Geometrical Optics · Physics · JEE Main
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
A convex lens of focal length 30 cm is placed in contact with a concave lens of focal length 20 cm. An object is placed at 20 cm to the left of this lens system. The distance of the image from the lens in cm is ________.
A concave-convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and the radii of curvature of its surfaces are 30 cm and 20 cm, respectively. The concave surface is upwards and is filled with a liquid of refractive index 1.3. The focal length of the liquid-glass combination will be
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Refractive index of glass is higher than that of air.
Reason (R): Optical density of a medium is directly proportionate to its mass density which results in a proportionate refractive index.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
A mirror is used to produce an image with magnification of $\frac{1}{4}$. If the distance between object and its image is 40 cm, then the focal length of the mirror is ________.
A transparent block A having refractive index $\mu = 1.25$ is surrounded by another medium of refractive index $\mu = 1.0$ as shown in the figure. A light ray is incident on the flat face of the block with incident angle $\theta$ as shown in the figure. What is the maximum value of $\theta$ for which light suffers total internal reflection at the top surface of the block?

Two thin convex lenses of focal lengths 30 cm and 10 cm are placed coaxially, 10 cm apart. The power of this combination is:
A lens having refractive index 1.6 has focal length of 12 cm , when it is in air. Find the focal length of the lens when it is placed in water. (Take refractive index of water as 1.28)
A finite size object is placed normal to the principal axis at a distance of 30 cm from a convex mirror of focal length 30 cm . A plane mirror is now placed in such a way that the image produced by both the mirrors coincide with each other. The distance between the two mirrors is :
When an object is placed 40 cm away from a spherical mirror an image of magnification $\frac{1}{2}$ is produced. To obtain an image with magnification of $\frac{1}{3}$, the object is to be moved :
Consider following statements for refraction of light through prism, when angle of deviation is minimum.
A. The refracted ray inside prism becomes parallel to the base.
B. Larger angle prisms provide smaller angle of minimum deviation.
C. Angle of incidence and angle of emergence becomes equal.
D. There are always two sets of angle of incidence for which deviation will be same except at minimum deviation setting.
E. Angle of refraction becomes double of prism angle.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :

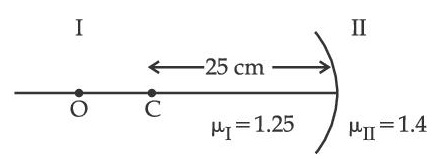
A spherical surface separates two media of refractive indices 1 and 1.5 as shown in figure. Distance of the image of an object ' O ', is :
( C is the center of curvature of the spherical surface and R is the radius of curvature)
A slanted object $A B$ is placed on one side of convex lens as shown in the diagram. The image is formed on the opposite side. Angle made by the image with principal axis is :

A convex lens made of glass (refractive index = 1.5) has focal length 24 cm in air. When it is totally immersed in water (refractive index = 1.33), its focal length changes to

Two concave refracting surfaces of equal radii of curvature and refractive index 1.5 face each other in air as shown in figure. A point object O is placed midway, between P and B. The separation between the images of O, formed by each refracting surface is :
Two identical symmetric double convex lenses of focal length f are cut into two equal parts L1, L2 by AB plane and L3, L4 by XY plane as shown in figure respectively. The ratio of focal lengths of lenses L1 and L3 is

Let u and v be the distances of the object and the image from a lens of focal length f. The correct graphical representation of u and v for a convex lens when |u| > f, is
A concave mirror produces an image of an object such that the distance between the object and image is 20 cm. If the magnification of the image is –3, then the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the mirror is :
A thin prism $\mathrm{P}_1$ with angle $4^{\circ}$ made of glass having refractive index 1.54 , is combined with another thin prism $\mathrm{P}_2$ made of glass having refractive index 1.72 to get dispersion without deviation. The angle of the prism $\mathrm{P}_2$ in degrees is
A hemispherical vessel is completely filled with a liquid of refractive index $\mu$. A small coin is kept at the lowest point $(\mathrm{O})$ of the vessel as shown in figure. The minimum value of the refractive index of the liquid so that a person can see the coin from point E (at the level of the vessel) is _________.

A photograph of a landscape is captured by a drone camera at a height of 18 km . The size of the camera film is $2 \mathrm{~cm} \times 2 \mathrm{~cm}$ and the area of the landscape photographed is $400 \mathrm{~km}^2$. The focal length of the lens in the drone camera is :
What is the relative decrease in focal length of a lens for an increase in optical power by 0.1 D from 2.5D ? ['D' stands for dioptre]
A thin plano convex lens made of glass of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.2. When the plane side of the lens is silver coated for complete reflection, the lens immersed in the liquid behaves like a concave mirror of focal length 0.2 m . The radius of curvature of the curved surface of the lens is
A plano-convex lens having radius of curvature of first surface 2 cm exhibits focal length of $f_1$ in air. Another plano-convex lens with first surface radius of curvature 3 cm has focal length of $f_2$ when it is immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.2. If both the lenses are made of same glass of refractive index 1.5 , the ratio of $f_1$ and $f_2$ will be
A concave mirror of focal length $f$ in air is dipped in a liquid of refractive index $\mu$. Its focal length in the liquid will be:
The refractive index of the material of a glass prism is $\sqrt{3}$. The angle of minimum deviation is equal to the angle of the prism. What is the angle of the prism?
What is the lateral shift of a ray refracted through a parallel-sided glass slab of thickness ' $h$ ' in terms of the angle of incidence ' $i$ ' and angle of refraction ' $r$ ', if the glass slab is placed in air medium?
A spherical surface of radius of curvature $R$, separates air from glass (refractive index $=1.5$ ). The centre of curvature is in the glass medium. A point object ' $O$ ' placed in air on the optic axis of the surface, so that its real image is formed at 'I' inside glass. The line OI intersects the spherical surface at $P$ and $P O=P I$. The distance $P O$ equals to
Given a thin convex lens (refractive index $\mu_2$ ), kept in a liquid (refractive index $\mu_1, \mu_1<\mu_2$ ) having radii of curvatures $\left|R_1\right|$ and $\left|R_2\right|$. Its second surface is silver polished. Where should an object be placed on the optic axis so that a real and inverted image is formed at the same place?
A symmetric thin biconvex lens is cut into four equal parts by two planes $A B$ and $C D$ as shown in figure. If the power of original lens is 4D then the power of a part of the divided lens is

In the diagram given below, there are three lenses formed. Considering negligible thickness of each of them as compared to $\left|R_1\right|$ and $\left|R_2\right|$, i.e., the radii of curvature for upper and lower surfaces of the glass lens, the power of the combination is

Given is a thin convex lens of glass (refractive index $\mu$ ) and each side having radius of curvature $R$. One side is polished for complete reflection. At what distance from the lens, an object be placed on the optic axis so that the image gets formed on the object itself?
The following figure represents two biconvex lenses $$L_1$$ and $$L_2$$ having focal length $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and $$15 \mathrm{~cm}$$ respectively. The distance between $$L_1$$ & $$L_2$$ is :

Given below are two statements :
Statement (I) : When an object is placed at the centre of curvature of a concave lens, image is formed at the centre of curvature of the lens on the other side.
Statement (II) : Concave lens always forms a virtual and erect image.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
The position of the image formed by the combination of lenses is :

Critical angle of incidence for a pair of optical media is $$45^{\circ}$$. The refractive indices of first and second media are in the ratio:
For the thin convex lens, the radii of curvature are at $$15 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and $$30 \mathrm{~cm}$$ respectively. The focal length the lens is $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The refractive index of the material is :
An effective power of a combination of 5 identical convex lenses which are kept in contact along the principal axis is $$25 \mathrm{D}$$. Focal length of each of the convex lens is:
In an experiment to measure focal length ($$f$$) of convex lens, the least counts of the measuring scales for the position of object (u) and for the position of image (v) are $$\Delta u$$ and $$\Delta v$$, respectively. The error in the measurement of the focal length of the convex lens will be:
The refractive index of a prism with apex angle $$A$$ is $$\cot A / 2$$. The angle of minimum deviation is :
If the distance between object and its two times magnified virtual image produced by a curved mirror is $$15 \mathrm{~cm}$$, the focal length of the mirror must be:
A convex mirror of radius of curvature $$30 \mathrm{~cm}$$ forms an image that is half the size of the object. The object distance is :
A biconvex lens of refractive index 1.5 has a focal length of $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$ in air. Its focal length when immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.6 will be:
If the refractive index of the material of a prism is $$\cot \left(\frac{A}{2}\right)$$, where $$A$$ is the angle of prism then the angle of minimum deviation will be
Identify the physical quantity that cannot be measured using spherometer :
A convex lens of focal length $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$ forms an image of an extended source of light on a photoelectric cell. A current I is produced. The lens is replaced by another convex lens having the same diameter but focal length $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The photoelectric current now is :
A vessel of depth '$$d$$' is half filled with oil of refractive index $$n_{1}$$ and the other half is filled with water of refractive index $$n_{2}$$. The apparent depth of this vessel when viewed from above will be-
An ice cube has a bubble inside. When viewed from one side the apparent distance of the bubble is $$12 \mathrm{~cm}$$. When viewed from the opposite side, the apparent distance of the bubble is observed as $$4 \mathrm{~cm}$$. If the side of the ice cube is $$24 \mathrm{~cm}$$, the refractive index of the ice cube is
When one light ray is reflected from a plane mirror with $$30^{\circ}$$ angle of reflection, the angle of deviation of the ray after reflection is :
The critical angle for a denser-rarer interface is $$45^{\circ}$$. The speed of light in rarer medium is $$3 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$$. The speed of light in the denser medium is:
An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a plane mirror. The virtual and erect image is formed by the mirror. Now the mirror is moved by 4 cm towards the stationary object. The distance by which the position of image would be shifted, will be
In a reflecting telescope, a secondary mirror is used to:
Given below are two statements: one is labelled as Assertion A and the other is labelled as Reason R
Assertion A: The phase difference of two light waves change if they travel through different media having same thickness, but different indices of refraction.
Reason R: The wavelengths of waves are different in different media.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below
A 2 meter long scale with least count of $$0.2 \mathrm{~cm}$$ is used to measure the locations of objects on an optical bench. While measuring the focal length of a convex lens, the object pin and the convex lens are placed at $$80 \mathrm{~cm}$$ mark and $$1 \mathrm{~m}$$ mark, respectively. The image of the object pin on the other side of lens coincides with image pin that is kept at $$180 \mathrm{~cm}$$ mark. The $$\%$$ error in the estimation of focal length is:
A monochromatic light wave with wavelength $$\lambda_{1}$$ and frequency $$v_{1}$$ in air enters another medium. If the angle of incidence and angle of refraction at the interface are $$45^{\circ}$$ and $$30^{\circ}$$ respectively, then the wavelength $$\lambda_{2}$$ and frequency $$v_{2}$$ of the refracted wave are:
Two objects A and B are placed at 15 cm and 25 cm from the pole in front of a concave mirror having radius of curvature 40 cm. The distance between images formed by the mirror is _______________.
A thin prism $P_1$ with an angle $6^{\circ}$ and made of glass of refractive index $1.54$ is combined with another prism $P_2$ made from glass of refractive index $1.72$ to produce dispersion without average deviation. The angle of prism $P_2$ is
A person has been using spectacles of power $$-1.0$$ dioptre for distant vision and a separate reading glass of power $$2.0$$ dioptres. What is the least distance of distinct vision for this person :
A scientist is observing a bacteria through a compound microscope. For better analysis and to improve its resolving power he should. (Select the best option)
The light rays from an object have been reflected towards an observer from a standard flat mirror, the image observed by the observer are :-
A. Real
B. Erect
C. Smaller in size then object
D. Laterally inverted
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
When a beam of white light is allowed to pass through convex lens parallel to principal axis, the different colours of light converge at different point on the principle axis after refraction. This is called :
Light enters from air into a given medium at an angle of $$45^{\circ}$$ with interface of the air-medium surface. After refraction, the light ray is deviated through an angle of $$15^{\circ}$$ from its original direction. The refractive index of the medium is:
The power of a lens (biconvex) is $$1.25 \mathrm{~m}^{-1}$$ in particular medium. Refractive index of the lens is 1.5 and radii of curvature are $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$ respectively. The refractive index of surrounding medium:
As shown in the figure, after passing through the medium 1 . The speed of light $$v_{2}$$ in medium 2 will be :
$$\left(\right.$$ Given $$\mathrm{c}=3 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$ )

In normal adujstment, for a refracting telescope, the distance between objective and eye piece is $$30 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The focal length of the objective, when the angular magnification of the telescope is 2 , will be :
A microscope was initially placed in air (refractive index 1). It is then immersed in oil (refractive index 2). For a light whose wavelength in air is $$\lambda$$, calculate the change of microscope's resolving power due to oil and choose the correct option.
Light travels in two media $$M_{1}$$ and $$M_{2}$$ with speeds $$1.5 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$ and $$2.0 \times 10^{8} \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$ respectively. The critical angle between them is :
For an object placed at a distance 2.4 m from a lens, a sharp focused image is observed on a screen placed at a distance 12 cm from the lens. A glass plate of refractive index 1.5 and thickness 1 cm is introduced between lens and screen such that the glass plate plane faces parallel to the screen. By what distance should the object be shifted so that a sharp focused image is observed again on the screen?
Which of the following statement is correct?
Time taken by light to travel in two different materials $$A$$ and $$B$$ of refractive indices $$\mu_{A}$$ and $$\mu_{B}$$ of same thickness is $$t_{1}$$ and $$t_{2}$$ respectively. If $$t_{2}-t_{1}=5 \times 10^{-10}$$ s and the ratio of $$\mu_{A}$$ to $$\mu_{B}$$ is $$1: 2$$. Then, the thickness of material, in meter is: (Given $$v_{\mathrm{A}}$$ and $$v_{\mathrm{B}}$$ are velocities of light in $$A$$ and $$B$$ materials respectively.)
The speed of light in media 'A' and 'B' are $$2.0 \times {10^{10}}$$ cm/s and $$1.5 \times {10^{10}}$$ cm/s respectively. A ray of light enters from the medium B to A at an incident angle '$$\theta$$'. If the ray suffers total internal reflection, then
The refracting angle of a prism is A and refractive index of the material of the prism is cot (A/2). Then the angle of minimum deviation will be -
The aperture of the objective is 24.4 cm. The resolving power of this telescope, if a light of wavelength 2440 $$\mathop A\limits^o $$ is used to see th object will be :
A convex lens has power P. It is cut into two halves along its principal axis. Further one piece (out of the two halves) is cut into two halves perpendicular to the principal axis (as shown in figures). Choose the incorrect option for the reported pieces.

Consider a light ray travelling in air is incident into a medium of refractive index $$\sqrt{2n}$$. The incident angle is twice that of refracting angle. Then, the angle of incidence will be :
A light wave travelling linearly in a medium of dielectric constant 4, incidents on the horizontal interface separating medium with air. The angle of incidence for which the total intensity of incident wave will be reflected back into the same medium will be :
(Given : relative permeability of medium $$\mu$$r = 1)
The difference of speed of light in the two media A and B (vA $$-$$ vB) is 2.6 $$\times$$ 107 m/s. If the refractive index of medium B is 1.47, then the ratio of refractive index of medium B to medium A is : (Given : speed of light in vacuum c = 3 $$\times$$ 108 ms$$-$$1)





The refractive indices of the material of the prism for red, green and blue wavelength are 1.27, 1.42 and 1.49 respectively. The colour of the ray(s) emerging out of the face PR is :
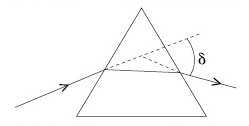
(A) Incident ray and emergent ray are symmetric to the prism.
(B) The refracted ray inside the prism becomes parallel to its base
(C) Angle of incidence is equal to that of the angle of emergence
(D) When angle of emergence is double the angle of incidence
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Assertion A : For a simple microscope, the angular size of the object equals the angular size of the image.
Reason R : Magnification is achieved as the small object can be kept much closer to the eye than 25 cm and hence it subtends a large angle.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
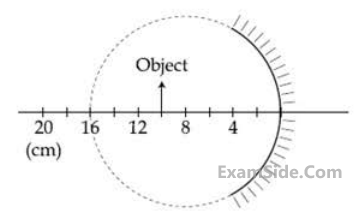 A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the
figure from a hollow glass sphere. If an object
is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be
the nature and magnification of the image of
the object?
A spherical mirror is obtained as shown in the
figure from a hollow glass sphere. If an object
is positioned in front of the mirror, what will be
the nature and magnification of the image of
the object? (Figure drawn as schematic and not to scale)
[Use the fact that surface area of a spherical cap of height h and radius of curvature r is 2$$\pi $$rh]:
(Graphs are drawn schematically and are not to scale)
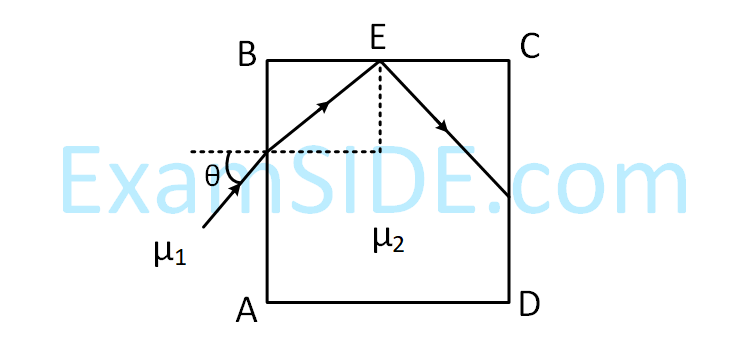
Then $$\theta $$ must satisfy :





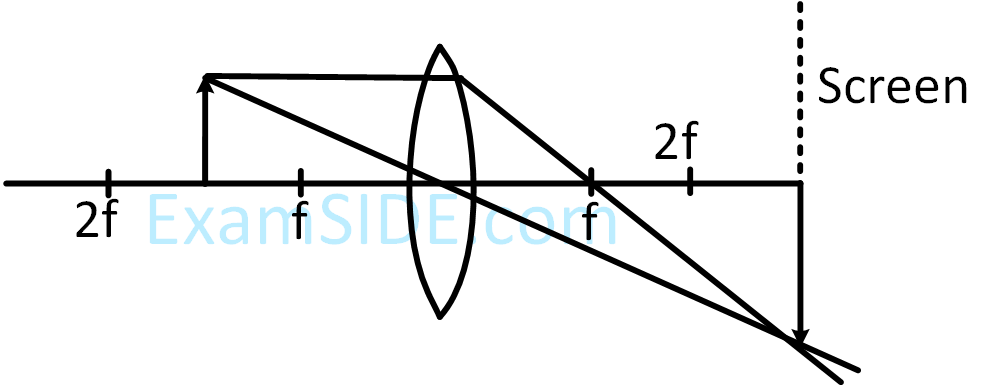
If the whole set up is immersed in water without disturbing the object and the screen positions, what will one observe on the screen ?




Identify the correct statements.
If the same lens is instead silvered on the curved surface and illuminated from other side as in Fig-B, it acts like an optical system of focal length $$10$$ $$cm.$$ The refractive index of the material of lens is :



| Object Pin |
Convex Lens |
Convex Mirror |
Image Pin |
|---|---|---|---|
| 22.2 cm | 32.2 cm | 45.8 cm | 71.2 cm |
The focal length of the convex lens is f1 and that of mirror is f2. Then taking index correction to be negligibly small, f1 and f2 are close to :

As the beam enters the medium, it will
The speed of light in the medium is

The incident angle $$\theta $$ for which the light ray grazes along the wall of the rod is :
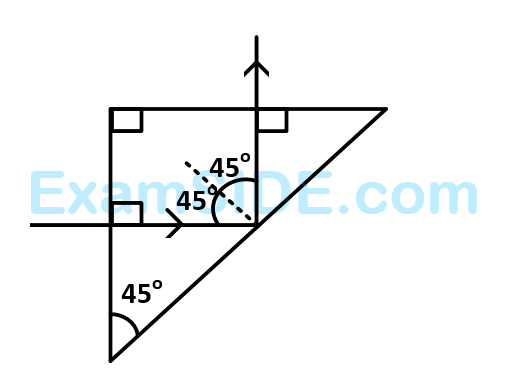
Numerical
A container contains a liquid with refractive index of 1.2 up to a height of 60 cm and another liquid having refractive index 1.6 is added to height H above first liquid. If viewed from above, the apparent shift in the position of bottom of container is 40 cm . The value of H is ________ cm . (Consider liquids are immisible)
Distance between object and its image (magnified by $-\frac{1}{3}$ ) is 30 cm . The focal length of the mirror used is $\left(\frac{x}{4}\right) \mathrm{cm}$, where magnitude of value of $x$ is _________.
Light from a point source in air falls on a spherical glass surface (refractive index, $\mu=1.5$ and radius of curvature $=50 \mathrm{~cm}$ ). The image is formed at a distance of 200 cm from the glass surface inside the glass. The magnitude of distance of the light source from the glass surface is ___________m.
Two light beams fall on a transparent material block at point 1 and 2 with angle $\theta_1$ and $\theta_2$, respectively, as shown in figure. After refraction, the beams intersect at point 3 which is exactly on the interface at other end of the block. Given : the distance between 1 and 2, $\mathrm{d}=4 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}$ and $\theta_1=\theta_2=\cos ^{-1}\left(\frac{n_2}{2 n_1}\right)$. where refractive index of the block $n_2>$ refractive index of the outside medium $\mathrm{n}_1$, then the thickness of the block is ______ cm .

The driver sitting inside a parked car is watching vehicles approaching from behind with the help of his side view mirror, which is a convex mirror with radius of curvature $\mathrm{R}=2 \mathrm{~m}$. Another car approaches him from behind with a uniform speed of $90 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{hr}$. When the car is at a distance of 24 m from him, the magnitude of the acceleration of the image of the car in the side view mirror is ' $a$ '. The value of $100 a$ is __________ $\mathrm{m} / \mathrm{s}^2$.
The refractive index of prism is $$\mu=\sqrt{3}$$ and the ratio of the angle of minimum deviation to the angle of prism is one. The value of angle of prism is _________$$^\circ$$.
A light ray is incident on a glass slab of thickness $$4 \sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}$$ and refractive index $$\sqrt{2}$$ The angle of incidence is equal to the critical angle for the glass slab with air. The lateral displacement of ray after passing through glass slab is ______ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.
(Given $$\sin 15^{\circ}=0.25$$)
Light from a point source in air falls on a convex curved surface of radius $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and refractive index 1.5. If the source is located at $$100 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the convex surface, the image will be formed at ________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$ from the object.
In an experiment to measure the focal length $$(f)$$ of a convex lens, the magnitude of object distance $$(x)$$ and the image distance $$(y)$$ are measured with reference to the focal point of the lens. The $$y$$-$$x$$ plot is shown in figure.
The focal length of the lens is ________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

The distance between object and its two times magnified real image as produced by a convex lens is $$45 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The focal length of the lens used is _______ cm.
Two immiscible liquids of refractive indices $$\frac{8}{5}$$ and $$\frac{3}{2}$$ respectively are put in a beaker as shown in the figure. The height of each column is $$6 \mathrm{~cm}$$. A coin is placed at the bottom of the beaker. For near normal vision, the apparent depth of the coin is $$\frac{\alpha}{4} \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of $$\alpha$$ is _________.

A bi convex lens of focal length $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ is cut in two identical parts along a plane perpendicular to the principal axis. The power of each lens after cut is ____________ D.
A fish rising vertically upward with a uniform velocity of $$8 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$, observes that a bird is diving vertically downward towards the fish with the velocity of $$12 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}$$. If the refractive index of water is $$\frac{4}{3}$$, then the actual velocity of the diving bird to pick the fish, will be __________ $$\mathrm{ms}^{-1}$$.
Two convex lenses of focal length $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$ each are placed coaxially with a separation of $$60 \mathrm{~cm}$$ between them. The image of the distant object formed by the combination is at _____________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$ from the first lens.
As shown in the figure, a plane mirror is fixed at a height of $$50 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the bottom of tank containing water $$\left(\mu=\frac{4}{3}\right)$$. The height of water in the tank is $$8 \mathrm{~cm}$$. A small bulb is placed at the bottom of the water tank. The distance of image of the bulb formed by mirror from the bottom of the tank is ___________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

The radius of curvature of each surface of a convex lens having refractive index 1.8 is $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The lens is now immersed in a liquid of refractive index 1.5 . The ratio of power of lens in air to its power in the liquid will be $$x: 1$$. The value of $$x$$ is _________.
A point object, 'O' is placed in front of two thin symmetrical coaxial convex lenses $$\mathrm{L}_{1}$$ and $$\mathrm{L}_{2}$$ with focal length $$24 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and $$9 \mathrm{~cm}$$ respectively. The distance between two lenses is $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ and the object is placed $$6 \mathrm{~cm}$$ away from lens $$\mathrm{L}_{1}$$ as shown in the figure. The distance between the object and the image formed by the system of two lenses is __________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

Two transparent media having refractive indices 1.0 and 1.5 are separated by a spherical refracting surface of radius of curvature $$30 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The centre of curvature of surface is towards denser medium and a point object is placed on the principle axis in rarer medium at a distance of $$15 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the pole of the surface. The distance of image from the pole of the surface is ____________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.
Two vertical parallel mirrors A and B are separated by $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$. A point object $$\mathrm{O}$$ is placed at a distance of $$2 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from mirror $$\mathrm{A}$$. The distance of the second nearest image behind mirror A from the mirror $$\mathrm{A}$$ is _________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

A pole is vertically submerged in swimming pool, such that it gives a length of shadow $$2.15 \mathrm{~m}$$ within water when sunlight is incident at angle of $$30^{\circ}$$ with the surface of water. If swimming pool is filled to a height of $$1.5 \mathrm{~m}$$, then the height of the pole above the water surface in centimeters is $$\left(n_{w}=4 / 3\right)$$ ____________.
A thin cylindrical rod of length $$10 \mathrm{~cm}$$ is placed horizontally on the principle axis of a concave mirror of focal length $$20 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The rod is placed in a such a way that mid point of the rod is at $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the pole of mirror. The length of the image formed by the mirror will be $$\frac{x}{3} \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of $$x$$ is _____________.
In an experiment for estimating the value of focal length of converging mirror, image of an object placed at $$40 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the pole of the mirror is formed at distance $$120 \mathrm{~cm}$$ from the pole of the mirror. These distances are measured with a modified scale in which there are 20 small divisions in $$1 \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of error in measurement of focal length of the mirror is $$\frac{1}{\mathrm{~K}} \mathrm{~cm}$$. The value of $$\mathrm{K}$$ is __________.
In an experiment of measuring the refractive index of a glass slab using travelling microscope in physics lab, a student measures real thickness of the glass slab as 5.25 mm and apparent thickness of the glass slab as 5.00 mm. Travelling microscope has 20 divisions in one cm on main scale and 20 divisions on vernier scale is equal to 49 divisions on main scale. The estimated uncertainty in the measurement of refractive index of the slab is $$\frac{x}{10}\times10^{-3}$$, where $$x$$ is ___________
An object is placed on the principal axis of convex lens of focal length 10cm as shown. A plane mirror is placed on the other side of lens at a distance of 20 cm. The image produced by the plane mirror is 5cm inside the mirror. The distance of the object from the lens is ___________ cm.

A ray of light is incident from air on a glass plate having thickness $$\sqrt3$$ cm and refractive index $$\sqrt2$$. The angle of incidence of a ray is equal to the critical angle for glass-air interface. The lateral displacement of the ray when it passes through the plate is ____________ $$\times$$ 10$$^{-2}$$ cm. (given $$\sin 15^\circ = 0.26$$)
A convex lens of refractive index 1.5 and focal length 18cm in air is immersed in water. The change in focal length of the lens will be ___________ cm.
(Given refractive index of water $$=\frac{4}{3}$$)
As shown in the figure, a combination of a thin plano concave lens and a thin plano convex lens is used to image an object placed at infinity. The radius of curvature of both the lenses is 30 cm and refraction index of the material for both the lenses is 1.75. Both the lenses are placed at distance of 40 cm from each other. Due to the combination, the image of the object is formed at distance $$x=$$ _________ cm, from concave lens.

The X-Y plane be taken as the boundary between two transparent media $$\mathrm{M}_{1}$$ and $$\mathrm{M}_{2}$$. $$\mathrm{M}_{1}$$ in $$Z \geqslant 0$$ has a refractive index of $$\sqrt{2}$$ and $$M_{2}$$ with $$Z<0$$ has a refractive index of $$\sqrt{3}$$. A ray of light travelling in $$\mathrm{M}_{1}$$ along the direction given by the vector $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{P}}=4 \sqrt{3} \hat{i}-3 \sqrt{3} \hat{j}-5 \hat{k}$$, is incident on the plane of separation. The value of difference between the angle of incident in $$\mathrm{M}_{1}$$ and the angle of refraction in $$\mathrm{M}_{2}$$ will be __________ degree.
An object 'O' is placed at a distance of $$100 \mathrm{~cm}$$ in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature $$200 \mathrm{~cm}$$ as shown in the figure. The object starts moving towards the mirror at a speed $$2 \mathrm{~cm} / \mathrm{s}$$. The position of the image from the mirror after $$10 \mathrm{~s}$$ will be at _________ $$\mathrm{cm}$$.

In an experiment with a convex lens, The plot of the image distance $$\left(v^{\prime}\right)$$ against the object distance ($$\left.\mu^{\prime}\right)$$ measured from the focus gives a curve $$v^{\prime} \mu^{\prime}=225$$. If all the distances are measured in $$\mathrm{cm}$$. The magnitude of the focal length of the lens is ___________ cm.
A thin prism of angle $$6^{\circ}$$ and refractive index for yellow light $$\left(\mathrm{n}_{\mathrm{Y}}\right) 1.5$$ is combined with another prism of angle $$5^{\circ}$$ and $$\mathrm{n}_{\mathrm{Y}}=1.55$$. The combination produces no dispersion. The net average deviation $$(\delta)$$ produced by the combination is $$\left(\frac{1}{x}\right)^{\circ}$$. The value of $$x$$ is ____________.

In the given figure, the face $$A C$$ of the equilateral prism is immersed in a liquid of refractive index '$$n$$'. For incident angle $$60^{\circ}$$ at the side $$A C$$, the refractive light beam just grazes along face $$A C$$. The refractive index of the liquid $$n=\frac{\sqrt{x}}{4}$$. The value of $$x$$ is ____________.
(Given refractive index of glass $$=1.5$$ )

The graph between $$\frac{1}{u}$$ and $$\frac{1}{v}$$ for a thin convex lens in order to determine its focal length is plotted as shown in the figure. The refractive index of lens is $$1.5$$ and its both the surfaces have same radius of curvature $$R$$. The value of $$R$$ will be ____________ $$\mathrm{cm} .$$ (where $$u=$$ object distance, $$v=$$ image distance)

A convex lens of focal length 20 cm is placed in front of a convex mirror with principal axis coinciding each other. The distance between the lens and mirror is 10 cm. A point object is placed on principal axis at a distance of 60 cm from the convex lens. The image formed by combination coincides the object itself. The focal length of the convex mirror is ____________ cm.
The refractive index of an equilateral prism is $$\sqrt 2 $$. The angle of emergence under minimum deviation position of prism, in degree, is ___________.
A parallel beam of light is allowed to fall on a transparent spherical globe of diameter 30 cm and refractive index 1.5. The distance from the centre of the globe at which the beam of light can converge is _____________ mm.
A small bulb is placed at the bottom of a tank containing water to a depth of $$\sqrt7$$ m. The refractive index of water is $${4 \over 3}$$. The area of the surface of water through which light from the bulb can emerge out is x$$\pi$$ m2. The value of x is __________.
A light ray is incident, at an incident angle $$\theta$$1, on the system of tow plane mirrors M1 and M2 having an inclination angle 75$$^\circ$$ between them (as shown in figure). After reflecting from mirror M1 it gets reflected back by the mirror M2 with an angle of reflection 30$$^\circ$$. The total deviation of the ray will be _____________ degree.

A ray of light is incident at an angle of incidence 60$$^\circ$$ on the glass slab of refractive index $$\sqrt3$$. After refraction, the light ray emerges out from other parallel faces and lateral shift between incident ray and emergent ray is 4$$\sqrt3$$ cm. The thickness of the glass slab is __________ cm.
Two identical thin biconvex lens of focal length 15 cm and refractive index 1.5 are in contact with each other. The space between the lenses is filled with a liquid of refractive index 1.25. The focal length of the combination is __________ cm.

When the convex mirror is removed, a real and inverted image is formed at a position. The distance of the image from the object will be .............. (cm)
$${n_1} = 1.2 + {{10.8 \times {{10}^{ - 14}}} \over {{\lambda ^2}}}$$ and $${n_2} = 1.45 + {{1.8 \times {{10}^{ - 14}}} \over {{\lambda ^2}}}$$
The wavelength for which rays incident at any angle on the interface BC pass through without bending at that interface will be _____________ nm.
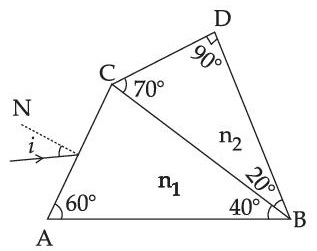

Value of N is ____.
The distance between an object and the objective lens, at which the strain on the eye is minimum is $${n \over {40}}$$ cm. The value of n is _____.
