Vector Algebra · Physics · JEE Main
Numerical
Two particles are located at equal distance from origin. The position vectors of those are represented by $\vec{A}=2 \hat{i}+3 n \hat{j}+2 \hat{k}$ and $\bar{B}=2 \hat{i}-2 \hat{j}+4 p \hat{k}$, respectively. If both the vectors are at right angle to each other, the value of $n^{-1}$ is ________ .
The resultant of two vectors $$\vec{A}$$ and $$\vec{B}$$ is perpendicular to $$\vec{A}$$ and its magnitude is half that of $$\vec{B}$$. The angle between vectors $$\vec{A}$$ and $$\vec{B}$$ is _________$$^\circ$$.
If $$\vec{a}$$ and $$\vec{b}$$ makes an angle $$\cos ^{-1}\left(\frac{5}{9}\right)$$ with each other, then $$|\vec{a}+\vec{b}|=\sqrt{2}|\vec{a}-\vec{b}|$$ for $$|\vec{a}|=n|\vec{b}|$$ The integer value of $$\mathrm{n}$$ is _________.
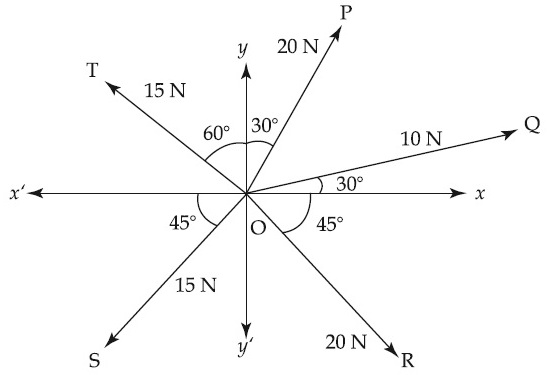
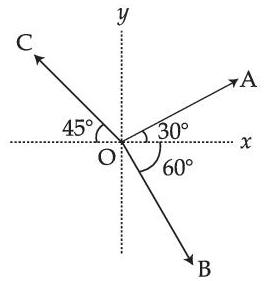
Three vectors $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OP}}, \overrightarrow{\mathrm{OQ}}$$ and $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{OR}}$$ each of magnitude $$\mathrm{A}$$ are acting as shown in figure. The resultant of the three vectors is $$\mathrm{A} \sqrt{x}$$. The value of $$x$$ is _________.

For three vectors $$\vec{A}=(-x \hat{i}-6 \hat{j}-2 \hat{k}), \vec{B}=(-\hat{i}+4 \hat{j}+3 \hat{k})$$ and $$\vec{C}=(-8 \hat{i}-\hat{j}+3 \hat{k})$$, if $$\vec{A} \cdot(\vec{B} \times \vec{C})=0$$, then value of $$x$$ is ________.
A vector has magnitude same as that of $$\vec{A}=3 \hat{i}+4 \hat{j}$$ and is parallel to $$\vec{B}=4 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}$$. The $$x$$ and $$y$$ components of this vector in first quadrant are $$x$$ and 3 respectively where $$x=$$ _________.
If $$\overrightarrow P = 3\widehat i + \sqrt 3 \widehat j + 2\widehat k$$ and $$\overrightarrow Q = 4\widehat i + \sqrt 3 \widehat j + 2.5\widehat k$$ then, the unit vector in the direction of $$\overrightarrow P \times \overrightarrow Q $$ is $${1 \over x}\left( {\sqrt 3 \widehat i + \widehat j - 2\sqrt 3 \widehat k} \right)$$. The value of $$x$$ is _________.
Vectors $$a\widehat i + b\widehat j + \widehat k$$ and $$2\widehat i - 3\widehat j + 4\widehat k$$ are perpendicular to each other when $$3a + 2b = 7$$, the ratio of $$a$$ to $$b$$ is $${x \over 2}$$. The value of $$x$$ is ____________.
If the projection of $$2 \hat{i}+4 \hat{j}-2 \hat{k}$$ on $$\hat{i}+2 \hat{j}+\alpha \hat{k}$$ is zero. Then, the value of $$\alpha$$ will be ___________.
If $$\vec{A}=(2 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}-\hat{k})\, \mathrm{m}$$ and $$\vec{B}=(\hat{i}+2 \hat{j}+2 \hat{k}) \,\mathrm{m}$$. The magnitude of component of vector $$\vec{A}$$ along vector $$\vec{B}$$ will be ____________ $$\mathrm{m}$$.
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
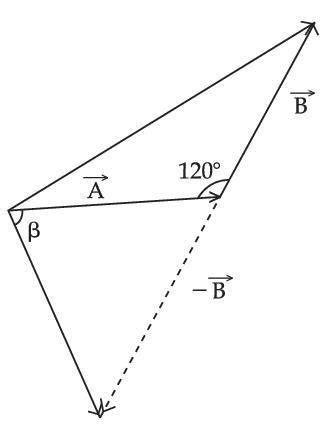
The angle between vector $$\vec{Q}$$ and the resultant of $$(2 \vec{Q}+2 \vec{P})$$ and $$(2 \vec{Q}-2 \vec{P})$$ is :
If two vectors $$\vec{A}$$ and $$\vec{B}$$ having equal magnitude $$R$$ are inclined at angle $$\theta$$, then
When vector $$\vec{A}=2 \hat{i}+3 \hat{j}+2 \hat{k}$$ is subtracted from vector $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$$, it gives a vector equal to $$2 \hat{j}$$. Then the magnitude of vector $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}$$ will be :
Two forces having magnitude $$A$$ and $$\frac{A}{2}$$ are perpendicular to each other. The magnitude of their resultant is:
If two vectors $$\overrightarrow P = \widehat i + 2m\widehat j + m\widehat k$$ and $$\overrightarrow Q = 4\widehat i - 2\widehat j + m\widehat k$$ are perpendicular to each other. Then, the value of m will be :
Two vectors $$\overrightarrow A $$ and $$\overrightarrow B $$ have equal magnitudes. If magnitude of $$\overrightarrow A $$ + $$\overrightarrow B $$ is equal to two times the magnitude of $$\overrightarrow A $$ $$-$$ $$\overrightarrow B $$, then the angle between $$\overrightarrow A $$ and $$\overrightarrow B $$ will be :
$$\overrightarrow A $$ is a vector quantity such that $$|\overrightarrow A |$$ = non-zero constant. Which of the following expression is true for $$\overrightarrow A $$ ?
Which of the following relations is true for two unit vector $$\widehat A$$ and $$\widehat B$$ making an angle $$\theta$$ to each other?
Two forces $$\left( {\overrightarrow P + \overrightarrow Q } \right)$$ and $$\left( {\overrightarrow P - \overrightarrow Q } \right)$$ where $$\overrightarrow P \bot \overrightarrow Q $$, when act at an angle $$\theta$$1 to each other, the magnitude of their resultant is $$\sqrt {3({P^2} + {Q^2})} $$, when they act at an angle $$\theta$$2, the magnitude of their resultant becomes $$\sqrt {2({P^2} + {Q^2})} $$. This is possible only when $${\theta _1} < {\theta _2}$$.
Statement II :
In the situation given above.
$$\theta$$1 = 60$$^\circ$$ and $$\theta$$2 = 90$$^\circ$$
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :-
[Take $$\sqrt 3 = 1.7$$, $$\sqrt 2 = 1.4$$ Given $$\widehat i$$ and $$\widehat j$$ unit vectors along x, y axis]
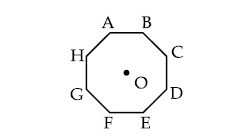
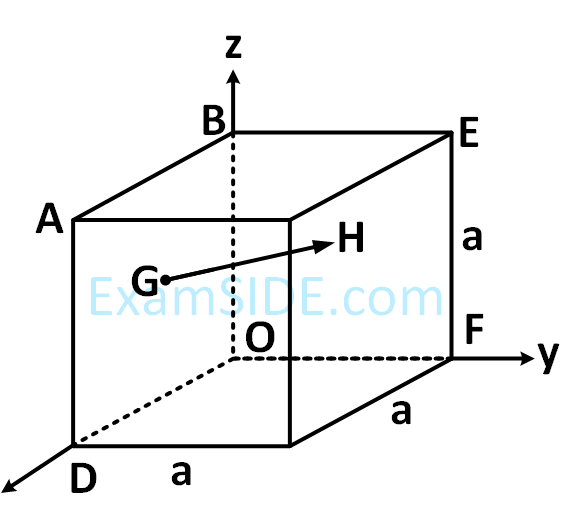
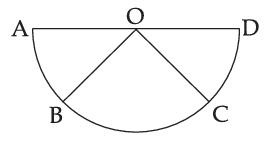
Reason R : Polygon law of vector addition yields $$\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {BC} + \overrightarrow {CD} + \overrightarrow {AD} = 2\overrightarrow {AO} $$
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
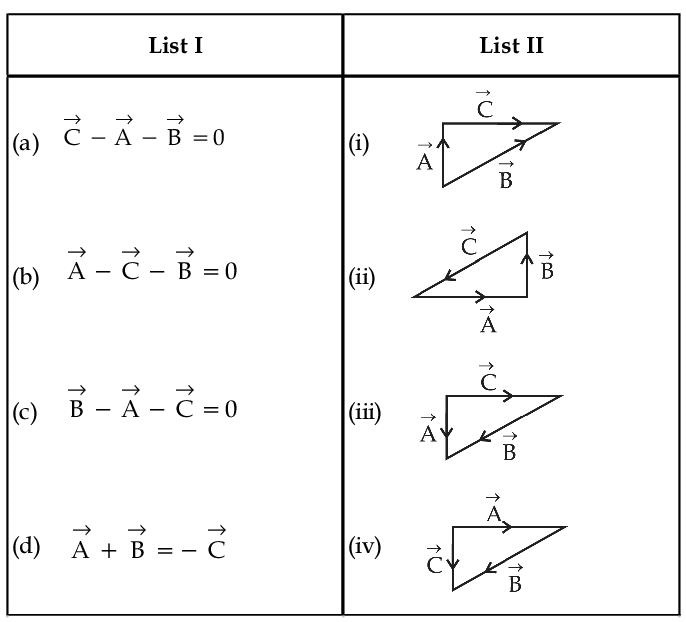
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
$$\overrightarrow {AB} + \overrightarrow {AC} + \overrightarrow {AD} + \overrightarrow {AE} + \overrightarrow {AF} + \overrightarrow {AG} + \overrightarrow {AH} $$,
if, $$\overrightarrow {AO} = 2\widehat i + 3\widehat j - 4\widehat k$$