Solutions · Chemistry · JEE Main
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
The freezing point depression of a 0.1 m aqueous solution of a monobasic weak acid HA is 0.20 °C. The dissociation constant for the acid is
Given: $K_f$(H2O) = 1.8 K kg mol−1, molality ≡ molarity
Which of the following binary mixture does not show the behaviour of minimum boiling azeotropes?
Liquid A and B form an ideal solution. The vapour pressures of pure liquids A and B are 350 and 750 mm Hg respectively at the same temperature. If $x_A$ and $x_B$ are the mole fraction of A and B in solution while $y_A$ and $y_B$ are the mole fraction of A and B in vapour phase, then,
Match List - I with List - II.
| List - I | List - II |
|---|---|
| (A) Solution of chloroform and acetone | (I) Minimum boiling azeotrope |
| (B) Solution of ethanol and water | (II) Dimerizes |
| (C) Solution of benzene and toluene | (III) Maximum boiling azeotrope |
| (D) Solution of acetic acid in benzene | (IV) ΔVmix = 0 |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Given below are two statements:
Statement (I) : Molal depression constant $\mathrm{K}_f$ is given by $\frac{\mathrm{M}_1 \mathrm{RT}_f}{\Delta \mathrm{~S}_{\mathrm{fus}}}$, where symbols have their usual meaning.
Statement (II) : $\mathrm{K}_f$ for benzene is less than the $\mathrm{K}_f$ for water.
In the light of the above statements, choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
$X Y$ is the membrane/partition between two chambers 1 and 2 containing sugar solutions of concentration $c_1$ and $c_2\left(c_1>c_2\right) \mathrm{mol} \mathrm{L}^{-1}$. For the reverse osmosis to take place identify the correct condition.
(Here $p_1$ and $p_2$ are pressures applied on chamber 1 and 2 ).

A. Membrane/Partition : Cellophane, $\mathrm{p}_1>\pi$
B. Membrane/Partition : Porous, $\mathrm{p}_2>\pi$
C. Membrane/Partition : Parchment paper, $p_1>\pi$
D. Membrane/Partition : Cellophane, $\mathrm{p}_2>\pi$
Choose the correct answer from the option given below:
Which of the following properties will change when system containing solution 1 will become solution 2 ?

' $x$ ' g of NaCl is added to water in a beaker with a lid. The temperature of the system is raised from $1^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. Which out of the following plots, is best suited for the change in the molarity $(\mathrm{M})$ of the solution with respect to temperature ?
[Consider the solubility of NaCl remains unchanged over the temperature range]
A solution is made by mixing one mole of volatile liquid $A$ with 3 moles of volatile liquid $B$. The vapour pressure of pure A is 200 mm Hg and that of the solution is 500 mm Hg . The vapour pressure of pure B and the least volatile component of the solution, respectively, are:
Which of the following graph correctly represents the plots of $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{H}}$ at 1 bar for gases in water versus temperature?
Given below are two statements :
Statement (I): NaCl is added to the ice at 0°C, present in the ice cream box to prevent the melting of ice cream.
Statement (II): On addition of NaCl to ice at 0°C, there is a depression in freezing point.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
1.24 g of AX2 (molar mass 124 g mol−1) is dissolved in 1 kg of water to form a solution with boiling point of 100.015°C, while 25.4 g of AY2 (molar mass 250 g mol−1) in 2 kg of water constitutes a solution with a boiling point of 100.0260°C.
Kb(H2O) = 0.52 kg mol−1
Which of the following is correct?
Assume a living cell with 0.9% (w/w) of glucose solution (aqueous). This cell is immersed in another solution having equal mole fraction of glucose and water.
(Consider the data upto first decimal place only)
The cell will :
What is the freezing point depression constant of a solvent, 50 g of which contain 1 g non volatile solute (molar mass $256 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$ ) and the decrease in freezing point is 0.40 K ?
Consider the given plots of vapour pressure (VP) vs temperature(T/K). Which amongst the following options is correct graphical representation showing $\Delta \mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{f}}$, depression in the freezing point of a solvent in a solution?
When a non-volatile solute is added to the solvent, the vapour pressure of the solvent decreases by 10 mm of Hg . The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2 . What would be the mole fraction of the solvent if decrease in vapour pressure is 20 mm of Hg ?
Consider a binary solution of two volatile liquid components 1 and $2 . x_1$ and $y_1$ are the mole fractions of component 1 in liquid and vapour phase, respectively. The slope and intercept of the linear plot of $\frac{1}{x_1}$ vs $\frac{1}{y_1}$ are given respectively as :
Arrange the following solutions in order of their increasing boiling points.
(i) $10^{-4} \mathrm{M} \mathrm{NaCl}$
(ii) $10^{-4} \mathrm{M}$ Urea
(iii) $10^{-3} \mathrm{M} \mathrm{NaCl}$
(iv) $10^{-2} \mathrm{M} \mathrm{NaCl}$
$$0.05 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{~CuSO}_4$$ when treated with $$0.01 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{~K}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7$$ gives green colour solution of $$\mathrm{Cu}_2 \mathrm{Cr}_2 \mathrm{O}_7$$. The two solutions are separated as shown below : [SPM : Semi Permeable Membrane]

Due to osmosis :
Identify the mixture that shows positive deviations from Raoult's Law
The solution from the following with highest depression in freezing point/lowest freezing point is
What happens to freezing point of benzene when small quantity of napthalene is added to benzene?
A solution of two miscible liquids showing negative deviation from Raoult's law will have :
What weight of glucose must be dissolved in $$100 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water to lower the vapour pressure by $$0.20 \mathrm{~mm} ~\mathrm{Hg}$$ ?
(Assume dilute solution is being formed)
Given : Vapour pressure of pure water is $$54.2 \mathrm{~mm} ~\mathrm{Hg}$$ at room temperature. Molar mass of glucose is $$180 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
A. The elevation in boiling point temperature of water will be same for $0.1 \mathrm{M} \, \mathrm{NaCl}$ and $0.1 \mathrm{M}$ urea.
B. Azeotropic mixtures boil without change in their composition.
C. Osmosis always takes place from hypertonic to hypotonic solution.
D. The density of $32 \% \, \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}$ solution having molarity $4.09 ~\mathrm{M}$ is approximately $1.26 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mL}^{-1}$
E. A negatively charged sol is obtained when KI solution is added to silver nitrate solution.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Match List I with List II
| List I | List II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| A. | van't Hoff factor, i | I. | Cryoscopic constant |
| B. | $$\mathrm{k_f}$$ | II. | Isotonic solutions |
| C. | Solutions with same osmotic pressure | III. | $$\mathrm{\frac{Normal\,molar\,mass}{Abnormal\,molar\,mass}}$$ |
| D. | Azeotropes | IV. | Solutions with same composition of vapour above it |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below :
In the depression of freezing point experiment
A. Vapour pressure of the solution is less than that of pure solvent
B. Vapour pressure of the solution is more than that of pure solvent
C. Only solute molecules solidify at the freezing point
D. Only solvent molecules solidify at the freezing point
Choose the most appropriate answer from the options given below :
Boiling point of a $$2 \%$$ aqueous solution of a non-volatile solute A is equal to the boiling point of $$8 \%$$ aqueous solution of a non-volatile solute B. The relation between molecular weights of A and B is
Two solutions A and B are prepared by dissolving 1 g of non-volatile solutes X and Y, respectively in 1 kg of water. The ratio of depression in freezing points for A and B is found to be 1 : 4. The ratio of molar masses of X and Y is
The depression in freezing point observed for a formic acid solution of concentration $$0.5 \mathrm{~mL} \mathrm{~L}^{-1}$$ is $$0.0405^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. Density of formic acid is $$1.05 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mL}^{-1}$$. The Van't Hoff factor of the formic acid solution is nearly : (Given for water $$\mathrm{k}_{\mathrm{f}}=1.86\, \mathrm{k} \,\mathrm{kg}\,\mathrm{mol}^{-1}$$ )
For a solution of the gases A, B, C and D in water at 298 K, the values of Henry's law constant (KH) are 30.40, 2.34, 1.56 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$5 and 0.513 k bar respectively. In the given graph, the lines marked as 'p' and 's' correspond respectively to :

Given below are two statements : one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R).
Assertion (A) : At 10$$^\circ$$C, the density of a 5 M solution of KCl [atomic masses of K & Cl are 39 & 35.5 g mol$$-$$1 respectively], is 'x' g ml$$-$$1. The solution is cooled to $$-$$21$$^\circ$$C. The molality of the solution will remain unchanged.
Reason (R) : The molality of a solution does not change with temperature as mass remains unaffected with temperature.
In the light of the above statements, choose the correct answer from the options given below :
Solute A associates in water. When 0.7 g of solute A is dissolved in 42.0 g of water, it depresses the freezing point by 0.2$$^\circ$$C. The percentage association of solute A in water, is :
[Given : Molar mass of A = 93 g mol$$-$$1. Molal depression constant of water is 1.86 K kg mol$$-$$1.]
[Given, molar mass of A = 100 g mol–1; B = 200 g mol–1; C = 10,000 g mol–1]
 The following inferences are made :
The following inferences are made :
(A) X has higher intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
(B) X has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
(C) Z has lower intermolecular interactions compared to Y.
The correct inference (s) is / are :
(R = 0.08206 L atm K–1 mol–1)
(Assume complete dissociation of the electrolyte)
(xM = Mole fraction of 'M' in solution ;
xN = Mole fraction of 'N' in solution ;
yM = Mole fraction of 'M' in vapour phase ;
yN = Mole fraction of 'N' in vapour phase)
(Kf for water=1.86oC kg mol−1) is approximately :
(molar mass of S = 32 g mol−1 and that of Na = 23 g mol−1)
Numerical
Sea water, which can be considered as a 6 molar $(6 \mathrm{M})$ solution of NaCl , has a density of $2 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mL}^{-1}$. The concentration of dissolved oxygen $\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right)$ in sea water is 5.8 ppm . Then the concentration of dissolved oxygen $\left(\mathrm{O}_2\right)$ in sea water, is $x \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m}$.
$x=$ ___________. (Nearest integer)
Given: Molar mass of NaCl is $58.5 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$
Molar mass of $\mathrm{O}_2$ is $32 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$
When 1 g each of compounds AB and $\mathrm{AB}_2$ are dissolved in 15 g of water separately, they increased the boiling point of water by 2.7 K and 1.5 K respectively. The atomic mass of A (in $a m u$ ) is____________ $\times 10^{-1}$ (Nearest integer)
(Given : Molal boiling point elevation constant is $0.5 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$ )
If A2B is 30% ionised in an aqueous solution, then the value of van't Hoff factor (i) is _______ × 10−1.
The vapor pressure of pure benzene and methyl benzene at $$27^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ is given as 80 Torr and 24 Torr, respectively. The mole fraction of methyl benzene in vapor phase, in equilibrium with an equimolar mixture of those two liquids (ideal solution) at the same temperature is _________ $$\times 10^{-2}$$ (nearest integer)
A solution containing $$10 \mathrm{~g}$$ of an electrolyte $$\mathrm{AB}_2$$ in $$100 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water boils at $$100.52^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. The degree of ionization of the electrolyte $$(\alpha)$$ is _________ $$\times 10^{-1}$$. (nearest integer)
[Given : Molar mass of $$\mathrm{AB}_2=200 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}, \mathrm{~K}_{\mathrm{b}}$$ (molal boiling point elevation const. of water) $$=0.52 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$, boiling point of water $$=100^{\circ} \mathrm{C} ; \mathrm{AB}_2$$ ionises as $$\mathrm{AB}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{A}^{2+}+2 \mathrm{~B}^{-}]$$
When '$$x$$' $$\times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~mL}$$ methanol (molar mass $$=32 \mathrm{~g}$$' density $$=0.792 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{cm}^3$$) is added to $$100 \mathrm{~mL}$$. water (density $$=1 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{cm}^3$$), the following diagram is obtained.

$$x=$$ ________ (nearest integer).
[Given : Molal freezing point depression constant of water at $$273.15 \mathrm{~K}$$ is $$1.86 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$]
Considering acetic acid dissociates in water, its dissociation constant is $$6.25 \times 10^{-5}$$. If $$5 \mathrm{~mL}$$ of acetic acid is dissolved in 1 litre water, the solution will freeze at $$-x \times 10^{-2}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$, provided pure water freezes at $$0{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$.
$$x=$$ _________. (Nearest integer)
$$\begin{aligned} \text{Given :} \quad & \left(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{f}}\right)_{\text {water }}=1.86 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}-1 \\ & \text { density of acetic acid is } 1.2 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \text {. } \\ & \text { molar mass of water }=18 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \text {. } \\ & \text { molar mass of acetic acid= } 60 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \text {. } \\ & \text { density of water }=1 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~cm}^{-3} \end{aligned}$$
Acetic acid dissociates as $$\mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COOH} \rightleftharpoons \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{\ominus}+\mathrm{H}^{\oplus}$$
An artificial cell is made by encapsulating $$0.2 \mathrm{~M}$$ glucose solution within a semipermeable membrane. The osmotic pressure developed when the artificial cell is placed within a $$0.05 \mathrm{~M}$$ solution of $$\mathrm{NaCl}$$ at $$300 \mathrm{~K}$$ is ________ $$\times 10^{-1}$$ bar. (nearest integer).
[Given : $$\mathrm{R}=0.083 \mathrm{~L} \mathrm{~bar} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}$$ ]
Assume complete dissociation of $$\mathrm{NaCl}$$
$$2.7 \mathrm{~kg}$$ of each of water and acetic acid are mixed. The freezing point of the solution will be $$-x^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. Consider the acetic acid does not dimerise in water, nor dissociates in water. $$x=$$ ________ (nearest integer)
[Given: Molar mass of water $$=18 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$, acetic acid $$=60 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
$${ }^{\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{f}}} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}: 1.86 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
$$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{f}}$$ acetic acid: $$3.90 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
freezing point: $$\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}=273 \mathrm{~K}$$, acetic acid $$=290 \mathrm{~K}$$]
$$2.5 \mathrm{~g}$$ of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte is dissolved in $$100 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water at $$25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. The solution showed a boiling point elevation by $$2^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. Assuming the solute concentration is negligible with respect to the solvent concentration, the vapor pressure of the resulting aqueous solution is _________ $$\mathrm{mm}$$ of $$\mathrm{Hg}$$ (nearest integer)
[Given : Molal boiling point elevation constant of water $\left(\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{b}}\right)=0.52 \mathrm{~K} . \mathrm{kg} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}$, $$1 \mathrm{~atm}$$ pressure $$=760 \mathrm{~mm}$$ of $$\mathrm{Hg}$$, molar mass of water $$=18 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}]$$
The osmotic pressure of a dilute solution is $$7 \times 10^5 \mathrm{~Pa}$$ at $$273 \mathrm{~K}$$. Osmotic pressure of the same solution at $$283 \mathrm{~K}$$ is _________ $$\times 10^4 \mathrm{Nm}^{-2}$$.
[Given : The density of $30 \%$ (w/v), aqueous solution of glucose is $1.2 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~cm}^{-3}$ and vapour pressure of pure water is $24 \mathrm{~mm}~ \mathrm{Hg}$.]
(Molar mass of glucose is $180 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$.)
Sea water contains $$29.25 \% ~\mathrm{NaCl}$$ and $$19 \% ~\mathrm{MgCl}_{2}$$ by weight of solution. The normal boiling point of the sea water is _____________ $${ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ (Nearest integer)
Assume $$100 \%$$ ionization for both $$\mathrm{NaCl}$$ and $$\mathrm{MgCl}_{2}$$
Given : $$\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{b}}\left(\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right)=0.52 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
Molar mass of $$\mathrm{NaCl}$$ and $$\mathrm{MgCl}_{2}$$ is 58.5 and 95 $$\mathrm{g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$ respectively.
Solution of $$12 \mathrm{~g}$$ of non-electrolyte (A) prepared by dissolving it in $$1000 \mathrm{~mL}$$ of water exerts the same osmotic pressure as that of $$0.05 ~\mathrm{M}$$ glucose solution at the same temperature. The empirical formula of $$\mathrm{A}$$ is $$\mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{O}$$. The molecular mass of $$\mathrm{A}$$ is __________ g. (Nearest integer)
80 mole percent of $$\mathrm{MgCl}_{2}$$ is dissociated in aqueous solution. The vapour pressure of $$1.0 ~\mathrm{molal}$$ aqueous solution of $$\mathrm{MgCl}_{2}$$ at $$38^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ is ____________ $$\mathrm{mm} ~\mathrm{Hg.} ~\mathrm{(Nearest} ~\mathrm{integer)}$$
Given : Vapour pressure of water at $$38^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ is $$50 \mathrm{~mm} ~\mathrm{Hg}$$
0.004 M K$$_2$$SO$$_4$$ solution is isotonic with 0.01 M glucose solution. Percentage dissociation of K$$_2$$SO$$_4$$ is ___________ (Nearest integer)
An aqueous solution of volume $$300 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}$$ contains $$0.63 \mathrm{~g}$$ of protein. The osmotic pressure of the solution at $$300 \mathrm{~K}$$ is 1.29 mbar. The molar mass of the protein is ___________ $$\mathrm{g} ~\mathrm{mol}^{-1}$$
Given : R = 0.083 L bar K$$^{-1}$$ mol$$^{-1}$$
If the degree of dissociation of aqueous solution of weak monobasic acid is determined to be 0.3, then the observed freezing point will be ___________% higher than the expected/theoretical freezing point. (Nearest integer)
If the boiling points of two solvents X and Y (having same molecular weights) are in the ratio $$2: 1$$ and their enthalpy of vaporizations are in the ratio $$1: 2$$, then the boiling point elevation constant of $$\mathrm{X}$$ is $$\underline{\mathrm{m}}$$ times the boiling point elevation constant of Y. The value of m is ____________ (nearest integer)
The vapour pressure vs. temperature curve for a solution solvent system is shown below.

The boiling point of the solvent is __________ $${ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$.
Consider the following pairs of solution which will be isotonic at the same temperature. The number of pairs of solutions is / are ___________.
A. $$1 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{NaCl}$$ and $$2 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. urea
B. $$1 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{CaCl}_{2}$$ and $$1.5 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{KCl}$$
C. $$1.5 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{AlCl}_{3}$$ and $$2 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{Na}_{2} \mathrm{SO}_{4}$$
D. $$2.5 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{KCl}$$ and $$1 ~\mathrm{M}$$ aq. $$\mathrm{Al}_{2}\left(\mathrm{SO}_{4}\right)_{3}$$
Mass of Urea $$\left(\mathrm{NH}_{2} \mathrm{CONH}_{2}\right)$$ required to be dissolved in $$1000 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water in order to reduce the vapour pressure of water by $$25 \%$$ is _________ g. (Nearest integer)
Given: Molar mass of N, C, O and H are $$14,12,16$$ and $$1 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$ respectively
$$20 \%$$ of acetic acid is dissociated when its $$5 \mathrm{~g}$$ is added to $$500 \mathrm{~mL}$$ of water. The depression in freezing point of such water is _________ $$\times 10^{-3}{ }^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$.
Atomic mass of $$\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{H}$$ and $$\mathrm{O}$$ are 12,1 and 16 a.m.u. respectively.
[Given : Molal depression constant and density of water are $$1.86 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$ and $$1 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~cm}^{-3}$$ respectively.]
25 mL of an aqueous solution of KCl was found to require 20 mL of 1 M $$\mathrm{AgNO_3}$$ solution when titrated using $$\mathrm{K_2CrO_4}$$ as an indicator. What is the depression in freezing point of KCl solution of the given concentration? _________ (Nearest integer).
(Given : $$\mathrm{K_f=2.0~K~kg~mol^{-1}}$$)
Assume 1) 100% ionization and 2) density of the aqueous solution as 1 g mL$$^{-1}$$
At $$27^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$, a solution containing $$2.5 \mathrm{~g}$$ of solute in $$250.0 \mathrm{~mL}$$ of solution exerts an osmotic pressure of $$400 \mathrm{~Pa}$$. The molar mass of the solute is ___________ $$\mathrm{g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$ (Nearest integer)
(Given : $$\mathrm{R}=0.083 \mathrm{~L} \mathrm{~bar} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$)
Given $\mathrm{K}_{f}=1.8 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$
A solution containing $$2 \mathrm{~g}$$ of a non-volatile solute in $$20 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water boils at $$373.52 \mathrm{~K}$$. The molecular mass of the solute is ___________ $$\mathrm{g} ~\mathrm{mol}^{-1}$$. (Nearest integer)
Given, water boils at $$373 \mathrm{~K}, \mathrm{~K}_{\mathrm{b}}$$ for water $$=0.52 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$
Solid Lead nitrate is dissolved in 1 litre of water. The solution was found to boil at 100.15$$^\circ$$C. When 0.2 mol of NaCl is added to the resulting solution, it was observed that the solution froze at $$-0.8^\circ$$ C. The solubility product of PbCl$$_2$$ formed is __________ $$\times$$ 10$$^{-6}$$ at 298 K. (Nearest integer)
Given : $$\mathrm{K_b=0.5}$$ K kg mol$$^{-1}$$ and $$\mathrm{K_f=1.8}$$ K kg mol$$^{-1}$$. Assume molality to the equal to molarity in all cases.
The number of pairs of the solutions having the same value of the osmotic pressure from the following is _________.
(Assume 100% ionization)
A. 0.500 $$\mathrm{M~C_2H_5OH~(aq)}$$ and 0.25 $$\mathrm{M~KBr~(aq)}$$
B. 0.100 $$\mathrm{M~K_4[Fe(CN)_6]~(aq)}$$ and 0.100 $$\mathrm{M~FeSO_4(NH_4)_2SO_4~(aq)}$$
C. 0.05 $$\mathrm{M~K_4[Fe(CN)_6]~(aq)}$$ and 0.25 $$\mathrm{M~NaCl~(aq)}$$
D. 0.15 $$\mathrm{M~NaCl~(aq)}$$ and 0.1 $$\mathrm{M~BaCl_2~(aq)}$$
E. 0.02 $$\mathrm{M~KCl.MgCl_2.6H_2O~(aq)}$$ and 0.05 $$\mathrm{M~KCl~(aq)}$$
The osmotic pressure of solutions of PVC in cyclohexanone at 300 K are plotted on the graph.
The molar mass of PVC is ____________ g mol$$^{-1}$$ (Nearest integer)

(Given : R = 0.083 L atm K$$^{-1}$$ mol$$^{-1}$$)
The total pressure observed by mixing two liquids A and B is 350 mm Hg when their mole fractions are 0.7 and 0.3 respectively.
The total pressure becomes 410 mm Hg if the mole fractions are changed to 0.2 and 0.8 respectively for A and B. The vapour pressure of pure A is __________ mm Hg. (Nearest integer)
Consider the liquids and solutions behave ideally.
$$1.80 \mathrm{~g}$$ of solute A was dissolved in $$62.5 \mathrm{~cm}^{3}$$ of ethanol and freezing point of the solution was found to be $$155.1 \mathrm{~K}$$. The molar mass of solute A is ________ g $$\mathrm{mol}^{-1}$$.
[Given : Freezing point of ethanol is 156.0 K.
Density of ethanol is 0.80 g cm$$-$$3.
Freezing point depression constant of ethanol is 2.00 K kg mol$$-$$1]
If $$\mathrm{O}_{2}$$ gas is bubbled through water at $$303 \mathrm{~K}$$, the number of millimoles of $$\mathrm{O}_{2}$$ gas that dissolve in 1 litre of water is __________. (Nearest Integer)
(Given : Henry's Law constant for $$\mathrm{O}_{2}$$ at $$303 \mathrm{~K}$$ is $$46.82 \,\mathrm{k}$$ bar and partial pressure of $$\mathrm{O}_{2}=0.920$$ bar)
(Assume solubility of $$\mathrm{O}_{2}$$ in water is too small, nearly negligible)
A gaseous mixture of two substances A and B, under a total pressure of $$0.8$$ atm is in equilibrium with an ideal liquid solution. The mole fraction of substance A is $$0.5$$ in the vapour phase and $$0.2$$ in the liquid phase. The vapour pressure of pure liquid $$\mathrm{A}$$ is __________ atm. (Nearest integer)
$$150 \mathrm{~g}$$ of acetic acid was contaminated with $$10.2 \mathrm{~g}$$ ascorbic acid $$\left(\mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{8} \mathrm{O}_{6}\right)$$ to lower down its freezing point by $$\left(x \times 10^{-1}\right)^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$. The value of $$x$$ is ___________. (Nearest integer)
[Given $$\mathrm{K}_{f}=3.9 \mathrm{~K} \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$; molar mass of ascorbic acid $$=176 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$$]
When a certain amount of solid A is dissolved in $$100 \mathrm{~g}$$ of water at $$25^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$$ to make a dilute solution, the vapour pressure of the solution is reduced to one-half of that of pure water. The vapour pressure of pure water is $$23.76 \,\mathrm{mmHg}$$. The number of moles of solute A added is _____________. (Nearest Integer)
The elevation in boiling point for 1 molal solution of non-volatile solute A is $$3 \mathrm{~K}$$. The depression in freezing point for 2 molal solution of $$\mathrm{A}$$ in the same solvent is 6 $$K$$. The ratio of $$K_{b}$$ and $$K_{f}$$ i.e., $$K_{b} / K_{f}$$ is $$1: X$$. The value of $$X$$ is [nearest integer]
Elevation in boiling point for 1.5 molal solution of glucose in water is 4 K. The depression in freezing point for 4.5 molal solution of glucose in water is 4 K. The ratio of molal elevation constant to molal depression constant (Kb/Kf) is _________.
1.2 mL of acetic acid is dissolved in water to make 2.0 L of solution. The depression in freezing point observed for this strength of acid is 0.0198$$^\circ$$C. The percentage of dissociation of the acid is ___________. (Nearest integer)
[Given : Density of acetic acid is 1.02 g mL$$-$$1, Molar mass of acetic acid is 60 g mol$$-$$1, Kf(H2O) = 1.85 K kg mol$$-$$1]
2.5 g of protein containing only glycine (C2H5NO2) is dissolved in water to make 500 mL of solution. The osmotic pressure of this solution at 300 K is found to be 5.03 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$3 bar. The total number of glycine units present in the protein is ____________.
(Given : R = 0.083 L bar K$$-$$1 mol$$-$$1)
The vapour pressures of two volatile liquids A and B at 25$$^\circ$$C are 50 Torr and 100 Torr, respectively. If the liquid mixture contains 0.3 mole fraction of A, then the mole fraction of liquid B in the vapour phase is $${x \over {17}}$$. The value of x is ______________.
A solution containing 2.5 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$3 kg of a solute dissolved in 75 $$\times$$ 10$$-$$3 kg of water boils at 373.535 K. The molar mass of the solute is ____________ g mol$$-$$1. [nearest integer] (Given : Kb(H2O) = 0.52 K kg mol$$-$$1 and boiling point of water = 373.15 K)
2 g of a non-volatile non-electrolyte solute is dissolved in 200 g of two different solvents A and B whose ebullioscopic constants are in the ratio of 1 : 8. The elevation in boiling points of A and B are in the ratio $${x \over y}$$ (x : y). The value of y is ______________. (Nearest integer)
The osmotic pressure exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 2.0 g of protein of molar mass 60 kg mol$$-$$1 in 200 mL of water at 27$$^\circ$$C is ______________ Pa. [integer value]
(use R = 0.083 L bar mol$$-$$1 K$$-$$1)
A 0.5 percent solution of potassium chloride was found to freeze at $$-$$0.24$$^\circ$$C. The percentage dissociation of potassium chloride is ______________. (Nearest integer)
(Molal depression constant for water is 1.80 K kg mol$$-$$1 and molar mass of KCl is 74.6 g mol$$-$$1)
A company dissolves 'x' amount of CO2 at 298 K in 1 litre of water to prepare soda water. X = __________ $$\times$$ 10$$-$$3 g. (nearest integer)
(Given : partial pressure of CO2 at 298 K = 0.835 bar.
Henry's law constant for CO2 at 298 K = 1.67 kbar.
Atomic mass of H, C and O is 1, 12, and 6 g mol$$-$$1, respectively)
The osmotic pressure of blood is 7.47 bar at 300 K. To inject glucose to a patient intravenously, it has to be isotonic with blood. The concentration of glucose solution in gL$$-$$1 is _____________.
(Molar mass of glucose = 180 g mol$$-$$1, R = 0.083 L bar K$$-$$1 mol$$-$$1) (Nearest integer)
[Given : Kf(H2O) = 1.86 K kg mol$$-$$1]
[Use : Molal Freezing point depression constant of water = 1.86 K kg mol$$-$$1]
Freezing Point of water = 273 K
Atomic masses : C : 12.0 u, O : 16.0 u, H : 1.0 u]
(i) 0.10 M Ba3(PO4)2
(ii) 0.10 M Na2SO4
(iii) 0.10 M KCl
(iv) 0.10 M Li3PO4
(Round off to the nearest integer)
The molar mass of the biopolymer is _____________ $$\times$$ 104 g mol$$-$$1. (Round off to the Nearest Integer)
[Use : R = 0.083 L bar mol$$-$$1 K$$-$$1]
[Given Kb for CCl4 is 5.0 K kg mol$$-$$1]
(Henry's law constant for CO2 at 298 K is 1.67 $$\times$$ 103 bar)
[Use : Kb for water = 0.52 K kg mol$$-$$1 Boiling point of water = 100$$^\circ$$C]
[Given : Molal depression constant of water = 1.85 K kg mol$$-$$1 Freezing point of pure water = 0$$^\circ$$ C]
[Given : Henry's law constant = KH = 8.0 $$\times$$ 104 kPa for O2. Density of water with dissolved oxygen = 1.0 kg dm$$-$$3 ]
[Given : Molal elevation constant of water Kb = 0.5 K kg mol$$-$$1 boiling point of pure water = 100$$^\circ$$C]
[Kb = 0.52 K kg mol$$-$$1]
[Given Kb for (H2O) = 0.52 K kg mol$$-$$1]
The value of x is ________. (Rounded off to the nearest integer)
[Kf(H20) = 1.86 K kg mol-1]
[Assume 100% ionisation of the complex and CaCl2, coordination number of Cr as 6, and that all NH3 molecules are present inside the coordination sphere]
the glucose solution is x $$ \times $$ 10–3 atm. x is _____. (nearest integer)
(Given, Kf (water) = 2.0 K kg mol–1,
R = 0.08 dm3 atm K–1 mol–1)
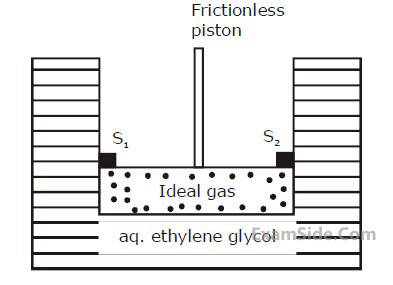
(The freezing point depression constant for water = 2K kg mol–1)