Uniform Plane Waves · Electromagnetics · GATE ECE
Marks 1
Consider a narrow band signal, propagating in a lossless dielectric medium $$(\varepsilon_r=4,\mu_r=1)$$, with phase velocity $$v_p$$ and group velocity $$v_g$$. Which of the following statement is true? ($$c$$ is the velocity of light in vacuum.)
Consider the following wave equation,
$${{{\partial ^2}f(x,t)} \over {\partial {t^2}}} = 10000{{{\partial ^2}f(x,t)} \over {\partial {x^2}}}$$
Which of the given options is/are solution(s) to the given wave equation?
The polarization of the wave is
The wavelength )in m) for the wave is
If the port - 2 of the two - port is short circuited, the $${{s_{11}}}$$ parameter for the resultant one - port network is
The wave is
$$\overline H \left( {x,y,z,t} \right) = 10\,\sin \left( {50000t + 0.004x + 30} \right){\mathop a\limits^ \cap _y}$$
Where $${\mathop a\limits^ \cap _y}$$ denotes the unit vector in $$y$$ direction. The wave is propagating with a phase velocity
Marks 2
The electric field of a plane electromagnetic wave is
$$E = {a_x}{C_{1x}}\cos (\omega t - \beta z) + {a_y}{C_{1y}}\cos (\omega t - \beta z + \theta )$$ V/m.
Which of the following combination(s) will give rise to a left handed elliptically polarized (LHEP) wave?
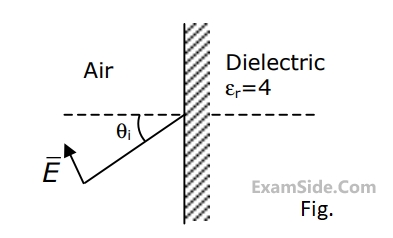
A transparent dielectric coating is applied to glass ($$\varepsilon _r=4,\mu_r=1$$) to eliminate the reflection of red light ($$\lambda_0=0.75~\mu\mathrm{m}$$). The minimum thickness of the dielectric coating, in $$\mu\mathrm{m}$$, that can be used is __________ (rounded off to two decimal places).
This wave is incident upon a receiving antenna placed at the origin and whose radiated electric field towards the incident wave is given by the following equation:
$$${\overrightarrow E _{_a}} = \left( {{{\widehat a}_{_x}} + 2{{\widehat a}_{_y}}} \right){E_1}{1 \over r}{e^{ - jkr}}$$$The polarization of the incident wave, the polarization of the antenna and losses due to the polarization mismatch are, respectively,
$$\overrightarrow E \left( {z,t} \right) = {\widehat a_x}5\cos \left( {2\pi \times {{10}^9}t + \beta z} \right)$$ $$$ + {\widehat a_y}3\cos \left( {2\pi \times {{10}^9}t + \beta z - {\pi \over 2}} \right)$$$
The type of the polarization is
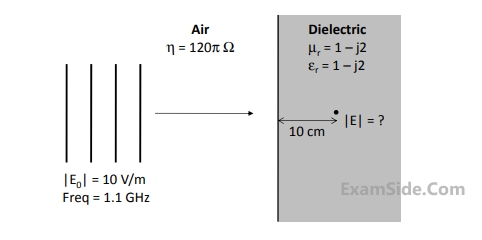
The magnitude of the transmitted electric field component (in V/m) after it has travelled a distance of $$10$$ cm inside the dielectric region is ________.
$$E\left( {x,t} \right) = {\widehat a_{_y}}24\pi \,\,\cos \left( {\omega t - {k_0}x} \right)\,\,\,\left( {V/m} \right)$$. In this field, consider a square area $$10 cm$$ $$ \times $$ $$10 cm$$ on a plane $$x + y = 1$$. The total time-averaged power $$(in mW)$$ passing through the square area is ________.
$$\overrightarrow E = 10\cos \left( {\omega t - 3x - \sqrt {3z} } \right){\widehat a_{_y}}\,\,\,V/m$$ is incident
on a non-magnetic dielectric slab of relative permittivity $$3$$ which covers the region $$z > 0$$ . The angle of transmission in the dielectric slab is _______ degrees.
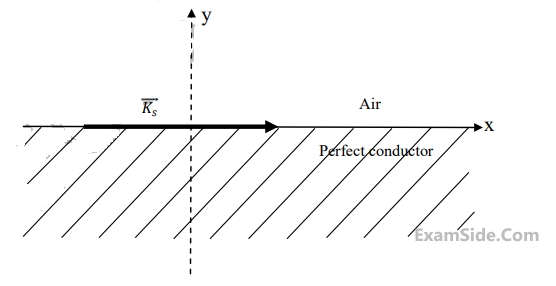
The polarization state of the plane wave is
and $$$H = {{0.265} \over r}\sin \,\theta \cos \left( {\omega t - \beta r} \right){\widehat a_{_\phi }}\,\,A/m$$$
Represent the electric and magnetic field components of the EM wave at large distances $$r$$ from a dipole antenna, in free space. The average power $$(W)$$ crossing the hemispherical shell located at $$r = 1\,\,km$$, $$0 \le \theta \le \pi /2$$ _______.
