Limits, Continuity and Differentiability · Mathematics · JEE Main
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
Given below are two statements:
Statement I: $ \lim\limits_{x \to 0} \left( \frac{\tan^{-1} x + \log_e \sqrt{\frac{1+x}{1-x}} - 2x}{x^5} \right) = \frac{2}{5} $
Statement II: $ \lim\limits_{x \to 1} \left( x^{\frac{2}{1-x}} \right) = \frac{1}{e^2} $
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below:
$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0^{+}} \frac{\tan \left(5(x)^{\frac{1}{3}}\right) \log _e\left(1+3 x^2\right)}{\left(\tan ^{-1} 3 \sqrt{x}\right)^2\left(e^{5(x)^{\frac{4}{3}}}-1\right)}$ is equal to
Let $f$ be a differentiable function on $\mathbf{R}$ such that $f(2)=1, f^{\prime}(2)=4$. Let $\lim \limits_{x \rightarrow 0}(f(2+x))^{3 / x}=\mathrm{e}^\alpha$. Then the number of times the curve $y=4 x^3-4 x^2-4(\alpha-7) x-\alpha$ meets $x$-axis is :
Let $f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be a continuous function satisfying $f(0)=1$ and $f(2 x)-f(x)=x$ for all $x \in \mathbb{R}$. If $\lim _\limits{n \rightarrow \infty}\left\{f(x)-f\left(\frac{x}{2^n}\right)\right\}=G(x)$, then $\sum_\limits{r=1}^{10} G\left(r^2\right)$ is equal to
If $\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 1^{+}} \frac{(x-1)(6+\lambda \cos (x-1))+\mu \sin (1-x)}{(x-1)^3}=-1$, where $\lambda, \mu \in \mathbb{R}$, then $\lambda+\mu$ is equal to
Let $\quad f(x)= \begin{cases}(1+a x)^{1 / x} & , x<0 \\ 1+b, & x=0 \\ \frac{(x+4)^{1 / 2}-2}{(x+c)^{1 / 3}-2}, & x>0\end{cases}$ be continuous at $x=0$. Then $e^a b c$ is equal to:
For $\alpha, \beta, \gamma \in \mathbf{R}$, if $\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{x^2 \sin \alpha x+(\gamma-1) \mathrm{e}^{x^2}}{\sin 2 x-\beta x}=3$, then $\beta+\gamma-\alpha$ is equal to :
The value of $\lim \limits_{n \rightarrow \infty}\left(\sum\limits_{k=1}^n \frac{k^3+6 k^2+11 k+5}{(k+3)!}\right)$ is :
Let $[x]$ denote the greatest integer function, and let m and n respectively be the numbers of the points, where the function $f(x)=[x]+|x-2|,-2< x<3$, is not continuous and not differentiable. Then $\mathrm{m}+\mathrm{n}$ is equal to :
$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \operatorname{cosec} x\left(\sqrt{2 \cos ^2 x+3 \cos x}-\sqrt{\cos ^2 x+\sin x+4}\right)$ is:
Let $f: \mathbb{R}-\{0\} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$ be a function such that $f(x)-6 f\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)=\frac{35}{3 x}-\frac{5}{2}$. If the $\lim\limits _{x \rightarrow 0}\left(\frac{1}{\alpha x}+f(x)\right)=\beta ; \alpha, \beta \in \mathbb{R}$, then $\alpha+2 \beta$ is equal to
$\lim \limits_{x \rightarrow \infty} \frac{\left(2 x^2-3 x+5\right)(3 x-1)^{\frac{x}{2}}}{\left(3 x^2+5 x+4\right) \sqrt{(3 x+2)^x}}$ is equal to :
If the function
$$
f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}
\frac{2}{x}\left\{\sin \left(k_1+1\right) x+\sin \left(k_2-1\right) x\right\}, \quad x<0 \\
4, \quad x=0 \\
\frac{2}{x} \log _e\left(\frac{2+k_1 x}{2+k_2 x}\right), \quad x>0
\end{array}\right.
$$
is continuous at $x=0$, then $k_1^2+k_2^2$ is equal to :
If $\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow \infty}\left(\left(\frac{\mathrm{e}}{1-\mathrm{e}}\right)\left(\frac{1}{\mathrm{e}}-\frac{x}{1+x}\right)\right)^x=\alpha$, then the value of $\frac{\log _{\mathrm{e}} \alpha}{1+\log _{\mathrm{e}} \alpha}$ equals :
If $\sum_\limits{r=1}^n T_r=\frac{(2 n-1)(2 n+1)(2 n+3)(2 n+5)}{64}$, then $\lim _\limits{n \rightarrow \infty} \sum_\limits{r=1}^n\left(\frac{1}{T_r}\right)$ is equal to :
$$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{e-(1+2 x)^{\frac{1}{2 x}}}{x}$$ is equal to
For $$\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{b}>0$$, let $$f(x)= \begin{cases}\frac{\tan ((\mathrm{a}+1) x)+\mathrm{b} \tan x}{x}, & x< 0 \\ 3, & x=0 \\ \frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{a} x+\mathrm{b}^2 x^2}-\sqrt{\mathrm{a} x}}{\mathrm{~b} \sqrt{\mathrm{a}} x \sqrt{x}}, & x> 0\end{cases}$$ be a continuous function at $$x=0$$. Then $$\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}$$ is equal to :
$$\lim _\limits{n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{\left(1^2-1\right)(n-1)+\left(2^2-2\right)(n-2)+\cdots+\left((n-1)^2-(n-1)\right) \cdot 1}{\left(1^3+2^3+\cdots \cdots+n^3\right)-\left(1^2+2^2+\cdots \cdots+n^2\right)}$$ is equal to :
Let ,$$f:[-1,2] \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ be given by $$f(x)=2 x^2+x+\left[x^2\right]-[x]$$, where $$[t]$$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $$t$$. The number of points, where $$f$$ is not continuous, is :
If the function $$f(x)=\frac{\sin 3 x+\alpha \sin x-\beta \cos 3 x}{x^3}, x \in \mathbf{R}$$, is continuous at $$x=0$$, then $$f(0)$$ is equal to :
If the function
$$f(x)= \begin{cases}\frac{72^x-9^x-8^x+1}{\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{1+\cos x}}, & x \neq 0 \\ a \log _e 2 \log _e 3 & , x=0\end{cases}$$
is continuous at $$x=0$$, then the value of $$a^2$$ is equal to
Let $$f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ be a function given by
$$f(x)= \begin{cases}\frac{1-\cos 2 x}{x^2}, & x < 0 \\ \alpha, & x=0, \\ \frac{\beta \sqrt{1-\cos x}}{x}, & x>0\end{cases}$$
where $$\alpha, \beta \in \mathbf{R}$$. If $$f$$ is continuous at $$x=0$$, then $$\alpha^2+\beta^2$$ is equal to :
If for some $\mathrm{a} \in \mathbf{N}, f(f(f(\mathrm{a})))=21$, then $\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow \mathrm{a}^{-}}\left\{\frac{|x|^3}{\mathrm{a}}-\left[\frac{x}{\mathrm{a}}\right]\right\}$, where $[t]$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $t$, is equal to :
$$ f(x)= \begin{cases}\frac{a-b \cos 2 x}{x^2} ; & x<0 \\\\ x^2+c x+2 ; & 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\\\ 2 x+1 ; & x>1\end{cases} $$
If $f$ is continuous everywhere in $\mathbf{R}$ and $m$ is the number of points where $f$ is NOT differential then $\mathrm{m}+\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}+\mathrm{c}$ equals :
Consider the function $$f:(0, \infty) \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$$ defined by $$f(x)=e^{-\left|\log _e x\right|}$$. If $$m$$ and $$n$$ be respectively the number of points at which $$f$$ is not continuous and $$f$$ is not differentiable, then $$m+n$$ is
$$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{e^{2|\sin x|}-2|\sin x|-1}{x^2}$$
Let $$g(x)$$ be a linear function and $$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl}g(x) & , x \leq 0 \\ \left(\frac{1+x}{2+x}\right)^{\frac{1}{x}} & , x>0\end{array}\right.$$, is continuous at $$x=0$$. If $$f^{\prime}(1)=f(-1)$$, then the value $$g(3)$$ is
Consider the function $$f:(0,2) \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ defined by $$f(x)=\frac{x}{2}+\frac{2}{x}$$ and the function $$g(x)$$ defined by
$$g(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll} \min \lfloor f(t)\}, & 0<\mathrm{t} \leq x \text { and } 0 < x \leq 1 \\ \frac{3}{2}+x, & 1 < x < 2 \end{array} .\right. \text { Then, }$$
$$\text { If } \lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{3+\alpha \sin x+\beta \cos x+\log _e(1-x)}{3 \tan ^2 x}=\frac{1}{3} \text {, then } 2 \alpha-\beta \text { is equal to : }$$
$$ f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc} \frac{\mathrm{a}\left(7 x-12-x^2\right)}{\mathrm{b}\left|x^2-7 x+12\right|} & , x<3 \\\\ 2^{\frac{\sin (x-3)}{x-[x]}} & , x>3 \\\\ \mathrm{~b} & , x=3, \end{array}\right. $$
where $[x]$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $x$. If $\mathrm{S}$ denotes the set of all ordered pairs (a, b) such that $f(x)$ is continuous at $x=3$, then the number of elements in $\mathrm{S}$ is :
$f(x)=\max \{1+x+[x], 2+x, x+2[x]\}, 0 \leq x \leq 2$. Let $m$ be the number of
points in $[0,2]$, where $f$ is not continuous and $n$ be the number of points in
$(0,2)$, where $f$ is not differentiable. Then $(m+n)^{2}+2$ is equal to :
If $$\lim_\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{e^{a x}-\cos (b x)-\frac{cx e^{-c x}}{2}}{1-\cos (2 x)}=17$$, then $$5 a^{2}+b^{2}$$ is equal to
Let $$f$$ and $$g$$ be two functions defined by
$$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}x+1, & x < 0 \\ |x-1|, & x \geq 0\end{array}\right.$$ and $$\mathrm{g}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}x+1, & x < 0 \\ 1, & x \geq 0\end{array}\right.$$
Then $$(g \circ f)(x)$$ is :
Let $$f(x)=\left[x^{2}-x\right]+|-x+[x]|$$, where $$x \in \mathbb{R}$$ and $$[t]$$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $$t$$. Then, $$f$$ is :
If $$\alpha > \beta > 0$$ are the roots of the equation $$a x^{2}+b x+1=0$$, and $$\lim_\limits{x \rightarrow \frac{1}{\alpha}}\left(\frac{1-\cos \left(x^{2}+b x+a\right)}{2(1-\alpha x)^{2}}\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}=\frac{1}{k}\left(\frac{1}{\beta}-\frac{1}{\alpha}\right), \text { then } \mathrm{k} \text { is equal to }$$ :
$$\lim_\limits{x \rightarrow 0}\left(\left(\frac{\left(1-\cos ^{2}(3 x)\right.}{\cos ^{3}(4 x)}\right)\left(\frac{\sin ^{3}(4 x)}{\left(\log _{e}(2 x+1)\right)^{5}}\right)\right)$$ is equal to _____________.
Let $$a_{1}, a_{2}, a_{3}, \ldots, a_{\mathrm{n}}$$ be $$\mathrm{n}$$ positive consecutive terms of an arithmetic progression. If $$\mathrm{d} > 0$$ is its common difference, then
$$\lim_\limits{n \rightarrow \infty} \sqrt{\frac{d}{n}}\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{1}}+\sqrt{a_{2}}}+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{2}}+\sqrt{a_{3}}}+\ldots \ldots \ldots+\frac{1}{\sqrt{a_{n-1}}+\sqrt{a_{n}}}\right)$$ is
$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}\frac{x}{|x|}, & x \neq 0 \\ 1, & x=0\end{array}\right.$
$g(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}\frac{\sin (x+1)}{(x+1)}, & x \neq-1 \\ 1, & x=-1\end{array}\right.$
and $h(x)=2[x]-f(x)$, where $[x]$ is the greatest integer $\leq x$. Then the
value of $\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow 1} g(h(x-1))$ is :
Suppose $$f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow(0, \infty)$$ be a differentiable function such that $$5 f(x+y)=f(x) \cdot f(y), \forall x, y \in \mathbb{R}$$. If $$f(3)=320$$, then $$\sum_\limits{n=0}^{5} f(n)$$ is equal to :
Let $$x=2$$ be a root of the equation $$x^2+px+q=0$$ and $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{1 - \cos ({x^2} - 4px + {q^2} + 8q + 16)} \over {{{(x - 2p)}^4}}},} & {x \ne 2p} \cr {0,} & {x = 2p} \cr } } \right.$$
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 2{p^ + }} [f(x)]$$, where $$\left[ . \right]$$ denotes greatest integer function, is
If the function $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {(1 + |\cos x|)^{\lambda \over {|\cos x|}}} & , & {0 < x < {\pi \over 2}} \cr \mu & , & {x = {\pi \over 2}} \cr e^{{{\cot 6x} \over {{}\cot 4x}}} & , & {{\pi \over 2} < x < \pi } \cr } } \right.$$
is continuous at $$x = {\pi \over 2}$$, then $$9\lambda + 6{\log _e}\mu + {\mu ^6} - {e^{6\lambda }}$$ is equal to
The value of $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{n \to \infty } {{1 + 2 - 3 + 4 + 5 - 6\, + \,.....\, + \,(3n - 2) + (3n - 1) - 3n} \over {\sqrt {2{n^4} + 4n + 3} - \sqrt {{n^4} + 5n + 4} }}$$ is :
The set of all values of $$a$$ for which $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to a} ([x - 5] - [2x + 2]) = 0$$, where [$$\alpha$$] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $$\alpha$$ is equal to
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to 0} {\left( {{1^{{1 \over {{{\sin }^2}t}}}} + {2^{{1 \over {{{\sin }^2}t}}}}\, + \,...\, + \,{n^{{1 \over {{{\sin }^2}t}}}}} \right)^{{{\sin }^2}t}}$$ is equal to
Let $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{x^2}\sin \left( {{1 \over x}} \right)} & {,\,x \ne 0} \cr 0 & {,\,x = 0} \cr } } \right.$$
Then at $$x=0$$
$$ \text { Let the function } f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cl} \frac{\log _{e}(1+5 x)-\log _{e}(1+\alpha x)}{x} & ;\text { if } x \neq 0 \\ 10 & ; \text { if } x=0 \end{array} \text { be continuous at } x=0 .\right. $$
Then $$\alpha$$ is equal to
If $$\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{\alpha \mathrm{e}^{x}+\beta \mathrm{e}^{-x}+\gamma \sin x}{x \sin ^{2} x}=\frac{2}{3}$$, where $$\alpha, \beta, \gamma \in \mathbf{R}$$, then which of the following is NOT correct?
The number of points, where the function $$f: \mathbf{R} \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$,
$$f(x)=|x-1| \cos |x-2| \sin |x-1|+(x-3)\left|x^{2}-5 x+4\right|$$, is NOT differentiable, is :
The function $$f: \mathbb{R} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$$ defined by
$$f(x)=\lim\limits_{n \rightarrow \infty} \frac{\cos (2 \pi x)-x^{2 n} \sin (x-1)}{1+x^{2 n+1}-x^{2 n}}$$ is continuous for all x in :
If for $$\mathrm{p} \neq \mathrm{q} \neq 0$$, the function $$f(x)=\frac{\sqrt[7]{\mathrm{p}(729+x)}-3}{\sqrt[3]{729+\mathrm{q} x}-9}$$ is continuous at $$x=0$$, then :
Let $$\beta=\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \frac{\alpha x-\left(e^{3 x}-1\right)}{\alpha x\left(e^{3 x}-1\right)}$$ for some $$\alpha \in \mathbb{R}$$. Then the value of $$\alpha+\beta$$ is :
Let f : R $$\to$$ R be a continuous function such that $$f(3x) - f(x) = x$$. If $$f(8) = 7$$, then $$f(14)$$ is equal to :
If the function $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{{{\log }_e}(1 - x + {x^2}) + {{\log }_e}(1 + x + {x^2})} \over {\sec x - \cos x}}} & , & {x \in \left( {{{ - \pi } \over 2},{\pi \over 2}} \right) - \{ 0\} } \cr k & , & {x = 0} \cr } } \right.$$ is continuous at x = 0, then k is equal to:
If $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x + a} & , & {x \le 0} \cr {|x - 4|} & , & {x > 0} \cr } } \right.$$ and $$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x + 1} & , & {x < 0} \cr {{{(x - 4)}^2} + b} & , & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ are continuous on R, then $$(gof)(2) + (fog)( - 2)$$ is equal to :
Let $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{x^3} - {x^2} + 10x - 7,} & {x \le 1} \cr { - 2x + {{\log }_2}({b^2} - 4),} & {x > 1} \cr } } \right.$$.
Then the set of all values of b, for which f(x) has maximum value at x = 1, is :
$$\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow \frac{\pi}{4}} \frac{8 \sqrt{2}-(\cos x+\sin x)^{7}}{\sqrt{2}-\sqrt{2} \sin 2 x}$$ is equal to
If $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{n \to \infty } \left( {\sqrt {{n^2} - n - 1} + n\alpha + \beta } \right) = 0$$, then $$8(\alpha+\beta)$$ is equal to :
The value of $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 1} {{({x^2} - 1){{\sin }^2}(\pi x)} \over {{x^4} - 2{x^3} + 2x - 1}}$$ is equal to:
Let f, g : R $$\to$$ R be functions defined by
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {[x]} & , & {x < 0} \cr {|1 - x|} & , & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ and $$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{e^x} - x} & , & {x < 0} \cr {{{(x - 1)}^2} - 1} & , & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ where [x] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to x. Then, the function fog is discontinuous at exactly :
The value of
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{n \to \infty } 6\tan \left\{ {\sum\limits_{r = 1}^n {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {{1 \over {{r^2} + 3r + 3}}} \right)} } \right\}$$ is equal to :
Let f : R $$\to$$ R be defined as
$$f(x) = \left[ {\matrix{ {[{e^x}],} & {x < 0} \cr {a{e^x} + [x - 1],} & {0 \le x < 1} \cr {b + [\sin (\pi x)],} & {1 \le x < 2} \cr {[{e^{ - x}}] - c,} & {x \ge 2} \cr } } \right.$$
where a, b, c $$\in$$ R and [t] denotes greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then, which of the following statements is true?
Let a be an integer such that $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 7} {{18 - [1 - x]} \over {[x - 3a]}}$$ exists, where [t] is greatest integer $$\le$$ t. Then a is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} {{\cos (\sin x) - \cos x} \over {{x^4}}}$$ is equal to :
Let f(x) = min {1, 1 + x sin x}, 0 $$\le$$ x $$\le$$ 2$$\pi $$. If m is the number of points, where f is not differentiable and n is the number of points, where f is not continuous, then the ordered pair (m, n) is equal to
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {1 \over {\sqrt 2 }}} {{\sin ({{\cos }^{ - 1}}x) - x} \over {1 - \tan ({{\cos }^{ - 1}}x)}}$$ is equal to :
Let f, g : R $$\to$$ R be two real valued functions defined as $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ { - |x + 3|} & , & {x < 0} \cr {{e^x}} & , & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ and $$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{x^2} + {k_1}x} & , & {x < 0} \cr {4x + {k_2}} & , & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$, where k1 and k2 are real constants. If (gof) is differentiable at x = 0, then (gof) ($$-$$ 4) + (gof) (4) is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {\pi \over 2}} \left( {{{\tan }^2}x\left( {{{(2{{\sin }^2}x + 3\sin x + 4)}^{{1 \over 2}}} - {{({{\sin }^2}x + 6\sin x + 2)}^{{1 \over 2}}}} \right)} \right)$$ is equal to
Let f(x) be a polynomial function such that $$f(x) + f'(x) + f''(x) = {x^5} + 64$$. Then, the value of $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 1} {{f(x)} \over {x - 1}}$$ is equal to:
Let $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{\sin (x - [x])} \over {x - [x]}}} & {,\,x \in ( - 2, - 1)} \cr {\max \{ 2x,3[|x|]\} } & {,\,|x| < 1} \cr 1 & {,\,otherwise} \cr } } \right.$$
where [t] denotes greatest integer $$\le$$ t. If m is the number of points where $$f$$ is not continuous and n is the number of points where $$f$$ is not differentiable, then the ordered pair (m, n) is :
$$f(x) = \left| {{x^2} - 2x - 3} \right|\,.\,{e^{\left| {9{x^2} - 12x + 4} \right|}}$$ is not differentiable at exactly :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{1 \over x}{{\log }_e}\left( {{{1 + {x \over a}} \over {1 - {x \over b}}}} \right)} & , & {x < 0} \cr k & , & {x = 0} \cr {{{{{\cos }^2}x - {{\sin }^2}x - 1} \over {\sqrt {{x^2} + 1} - 1}}} & , & {x > 0} \cr } } \right.$$ is continuous
at x = 0, then $${1 \over a} + {1 \over b} + {4 \over k}$$ is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \beta } {{{e^{2({x^2} + bx + c)}} - 1 - 2({x^2} + bx + c)} \over {{{(x - \beta )}^2}}}$$ is equal to :
f(x) = x $$-$$ [x], g(x) = 1 $$-$$ x + [x], and h(x) = min{f(x), g(x)}, x $$\in$$ [$$-$$2, 2]. Then h is :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \left( {{x \over {\root 8 \of {1 - \sin x} - \root 8 \of {1 + \sin x} }}} \right)$$ is equal to :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {\max \{ \sin t:0 \le t \le x\} ,} & {0 \le x \le \pi } \cr {2 + \cos x,} & {x > \pi } \cr } } \right.$$
Then which of the following is true?
If f is continuous at x = 0, then the value of 6a + b2 is equal to :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{\lambda \left| {{x^2} - 5x + 6} \right|} \over {\mu (5x - {x^2} - 6)}},} & {x < 2} \cr {{e^{{{\tan (x - 2)} \over {x - [x]}}}},} & {x > 2} \cr {\mu ,} & {x = 2} \cr } } \right.$$
where [x] is the greatest integer is than or equal to x. If f is continuous at x = 2, then $$\lambda$$ + $$\mu$$ is equal to :
If f is continuous at x = 0, then $$\alpha$$ is equal to :
where [ x ] is the greatest integer less than or equal to x. If f is continuous on R, then (a + b) is equal to:
$$f(x) = \left\{ \matrix{ {{\sin (a + 1)x + \sin 2x} \over {2x}},if\,x < 0 \hfill \cr b,\,if\,x\, = 0 \hfill \cr {{\sqrt {x + b{x^3}} - \sqrt x } \over {b{x^{5/2}}}},\,if\,x > 0 \hfill \cr} \right.$$
If f is continuous at x = 0, then the value of a + b is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{\theta \to 0} {{\tan (\pi {{\cos }^2}\theta )} \over {\sin (2\pi {{\sin }^2}\theta )}}$$ is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} {{{{\cos }^{ - 1}}(x - {{[x]}^2}).{{\sin }^{ - 1}}(x - {{[x]}^2})} \over {x - {x^3}}}$$, where [ x ] denotes the greatest integer $$ \le $$ x is :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x + 2,} & {x < 0} \cr {{x^2},} & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ and
$$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{x^3},} & {x < 1} \cr {3x - 2,} & {x \ge 1} \cr } } \right.$$
Then, the number of points in R where (fog) (x) is NOT differentiable is equal to :
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to a} {{xf(a) - af(x)} \over {x - a}}$$ equals :
$$f(x) = \left\{ \matrix{ 2\sin \left( { - {{\pi x} \over 2}} \right),if\,x < - 1 \hfill \cr |a{x^2} + x + b|,\,if - 1 \le x \le 1 \hfill \cr \sin (\pi x),\,if\,x > 1 \hfill \cr} \right.$$ If f(x) is continuous on R, then a + b equals :
f(x) = max {x, x2}. Let S denote the set of all points in R, where f is not differentiable. Then :
with f(0) = f(1) = f'(0) = 0
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{k_1}{{\left( {x - \pi } \right)}^2} - 1,} & {x \le \pi } \cr {{k_2}\cos x,} & {x > \pi } \cr } } \right.$$ is
twice differentiable, then the ordered pair (k1, k2) is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {\alpha ^ + }} {{\sqrt {1 - \cos \left( {p\left( x \right)} \right)} } \over {x + \alpha - 4}}$$ is equal to :
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{t \to x} {{{t^2}{f^2}(x) - {x^2}{f^2}(t)} \over {t - x}} = 0$$. If f(x) = 1, then x is equal to :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{\pi \over 4} + {{\tan }^{ - 1}}x,} & {\left| x \right| \le 1} \cr {{1 \over 2}\left( {\left| x \right| - 1} \right),} & {\left| x \right| > 1} \cr } } \right.$$ is :
$$\lambda $$ $$ \in $$ R - {1, 0}, $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} \left| {{{1 - x + \left| x \right|} \over {\lambda - x + \left[ x \right]}}} \right|$$ = L, then L is equal to :
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {a{e^x} + b{e^{ - x}},} & { - 1 \le x < 1} \cr {c{x^2},} & {1 \le x \le 3} \cr {a{x^2} + 2cx,} & {3 < x \le 4} \cr } } \right.$$
be continuous for some $$a$$, b, c $$ \in $$ R and f'(0) + f'(2) = e, then the value of of $$a$$ is :
Then the function, f(x) = [x2]sin($$\pi $$x) is discontinuous, when x is equal to :
is continuous at x = 0, then a + 2b is equal to :
is continuous at x = 0, then the ordered pair (p, q) is equal to
is continuous at x = 5, then the value of a – b is :-
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} {\left( {{{1 + f(3 + x) - f(3)} \over {1 + f(2 - x) - f(2)}}} \right)^{{1 \over x}}}$$ is equal to
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {\left| x \right| + \left[ x \right]} & , & { - 1 \le x < 1} \cr {x + \left| x \right|} & , & {1 \le x < 2} \cr {x + \left[ x \right]} & , & {2 \le x \le 3} \cr } } \right.$$
where [t] denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then, ƒ is discontinuous at:
$$g(x) = \left| {f\left( x \right)} \right| + f\left( {\left| x \right|} \right).$$
Then, in the interval (–2, 2), g is :
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 1^ + } {{\left( {1 - \left| x \right| + \sin \left| {1 - x} \right|} \right)\sin \left( {{\pi \over 2}\left[ {1 - x} \right]} \right)} \over {\left| {1 - x} \right|.\left[ {1 - x} \right]}}$$
Let S be the set of points in the interval (– 4, 4) at which f is not differentiable. Then S
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ - }} \,\,{{x\left( {\left[ x \right] + \left| x \right|} \right)\sin \left[ x \right]} \over {\left| x \right|}}$$ is equal to :
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ 5 & ; & {x \le 1} \cr {a + bx} & ; & {1 < x < 3} \cr {b + 5x} & ; & {3 \le x < 5} \cr {30} & ; & {x \ge 5} \cr } } \right.$$
Then, f is
$$f\left( x \right) = {1 \over x} - {{k - 1} \over {{e^{2x}} - 1}},x \ne 0,$$ is continuous at
x = 0, then the ordered pair (k, f(0)) is equal to :
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to {0^ + }} x\left( {\left[ {{1 \over x}} \right] + \left[ {{2 \over x}} \right] + ..... + \left[ {{{15} \over x}} \right]} \right)$$
If $$\mathop {lim}\limits_{x \to 0} \left( {{{f\left( x \right)} \over {{x^2}}} + 1} \right) = 3$$ then f($$-$$1) is equal to :
Thevaue of k for which f s continuous at x = 2 is :
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{\left( {{4 \over 5}} \right)}^{{{\tan \,4x} \over {\tan \,5x}}}}\,\,,} & {0 < x < {\pi \over 2}} \cr {k + {2 \over 5}\,\,\,,} & {x = {\pi \over 2}} \cr } } \right.$$
is continuous at x = $${\pi \over 2},$$ is :
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{2{x^2}} \over a}\,\,,} & {0 \le x < 1} \cr {a\,\,\,,} & {1 \le x < \sqrt 2 } \cr {{{2{b^2} - 4b} \over {{x^3}}},} & {\sqrt 2 \le x < \infty } \cr } } \right.$$
is continuous in the interval [0, $$\infty $$), then an ordered pair ( a, b) is :
f(x) = $$\left\{ {\matrix{ { - x} & {x < 1} \cr {a + {{\cos }^{ - 1}}\left( {x + b} \right),} & {1 \le x \le 2} \cr } } \right.$$
is differentiable at x = 1, then $${a \over b}$$ is equal to :
and $$\,\,g\left( x \right) = f\left( {f\left( x \right)} \right),\,\,$$ then :
$$g\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {k\sqrt {x + 1} ,} & {0 \le x \le 3} \cr {m\,x + 2,} & {3 < x \le 5} \cr } } \right.$$
is differentiable, then the value of $$k+m$$ is :
Statement - 1 : $$f'\left( 4 \right) = 0$$
Statement - 2 : $$f$$ is continuous in [2, 5], differentiable in (2, 5) and $$f$$(2) = $$f$$(5)
$$f\left( x \right) = \left[ x \right]\cos \left( {{{2x - 1} \over 2}} \right)\pi $$,
where [x] denotes the greatest integer function, then $$f$$ is
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{{\sin (p + 1)x + \sin x} \over x}} & {,x < 0} \cr q & {,x = 0} \cr {{{\sqrt {x + {x^2}} - \sqrt x } \over {{x^{3/2}}}}} & {,x > 0} \cr } } \right.$$
is continuous for all $$x$$ in R, are
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {{f(3x)} \over {f(x)}} = 1$$. Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \infty } {{f(2x)} \over {f(x)}} = $$
Statement-1: gof is differentiable at $$x=0$$ and its derivative is continuous at that point.
Statement-2: gof is twice differentiable at $$x=0$$.
Then which one of the following is true?
$$f(x) = \min \left\{ {x + 1,\left| x \right| + 1} \right\}$$, then which of the following is true?
$$f\left( x \right) = {1 \over x} - {2 \over {{e^{2x}} - 1}}$$
can be made continuous at $$x$$ = 0 by defining $$f$$(0) as
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to \alpha } {{1 - \cos \left( {a{x^2} + bx + c} \right)} \over {{{\left( {x - \alpha } \right)}^2}}}$$ is equal to
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} {1 \over h}f\left( {1 + h} \right) = 5$$, then $$f'\left( 1 \right)$$ equals
$$\left| {f\left( x \right) - f\left( y \right)} \right|$$ $$ \le {\left( {x - y} \right)^2}$$, $$x, y$$ $$ \in R$$
and $$f(0)$$ = 0, then $$f(1)$$ equals
If $$f(x)$$ is continuous in $$\left[ {0,{\pi \over 2}} \right]$$, then $$f\left( {{\pi \over 4}} \right)$$ is
$${f^n}(a)$$, $${g^n}(a)$$ exist and are not equal for some n. Further if
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to a} {{f(a)g(x) - f(a) - g(a)f(x) + f(a)} \over {g(x) - f(x)}} = 4$$
then the value of k is
then $$f(x)$$ is
Then $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 2} {{xf\left( 2 \right) - 2f\left( x \right)} \over {x - 2}}$$ is given by
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 1} {{\sqrt {f\left( x \right)} - 1} \over {\sqrt x - 1}}$$ is
$$f\left( x \right) = x$$ if $$x$$ is rational
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$$ $$ = - x$$ if $$x$$ is irrational. Then
f''(x) - g''(x) = 0, f'(1) = 2, g'(1) = 4, f(2) = 3, g(2) = 9
then f(x) - g(x) at x = $${3 \over 2}$$ is
f'(5) is
Numerical
For $\mathrm{t}>-1$, let $\alpha_{\mathrm{t}}$ and $\beta_{\mathrm{t}}$ be the roots of the equation
$$ \left((\mathrm{t}+2)^{1 / 7}-1\right) x^2+\left((\mathrm{t}+2)^{1 / 6}-1\right) x+\left((\mathrm{t}+2)^{1 / 21}-1\right)=0 \text {. If } \lim \limits_{\mathrm{t} \rightarrow-1^{+}} \alpha_{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{a} \text { and } \lim \limits_{\mathrm{t} \rightarrow-1^{+}} \beta_{\mathrm{t}}=\mathrm{b} \text {, } $$
then $72(a+b)^2$ is equal to ___________.
The number of points of discontinuity of the function $f(x)=\left[\frac{x^2}{2}\right]-[\sqrt{x}], x \in[0,4]$, where $[\cdot]$ denotes the greatest integer function, is ________.
Let $m$ and $n$ be the number of points at which the function $f(x)=\max \left\{x, x^3, x^5, \ldots x^{21}\right\}, x \in \mathbb{R}$, is not differentiable and not continuous, respectively. Then $m+n$ is equal to _________.
Let [t] be the greatest integer less than or equal to t. Then the least value of p ∈ N for which
$ \lim\limits_{x \to 0^+} \left( x (\left[ \frac{1}{x} \right] + \left[ \frac{2}{x} \right] + \ldots + \left[ \frac{p}{x} \right] \right) - x^2 \left( \left[ \frac{1}{x^2} \right] + \left[ \frac{2^2}{x^2} \right] + \ldots + \left[ \frac{9^2}{x^2} \right] \right) \geq 1 $ is equal to _______.
Let $f(x)=\lim \limits_{n \rightarrow \infty} \sum\limits_{r=0}^n\left(\frac{\tan \left(x / 2^{r+1}\right)+\tan ^3\left(x / 2^{r+1}\right)}{1-\tan ^2\left(x / 2^{r+1}\right)}\right)$ Then $\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{e^x-e^{f(x)}}{(x-f(x))}$ is equal to ___________.
Let $\mathrm{f}(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{lc}3 x, & x<0 \\ \min \{1+x+[x], x+2[x]\}, & 0 \leq x \leq 2 \\ 5, & x>2\end{array}\right.$
where [.] denotes greatest integer function. If $\alpha$ and $\beta$ are the number of points, where $f$ is not continuous and is not differentiable, respectively, then $\alpha+\beta$ equals _______ .
Let the function,
$$f(x)= \begin{cases}-3 \mathrm{ax}^2-2, & x<1 \\ \mathrm{a}^2+\mathrm{b} x, & x \geqslant 1\end{cases}$$
be differentiable for all $x \in \mathbf{R}$, where $\mathrm{a}>1, \mathrm{~b} \in \mathbf{R}$. If the area of the region enclosed by $y=f(x)$ and the line $y=-20$ is $\alpha+\beta \sqrt{3}, \alpha, \beta \in Z$, then the value of $\alpha+\beta$ is ___________ .
Let $$f:(0, \pi) \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ be a function given by $$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}\left(\frac{8}{7}\right)^{\frac{\tan 8 x}{\tan 7 x}}, & 0< x<\frac{\pi}{2} \\ \mathrm{a}-8, & x=\frac{\pi}{2} \\ (1+\mid \cot x)^{\frac{\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{a}}|\tan x|}, & \frac{\pi}{2} < x < \pi\end{array}\right.$$
where $$\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{b} \in \mathbf{Z}$$. If $$f$$ is continuous at $$x=\frac{\pi}{2}$$, then $$\mathrm{a}^2+\mathrm{b}^2$$ is equal to _________.
If $$\alpha=\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0^{+}}\left(\frac{\mathrm{e}^{\sqrt{\tan x}}-\mathrm{e}^{\sqrt{x}}}{\sqrt{\tan x}-\sqrt{x}}\right)$$ and $$\beta=\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0}(1+\sin x)^{\frac{1}{2} \cot x}$$ are the roots of the quadratic equation $$\mathrm{a} x^2+\mathrm{b} x-\sqrt{\mathrm{e}}=0$$, then $$12 \log _{\mathrm{e}}(\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b})$$ is equal to _________.
The value of $$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} 2\left(\frac{1-\cos x \sqrt{\cos 2 x} \sqrt[3]{\cos 3 x} \ldots \ldots . \sqrt[10]{\cos 10 x}}{x^2}\right)$$ is __________.
Let $$[t]$$ denote the greatest integer less than or equal to $$t$$. Let $$f:[0, \infty) \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ be a function defined by $$f(x)=\left[\frac{x}{2}+3\right]-[\sqrt{x}]$$. Let $$\mathrm{S}$$ be the set of all points in the interval $$[0,8]$$ at which $$f$$ is not continuous. Then $$\sum_\limits{\text {aes }} a$$ is equal to __________.
Let $$\mathrm{a}>0$$ be a root of the equation $$2 x^2+x-2=0$$. If $$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow \frac{1}{a}} \frac{16\left(1-\cos \left(2+x-2 x^2\right)\right)}{(1-a x)^2}=\alpha+\beta \sqrt{17}$$, where $$\alpha, \beta \in Z$$, then $$\alpha+\beta$$ is equal to _________.
Let $$f$$ be a differentiable function in the interval $$(0, \infty)$$ such that $$f(1)=1$$ and $$\lim _\limits{t \rightarrow x} \frac{t^2 f(x)-x^2 f(t)}{t-x}=1$$ for each $$x>0$$. Then $$2 f(2)+3 f(3)$$ is equal to _________.
If $$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 1} \frac{(5 x+1)^{1 / 3}-(x+5)^{1 / 3}}{(2 x+3)^{1 / 2}-(x+4)^{1 / 2}}=\frac{\mathrm{m} \sqrt{5}}{\mathrm{n}(2 \mathrm{n})^{2 / 3}}$$, where $$\operatorname{gcd}(\mathrm{m}, \mathrm{n})=1$$, then $$8 \mathrm{~m}+12 \mathrm{n}$$ is equal to _______.
If $$\lim _\limits{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{a x^2 e^x-b \log _e(1+x)+c x e^{-x}}{x^2 \sin x}=1$$, then $$16\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)$$ is equal to ________.
If the function
$$f(x)= \begin{cases}\frac{1}{|x|}, & |x| \geqslant 2 \\ \mathrm{a} x^2+2 \mathrm{~b}, & |x|<2\end{cases}$$
is differentiable on $$\mathbf{R}$$, then $$48(a+b)$$ is equal to __________.
Let $$f(x)=\sqrt{\lim _\limits{r \rightarrow x}\left\{\frac{2 r^2\left[(f(r))^2-f(x) f(r)\right]}{r^2-x^2}-r^3 e^{\frac{f(r)}{r}}\right\}}$$ be differentiable in $$(-\infty, 0) \cup(0, \infty)$$ and $$f(1)=1$$. Then the value of ea, such that $$f(a)=0$$, is equal to _________.
Let $$[x]$$ be the greatest integer $$\leq x$$. Then the number of points in the interval $$(-2,1)$$, where the function $$f(x)=|[x]|+\sqrt{x-[x]}$$ is discontinuous, is ___________.
Let $$f:( - 2,2) \to R$$ be defined by $$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x[x],} & { - 2 < x < 0} \cr {(x - 1)[x],} & {0 \le x \le 2} \cr } } \right.$$ where $$[x]$$ denotes the greatest integer function. If m and n respectively are the number of points in $$( - 2,2)$$ at which $$y = |f(x)|$$ is not continuous and not differentiable, then $$m + n$$ is equal to ____________.
Let $$\mathrm{k}$$ and $$\mathrm{m}$$ be positive real numbers such that the function $$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}3 x^{2}+k \sqrt{x+1}, & 0 < x < 1 \\ m x^{2}+k^{2}, & x \geq 1\end{array}\right.$$ is differentiable for all $$x > 0$$. Then $$\frac{8 f^{\prime}(8)}{f^{\prime}\left(\frac{1}{8}\right)}$$ is equal to ____________.
Let $$a \in \mathbb{Z}$$ and $$[\mathrm{t}]$$ be the greatest integer $$\leq \mathrm{t}$$. Then the number of points, where the function $$f(x)=[a+13 \sin x], x \in(0, \pi)$$ is not differentiable, is __________.
If $$[t]$$ denotes the greatest integer $$\leq t$$, then the number of points, at which the function $$f(x)=4|2 x+3|+9\left[x+\frac{1}{2}\right]-12[x+20]$$ is not differentiable in the open interval $$(-20,20)$$, is __________.
Let $$f:[0,1] \rightarrow \mathbf{R}$$ be a twice differentiable function in $$(0,1)$$ such that $$f(0)=3$$ and $$f(1)=5$$. If the line $$y=2 x+3$$ intersects the graph of $$f$$ at only two distinct points in $$(0,1)$$, then the least number of points $$x \in(0,1)$$, at which $$f^{\prime \prime}(x)=0$$, is ____________.
$$\lim\limits_{x \rightarrow 0}\left(\frac{(x+2 \cos x)^{3}+2(x+2 \cos x)^{2}+3 \sin (x+2 \cos x)}{(x+2)^{3}+2(x+2)^{2}+3 \sin (x+2)}\right)^{\frac{100}{x}}$$ is equal to ___________.
Let $$f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{l}\left|4 x^{2}-8 x+5\right|, \text { if } 8 x^{2}-6 x+1 \geqslant 0 \\ {\left[4 x^{2}-8 x+5\right], \text { if } 8 x^{2}-6 x+1<0,}\end{array}\right.$$ where $$[\alpha]$$ denotes the greatest integer less than or equal to $$\alpha$$. Then the number of points in $$\mathbf{R}$$ where $$f$$ is not differentiable is ___________.
Suppose $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} {{F(x)} \over {{x^3}}}$$ exists and is equal to L, where
$$F(x) = \left| {\matrix{ {a + \sin {x \over 2}} & { - b\cos x} & 0 \cr { - b\cos x} & 0 & {a + \sin {x \over 2}} \cr 0 & {a + \sin {x \over 2}} & { - b\cos x} \cr } } \right|$$.
Then, $$-$$112 L is equal to ___________.
If $$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 1} {{\sin (3{x^2} - 4x + 1) - {x^2} + 1} \over {2{x^3} - 7{x^2} + ax + b}} = - 2$$, then the value of (a $$-$$ b) is equal to ___________.
Let [t] denote the greatest integer $$\le$$ t and {t} denote the fractional part of t. The integral value of $$\alpha$$ for which the left hand limit of the function
$$f(x) = [1 + x] + {{{\alpha ^{2[x] + {\{x\}}}} + [x] - 1} \over {2[x] + \{ x\} }}$$ at x = 0 is equal to $$\alpha - {4 \over 3}$$, is _____________.
Let $$f(x) = \left[ {2{x^2} + 1} \right]$$ and $$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {2x - 3,} & {x < 0} \cr {2x + 3,} & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$, where [t] is the greatest integer $$\le$$ t. Then, in the open interval ($$-$$1, 1), the number of points where fog is discontinuous is equal to ______________.
The number of points where the function
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {|2{x^2} - 3x - 7|} & {if} & {x \le - 1} \cr {[4{x^2} - 1]} & {if} & { - 1 < x < 1} \cr {|x + 1| + |x - 2|} & {if} & {x \ge 1} \cr } } \right.$$
[t] denotes the greatest integer $$\le$$ t, is discontinuous is _____________.
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {a\sin {\pi \over 2}(x - 1),} & {for\,x \le 0} \cr {{{\tan 2x - \sin 2x} \over {b{x^3}}},} & {for\,x > 0} \cr } } \right.$$.
If f is continuous at x = 0, then 10 $$-$$ ab is equal to ________________.
where P(x) is a polynomial such that P'' (x) is always a constant and P(3) = 9. If f(x) is continuous at x = 2, then P(5) is equal to _____________.
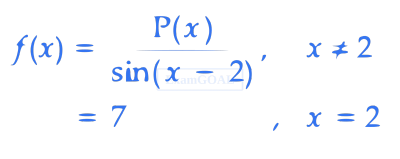
Let g : R $$\to$$ R be given by $$g(x) = f(x + 2) - f(x - 2)$$. If n and m denote the number of points in R where g is not continuous and not differentiable, respectively, then n + m is equal to ______________.
$$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {\mathop {\max }\limits_{0 \le t \le x} \{ {t^3} - 6{t^2} + 9t - 3),} & {0 \le x \le 3} \cr {4 - x,} & {3 < x \le 4} \cr } } \right.$$, then the number of points in the interval (0, 4) where g(x) is NOT differentiable, is ____________.
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{h \to 0} {1 \over h}(f(h) - 1)$$ is equal to ____________.
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x + a,} & {x < 0} \cr {|x - 1|,} & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$ and
$$g(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {x + 1,} & {x < 0} \cr {{{(x - 1)}^2} + b,} & {x \ge 0} \cr } } \right.$$,
where a, b are non-negative real numbers. If (gof) (x) is continuous for all x $$\in$$ R, then a + b is equal to ____________.
$$f(x) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {\min \{ |x|,2 - {x^2}\} ,} & { - 2 \le x \le 2} \cr {[|x|],} & {2 < |x| \le 3} \cr } } \right.$$ where [x] denotes the greatest integer $$ \le $$ x. The number of points, where f is not differentiable in ($$-$$3, 3) is ___________.
f(x) = | 2x + 1 | $$-$$ 3| x + 2 | + | x2 + x $$-$$ 2 |, x$$\in$$R is not differentiable, is __________.
$$f\left( x \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{x^5}\sin \left( {{1 \over x}} \right) + 5{x^2},} & {x < 0} \cr {0,} & {x = 0} \cr {{x^5}\cos \left( {{1 \over x}} \right) + \lambda {x^2},} & {x > 0} \cr } } \right.$$
The value of $$\lambda $$ for which f ''(0) exists, is _______.
f(x+y) = f(x) + f(y) + xy2 + x2y, for all real x and y.
$$\mathop {\lim }\limits_{x \to 0} {{f\left( x \right)} \over x} = 1$$, then f'(3) is equal to ______.
then the value of k is _______ .
(n $$ \in $$ N) then the value of n is equal to _______.
f(x) = $$\left\{ {\matrix{ {{1 \over x}{{\log }_e}\left( {{{1 + 3x} \over {1 - 2x}}} \right),} & {when\,x \ne 0} \cr {k,} & {when\,x = 0} \cr } } \right.$$
is continuous, then k is equal to_______.