1
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A finite state machine (FSM) is implemented using the D flip-flops A and B and logic gates, as shown in the figure below. The four possible states of the FSM are QA QB = 00, 01, 10, and 11.
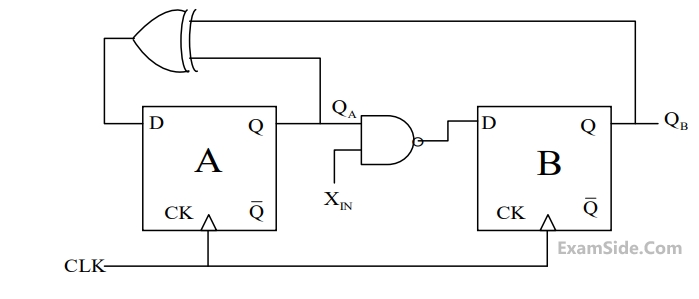

Assume that XIN is held at a logic level throughout the operation of the FSM. When the FSM is initialized to the state QA QB = 100 and clocked, after a few clock cycles, it starts cycling through
2
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
The state diagram of a finite state machine (FSM) designed to detect an overlapping sequence of three bits is shown in the figure. The FSM has an input 'In' and an output 'Out'. The initial state of the FSM is S0.


If the input sequence is 10101101001101, starting with the left-most bit, then the number of times 'Out' will be 1 is __________.
Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The state transition diagram for a finite state machine with states A, B and C, and binary inputs X, Y and Z, is shown in the figure.


Which one of the following statements is correct?
4
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
For the circuit shown in the figure, the delay of the bubbled NAND gate is 2ns and that of the counter is assumed to be zero


If the clock (Clk) frequency is 1 GHz, then the counter behaves as a
Questions Asked from Sequential Circuits (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (2)
GATE ECE 2024 (1)
GATE ECE 2023 (1)
GATE ECE 2022 (2)
GATE ECE 2018 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (2)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (2)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2012 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (2)
GATE ECE 2009 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2007 (2)
GATE ECE 2006 (1)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 2000 (2)
GATE ECE 1999 (1)
GATE ECE 1998 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics