf $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$]

Two wires $$A$$ and $$B$$ are made up of the same material and have the same mass. Wire $$A$$ has radius of $$2.0 \mathrm{~mm}$$ and wire $$B$$ has radius of $$4.0 \mathrm{~mm}$$. The resistance of wire $$B$$ is $$2 \Omega$$. The resistance of wire $$A$$ is ________ $$\Omega$$.
Twelve wires each having resistance $$2 \Omega$$ are joined to form a cube. A battery of $$6 \mathrm{~V}$$ emf is joined across point $$a$$ and $$c$$. The voltage difference between $$e$$ and $$f$$ is ________ V.

In the following circuit, the battery has an emf of $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$ and an internal resistance of $$\frac{2}{3} \Omega$$. The power consumption in the entire circuit is _________ W.

Equivalent resistance of the following network is __________ $$\Omega$$.

Two resistance of $$100 \Omega$$ and $$200 \Omega$$ are connected in series with a battery of $$4 \mathrm{~V}$$ and negligible internal resistance. A voltmeter is used to measure voltage across $$100 \Omega$$ resistance, which gives reading as $$1 \mathrm{~V}$$. The resistance of voltmeter must be _______ $$\Omega$$.
Two cells are connected in opposition as shown. Cell $$\mathrm{E}_1$$ is of $$8 \mathrm{~V}$$ emf and $$2 \Omega$$ internal resistance; the cell $$\mathrm{E}_2$$ is of $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$ emf and $$4 \Omega$$ internal resistance. The terminal potential difference of cell $$\mathrm{E}_2$$ is __________ V.

In the given circuit, the current flowing through the resistance $$20 \Omega$$ is $$0.3 \mathrm{~A}$$, while the ammeter reads $$0.9 \mathrm{~A}$$. The value of $$\mathrm{R}_1$$ is _________ $$\Omega$$.


When a resistance of $$5 ~\Omega$$ is shunted with a moving coil galvanometer, it shows a full scale deflection for a current of $$250 \mathrm{~mA}$$, however when $$1050 ~\Omega$$ resistance is connected with it in series, it gives full scale deflection for 25 volt. The resistance of galvanometer is ____________ $$\Omega$$.
A potential $$\mathrm{V}_{0}$$ is applied across a uniform wire of resistance $$R$$. The power dissipation is $$P_{1}$$. The wire is then cut into two equal halves and a potential of $$V_{0}$$ is applied across the length of each half. The total power dissipation across two wires is $$P_{2}$$. The ratio $$P_{2}: \mathrm{P}_{1}$$ is $$\sqrt{x}: 1$$. The value of $$x$$ is ___________.
The current flowing through a conductor connected across a source is $$2 \mathrm{~A}$$ and 1.2 $$\mathrm{A}$$ at $$0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ and $$100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ respectively. The current flowing through the conductor at $$50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ will be ___________ $$\times 10^{2} \mathrm{~mA}$$.
Two identical cells each of emf $$1.5 \mathrm{~V}$$ are connected in series across a $$10 ~\Omega$$ resistance. An ideal voltmeter connected across $$10 ~\Omega$$ resistance reads $$1.5 \mathrm{~V}$$. The internal resistance of each cell is __________ $$\Omega$$.
In the circuit diagram shown in figure given below, the current flowing through resistance $$3 ~\Omega$$ is $$\frac{x}{3} A$$.
The value of $$x$$ is ___________

A rectangular parallelopiped is measured as $$1 \mathrm{~cm} \times 1 \mathrm{~cm} \times 100 \mathrm{~cm}$$. If its specific resistance is $$3 \times 10^{-7} ~\Omega \mathrm{m}$$, then the resistance between its two opposite rectangular faces will be ___________ $$\times 10^{-7} ~\Omega$$.
10 resistors each of resistance 10 $$\Omega$$ can be connected in such as to get maximum and minimum equivalent resistance. The ratio of maximum and minimum equivalent resistance will be ___________.
The number density of free electrons in copper is nearly $$8 \times 10^{28} \mathrm{~m}^{-3}$$. A copper wire has its area of cross section $$=2 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~m}^{2}$$ and is carrying a current of $$3.2 \mathrm{~A}$$. The drift speed of the electrons is ___________ $$\times 10^{-6} \mathrm{ms}^{-1}$$
A current of $$2 \mathrm{~A}$$ flows through a wire of cross-sectional area $$25.0 \mathrm{~mm}^{2}$$. The number of free electrons in a cubic meter are $$2.0 \times 10^{28}$$. The drift velocity of the electrons is __________ $$\times 10^{-6} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$ (given, charge on electron $$=1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}$$ ).
As shown in the figure, the voltmeter reads $$2 \mathrm{~V}$$ across $$5 ~\Omega$$ resistor. The resistance of the voltmeter is _________ $$\Omega$$.

The length of a metallic wire is increased by $$20 \%$$ and its area of cross section is reduced by $$4 \%$$. The percentage change in resistance of the metallic wire is __________.
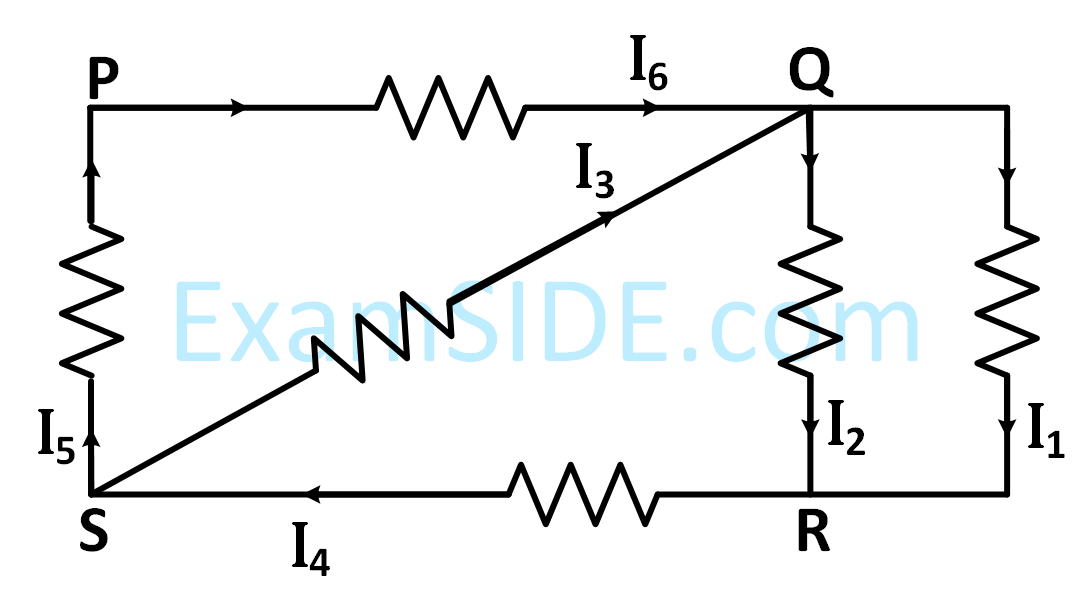
In the given circuit, the value of $$\left| {{{{\mathrm{I_1}} + {\mathrm{I_3}}} \over {{\mathrm{I_2}}}}} \right|$$ is _____________

In an experiment to find emf of a cell using potentiometer, the length of null point for a cell of emf $$1.5 \mathrm{~V}$$ is found to be $$60 \mathrm{~cm}$$. If this cell is replaced by another cell of emf E, the length-of null point increases by $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of $$E$$ is $$\frac{x}{10} V$$. The value of $$x$$ is ____________.
Two identical cells, when connected either in parallel or in series gives same current in an external resistance $$5 ~\Omega$$. The internal resistance of each cell will be ___________ $$\Omega$$.
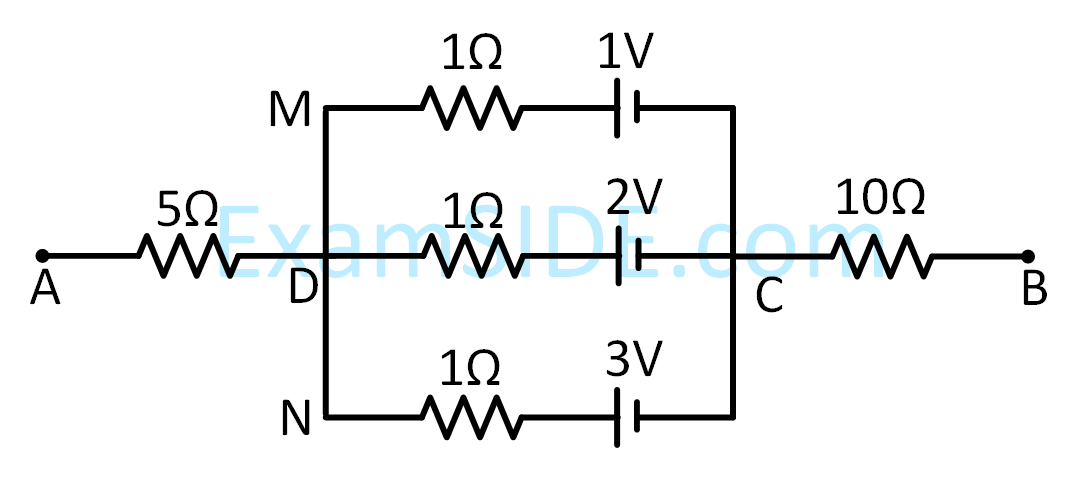
If the potential difference between $\mathrm{B}$ and $\mathrm{D}$ is zero, the value of $x$ is $\frac{1}{n} \Omega$. The value of $n$ is __________.

In the following circuit, the magnitude of current I1, is ___________ A.

A null point is found at 200 cm in potentiometer when cell in secondary circuit is shunted by 5$$\Omega$$. When a resistance of 15$$\Omega$$ is used for shunting, null point moves to 300 cm. The internal resistance of the cell is ___________$$\Omega$$.
When two resistance $$\mathrm{R_1}$$ and $$\mathrm{R_2}$$ connected in series and introduced into the left gap of a meter bridge and a resistance of 10 $$\Omega$$ is introduced into the right gap, a null point is found at 60 cm from left side. When $$\mathrm{R_1}$$ and $$\mathrm{R_2}$$ are connected in parallel and introduced into the left gap, a resistance of 3 $$\Omega$$ is introduced into the right gap to get null point at 40 cm from left end. The product of $$\mathrm{R_1}$$ $$\mathrm{R_2}$$ is ____________$$\Omega^2$$
In a metre bridge experiment the balance point is obtained if the gaps are closed by 2$$\Omega$$ and 3$$\Omega$$. A shunt of X $$\Omega$$ is added to 3$$\Omega$$ resistor to shift the balancing point by 22.5 cm. The value of X is ___________.
Two cells are connected between points A and B as shown. Cell 1 has emf of 12 V and internal resistance of 3$$\Omega$$. Cell 2 has emf of 6V and internal resistance of 6$$\Omega$$. An external resistor R of 4$$\Omega$$ is connected across A and B. The current flowing through R will be ____________ A.

In the given circuit, the equivalent resistance between the terminal A and B is __________ $$\Omega$$.

If a copper wire is stretched to increase its length by 20%. The percentage increase in resistance of the wire is __________%.
A hollow cylindrical conductor has length of 3.14 m, while its inner and outer diameters are 4 mm and 8 mm respectively. The resistance of the conductor is $$n\times10^{-3}\Omega$$. If the resistivity of the material is $$\mathrm{2.4\times10^{-8}\Omega m}$$. The value of $$n$$ is ___________.
The current I flowing through the given circuit will be __________A.

An electrical bulb rated 220 V, 100 W, is connected in series with another bulb rated 220 V, 60 W. If the voltage across combination is 220 V, the power consumed by the 100 W bulb will be about _______ W.
As shown in the figure, a potentiometer wire of resistance $$20 \,\Omega$$ and length $$300 \mathrm{~cm}$$ is connected with resistance box (R.B.) and a standard cell of emf $$4 \mathrm{~V}$$. For a resistance '$$R$$' of resistance box introduced into the circuit, the null point for a cell of $$20 \,\mathrm{mV}$$ is found to be $$60 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of '$$R$$' is ___________ $$\Omega .$$

In the given figure of meter bridge experiment, the balancing length AC corresponding to null deflection of the galvanometer is $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The balancing length, if the radius of the wire $$\mathrm{AB}$$ is doubled, will be ______________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

In a meter bridge experiment, for measuring unknown resistance 'S', the null point is obtained at a distance $$30 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the left side as shown at point D. If R is $$5.6$$ $$\mathrm{k} \Omega$$, then the value of unknown resistance 'S' will be __________ $$\Omega$$.

A $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ long copper wire carries a current of $$1 \mathrm{~A}$$. If the cross section of the wire is $$2.0 \mathrm{~mm}^{2}$$ and the resistivity of copper is $$1.7 \times 10^{-8}\, \Omega \mathrm{m}$$, the force experienced by moving electron in the wire is ____________ $$\times 10^{-23} \mathrm{~N}$$.
(charge on electorn $$=1.6 \times 10^{-19} \,\mathrm{C}$$)
A potentiometer wire of length $$300 \mathrm{~cm}$$ is connected in series with a resistance 780 $$\Omega$$ and a standard cell of emf $$4 \mathrm{V}$$. A constant current flows through potentiometer wire. The length of the null point for cell of emf $$20\, \mathrm{mV}$$ is found to be $$60 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The resistance of the potentiometer wire is ____________ $$\Omega$$.
Resistances are connected in a meter bridge circuit as shown in the figure. The balancing length $$l_{1}$$ is $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$. Now an unknown resistance $$x$$ is connected in series with $$\mathrm{P}$$ and new balancing length is found to be $$80 \mathrm{~cm}$$ measured from the same end. Then the value of $$x$$ will be ____________ $$\Omega$$.

In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell of emf 1.20 V gives a balance point at 36 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of emf 1.80 V. The difference in balancing length of potentiometer wire in above conditions will be ___________ cm.
In the given figure, the value of Vo will be _____________ V.

Eight copper wire of length $$l$$ and diameter $$d$$ are joined in parallel to form a single composite conductor of resistance $$R$$. If a single copper wire of length $$2 l$$ have the same resistance $$(R)$$ then its diameter will be ____________ d.
The circuit diagram of potentiometer used to measure the internal resistance of a cell (E) is shown in figure. The key 'K' is kept closed so as to send constant current through potentiometer wire. When key 'K1' is kept open the null point is found to be at 120 cm on the potentiometer wire. When the key 'K1' is closed the null point is shifted at 80 cm at the potentiometer wire. The internal resistance of the given cell is _____________ $$\Omega$$.

Two resistors are connected in series across a battery as shown in figure. If a voltmeter of resistance 2000 $$\Omega$$ is used to measure the potential difference across 500 $$\Omega$$ resistor, the reading of the voltmeter will be ___________ V.

The variation of applied potential and current flowing through a given wire is shown in figure. The length of wire is 31.4 cm. The diameter of wire is measured as 2.4 cm. The resistivity of the given wire is measured as x $$\times$$ 10$$-$$3 $$\Omega$$ cm. The value of x is ____________. [Take $$\pi$$ = 3.14]

For the network shown below, the value of VB $$-$$ VA is ____________ V.

All resistances in figure are 1 $$\Omega$$ each. The value of current 'I' is $${a \over 5}$$ A. The value of a is _________.

A meter bridge setup is shown in the figure. It is used to determine an unknown resistance R using a given resistor of 15 $$\Omega$$. The galvanometer (G) shows null deflection when tapping key is at 43 cm mark from end A. If the end correction for end A is 2 cm, then the determined value of R will be ____________ $$\Omega$$.

Current measured by the ammeter (A) in the reported circuit when no current flows through 10 $$\Omega$$ resistance, will be ________________ A.

The current density in a cylindrical wire of radius r = 4.0 mm is 1.0 $$\times$$ 106 A/m2. The current through the outer portion of the wire between radial distances $${r \over 2}$$ and r is x$$\pi$$ A; where x is __________.
In the given circuit 'a' is an arbitrary constant. The value of m for which the equivalent circuit resistance is minimum, will be $$\sqrt {{x \over 2}} $$. The value of x is __________.

A cell, shunted by a 8 $$\Omega$$ resistance, is balanced across a potentiometer wire of length 3 m. The balancing length is 2 m when the cell is shunted by 4 $$\Omega$$ resistance. The value of internal resistance of the cell will be ____________ $$\Omega$$.
The current density in a cylindrical wire of radius 4 mm is 4 $$\times$$ 106 Am$$-$$2. The current through the outer portion of the wire between radial distances $${R \over 2}$$ and R is ____________ $$\pi$$ A.
The length of a given cylindrical wire is increased to double of its original length. The percentage increase in the resistance of the wire will be ____________ %.
A resistor develops 300 J of thermal energy in 15 s, when a current of 2 A is passed through it. If the current increases to 3 A, the energy developed in 10 s is ____________ J.
The total current supplied to the circuit as shown in figure by the 5 V battery is ____________ A.

A potentiometer wire of length 10 m and resistance 20 $$\Omega$$ is connected in series with a 25 V battery and an external resistance 30 $$\Omega$$. A cell of emf E in secondary circuit is balanced by 250 cm long potentiometer wire. The value of E (in volt) is $${x \over {10}}$$. The value of x is __________.
In a potentiometer arrangement, a cell gives a balancing point at 75 cm length of wire. This cell is now replaced by another cell of unknown emf. If the ratio of the emf's of two cells respectively is 3 : 2, the difference in the balancing length of the potentiometer wire in above two cases will be ___________ cm.


[Voltage distribution V(t) is shown by Fig. (1) and the circuit is shown in Fig. (2)]


The value of x, to the nearest integer, is ___________.

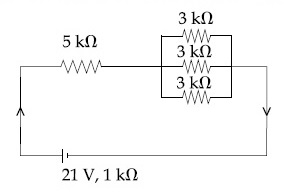
The value of 'x' to the nearest integer is _________.
The value of x to the nearest integer is ____________.