FET and MOSFET · Analog Circuits · GATE ECE
Marks 1
In the circuit below, assume that the long channel NMOS transistor is biased in saturation. The small signal trans-conductance of the transistor is $g_m$. Neglect body effect, channel length modulation, and intrinsic device capacitances. The small signal input impedance $Z_{in}(j\omega)$ is _______

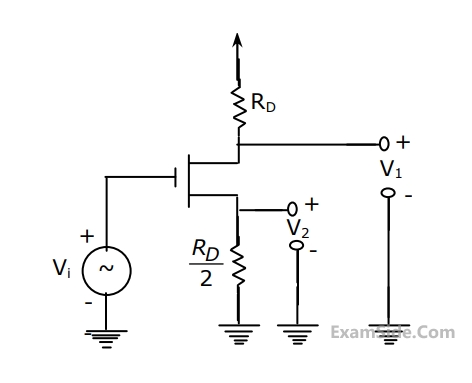
In the circuit shown below, $$V_1$$ and $$V_2$$ are bias voltages. Based on input and output impedances, the circuit behaves as a

Consider the CMOS circuit shown in the figure (substrates are connected to their respective sources). The gate width (W) to gate length (L) ratios $$\left( {{W \over L}} \right)$$ of the transistors are as shown. Both the transistors have the same gate oxide capacitance per unit area. For the pMOSFET, the threshold voltage is $$-$$1 V and the mobility of holes is $$40{{c{m^2}} \over {V.s}}$$. For the nMOSFET, the threshold voltage is 1 V and the mobility of electrons is $$300{{c{m^2}} \over {V.s}}$$. The steady state output voltage V0 is ___________.

The ideal long channel nMOSFET and pMOSFET devices shown in the circuits have threshold voltages of 1 V and $$-$$1 V, respectively. The MOSFET substrates are connected to their respectively sources. Ignore leakage currents and assume that the capacitors are initially discharged. For the applied voltages as shown, the steady state voltages are ____________.

Marks 2
The identical MOSFETs $M_1$ and $M_2$ in the circuit given below are ideal and biased in the saturation region. $M_1$ and $M_2$ have a transconductance $g_m$ of 5 mS .
The input signals (in Volts) are:
$$ \begin{aligned} & V_1=2.5+0.01 \sin \omega t \\ & V_2=2.5-0.01 \sin \omega t \end{aligned} $$
The output signal $V_3$ (in Volts) is _ .

In the circuit shown below, the transistors $M_1$ and $M_2$ are biased in saturation. Their small signal transconductances are $g_{m1}$ and $g_{m2}$ respectively. Neglect body effect, channel length modulation and intrinsic device capacitances.

Assuming that capacitor $C_i$ is a short circuit for AC analysis, the exact magnitude of small signal voltage gain $\left| \frac{v_{out}}{v_{in}} \right|$ is ______.
An NMOS transistor operating in the linear region has $I_{D}$ of 5 $\mu$A at $V_{DS}$ of 0.1 V. Keeping $V_{GS}$ constant, the $V_{DS}$ is increased to 1.5 V.
Given that $\mu_{n}C_{ox} \frac{W}{L}$ = 50 $\mu$A/$V^2$, the transconductance at the new operating point (in $\mu$A/V, rounded off to two decimal places) is ______.
Consider an ideal long channel nMOSFET (enhancement-mode) with gate length 10 $$\mu$$m and width 100 $$\mu$$m. The product of electron mobility ($$\mu$$n) and oxide capacitance per unit area (Cox) is $$\mu$$nCox = 1 mA/V2. The threshold voltage of the transistor is 1 V. For a gate-to-source voltage VGS = [2 $$-$$ sin(2t)] V and drain-to source voltage VDS = 1 V (substrate connected to the source), the maximum value of the drain-to-source current is ___________.
Consider the circuit shown with an ideal long channel nMOSFET (enhancement mode, substrate is connected to the source). The transistor is appropriately biased in the saturation region with VGG and VDD such that it acts as a linear amplifier. vi is the small-signal ac input voltage. vA and vB represent the small-signal voltages at the nodes A and B, respectively. The value of $${{{v_A}} \over {{v_B}}}$$ is __________ (rounded off to one decimal place).


(i)VGS = 0 at Id = 12 mA and
(ii)VGS = -6 Volts at Zo =$$\infty $$
Which of the following Q-points will give the highest transconductance gain for small signals?
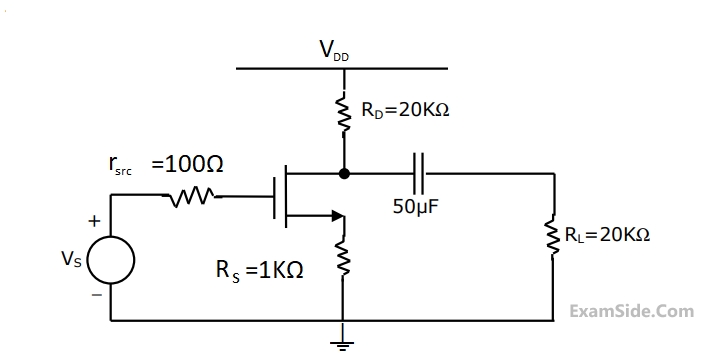
$${r_d} = 20K\Omega ,\,\,{I_{DSS}}\, = \,10mA,\,\,{V_P} = - 8V$$

Transconductance in milli-Siemens (mS) and voltage gain of the amplifier are respectively.
$${r_d} = 20K\Omega ,\,\,{I_{DSS}}\, = \,10mA,\,\,{V_P} = - 8V$$

ID and VDS under DC conditions are respectively


$${r_d} = 20K\Omega ,\,\,{I_{DSS}}\, = \,10mA,\,\,{V_P} = - 8V$$

Zi and Zo of the circuit are respectively
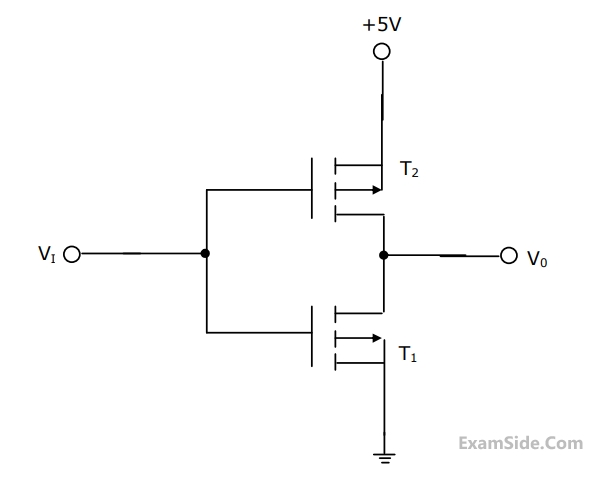
Statement 1: T1 conducts when Vi $$ \ge \,2\,V$$.
Statement 2: T1 is always in saturation when $${V_0}\, = \,0\,V$$.
Which of the following is correct?

Marks 5