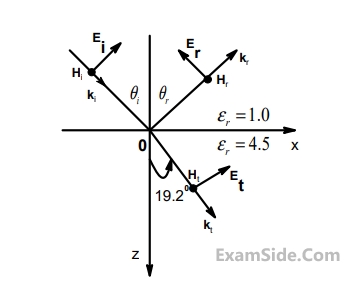
The expression for $${\overrightarrow E _r}$$ is

The angle of incidence $${\theta _i}$$ and the expression for $${\overrightarrow E _i}$$ are
Assuming the speed of light in free space to be $$3\,\, \times {10^8}\,\,\,m/s,$$ the intrinsic impedance of free space to be $$120\,\,\,\pi $$, the relative permittivity $${\varepsilon _r}$$ of the medium and the electric field amplitude $${E_p}$$ are
and traveling in free space is incident normally on a lossless medium with $$\mu = {\mu _0}$$ and $$\varepsilon = 9\,\,{\varepsilon _0},$$ which occupies the region $$y \ge 0.$$ The reflected magnetic field component is given by
The time average power flow density in Watts is
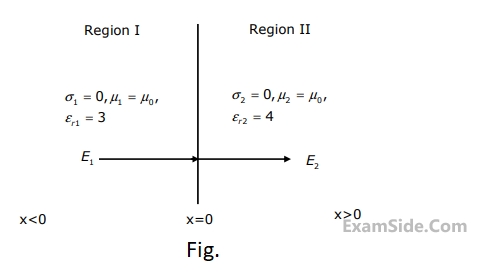
$$E\left( {z,\,t} \right) = \,10\,\cos \left( {2\pi \times {{10}^7}\,\,t - 0.1\,\,\pi z} \right)\,$$ volt/m, the velocity of the traveling wave is
This wave is
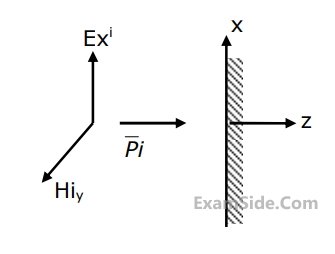
Marks 5
$$\overrightarrow E = \left( {\sqrt \pi } \right)\left( {10.0\,\widehat x + 11.8\,\widehat y} \right)\exp \left[ {j\left( {4\pi \times {{10}^8}\,t - k\,z} \right)} \right]$$
where $$\widehat x$$ and $$\widehat y$$ are unit vectors in the $$x$$- and $$y$$-directions respectively is incident normally on a semi-infinite block of ice as shown in Fig. For ice, $$\mu = {\mu _0},\,\,\,\sigma = 0$$ and $$\varepsilon = 9{\varepsilon _0}\left( {1 - j0.001} \right)$$.
(a) Calculate the average power density associated with the incident wave.
(b) Calculate the skin depth in ice.
(c) Estimate the average power density at a distance of 5 times the skins depth in the ice block, measured from the interface.
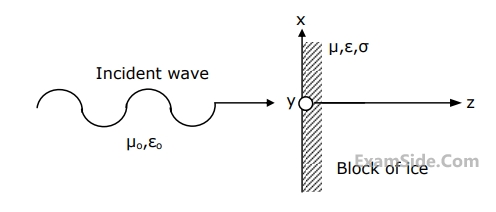
Its frequency is 10 GHz.
(i) Investigate if this wave is a plane wave.
(ii) Determine its propagation constant, and
(iii) Calculate the phase velocity in $$y$$-direction.

(i) The angle of incidence $${\theta _i}$$ for which there is no reflection of the wave.
(ii) The surface charge density at the interface.
Determine
(1) The axial ratio
(2) The angle between the major axis of the polarization ellipse and the $$+x$$-axis.
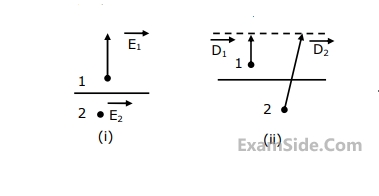
(a) Medium $$1$$ and medium $$2$$ are dielectrics with $${\varepsilon _1} > {\varepsilon _2}$$
(b) Medium $$1$$ and medium $$2$$ are dielectrics with $${\varepsilon _1} < {\varepsilon _2}$$
(c) Medium $$2$$ is a perfect conductor
(d) Impossible
(e) Medium $$1$$ is a perfect conduct
Marks 8
Calculate the power per square metre that causes heating of the brass sheet, taking $${ \in _r} = 1,\,\,\,{\mu _r} = 1$$ and $$\sigma = 1.649 \times {10^7}\,\,\,\,\,$$ mhos/metre for brass.
(a) Attenuation constant
(b) Phase constant
(c) Skin depth
(d) Phase velocity and
(e) Group velocity
for copper assume the following values
Conductivity $$\sigma = 5.8 \times {10^7}$$ $$mho/m$$
Permeability $$\mu = 4\pi \times {10^{ - 7}}$$ $$H/m$$
Permeability $$\varepsilon = {1 \over {36\pi }} \times {10^{ - 9}}$$ $$F/m$$
(a) Determine the associated magnetic field.
(b) What type of wave does the above field represent?