1
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Consider the given circuit. In this circuit, the race around


2
GATE ECE 2011
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
When the output Y in the circuit below is ‘1’, it implies that data has


3
GATE ECE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Assuming that all flip-flops are in reset condition initially, the count sequence
observed at QA in the circuit shown is
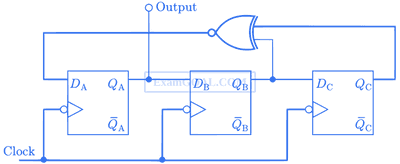

4
GATE ECE 2005
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
The given figure shows a ripple counter using positive edge triggered flip-flops. If the
present state of counter is Q2 Q1 Q0 = 011, then its next state ( Q2 Q1 Q0 ) will be


Questions Asked from Sequential Circuits (Marks 1)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2023 (1)
GATE ECE 2018 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (2)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (2)
GATE ECE 2012 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2010 (1)
GATE ECE 2005 (2)
GATE ECE 2004 (2)
GATE ECE 2003 (1)
GATE ECE 1998 (1)
GATE ECE 1997 (1)
GATE ECE 1995 (2)
GATE ECE 1994 (1)
GATE ECE 1993 (1)
GATE ECE 1992 (1)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (1)
GATE ECE 1988 (1)
GATE ECE 1987 (2)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude