1
GATE ECE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The silicon sample with unit cross-sectional area shown below is in thermal
equilibrium. The following information is given: T=300K, electronic charge=1.6x10-
19C, thermal voltage=26mV and electron mobility = 1350cm2/V-s
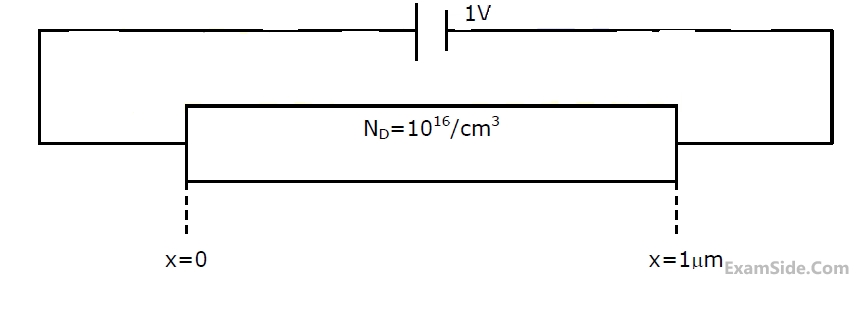

The magnitude of the electric field at x=0.5 μm is
2
GATE ECE 2005
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A silicon sample 'A' is doped with 1018 atoms/cm3 of Boron. Another sample 'B' of
identical dimensions is doped with 1018 atoms/cm3 of Phosphorus. The ratio of
electron to hole mobility is 1/3. The ratio of conductivity of the sample A to B is
3
GATE ECE 2003
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
An n-type silicon bar 0.1 cm long and $$100\;\mu m^2$$ in cross-sectional area has a majority
carrier concentration of $$5\times10^{20}/m^3$$ and the carrier mobility is $$0.13\;\;m^2/v-s\;$$ at
300oK. if the charge of an electron is 1.6×10-19 coulomb, then the resistance of the
bar is
4
GATE ECE 2003
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The electron concentration in a sample of uniformly doped n-type silicon at 300oK varies linearly from $$10^{17}/cm^3$$ at x = 0 to $$6\times10^{16}/cm^3$$ at x = 2 $$\mu m$$. Assume a situation that electrons are supplied to keep this concentration gradient constant with time.If electronic charge is $$1.6\times10^{-19}\;coulomb$$ and the diffusion constant $$D_n=3\;cm^2/s$$, the current density in the silicon, if no electric field is present is
Questions Asked from Semiconductor Physics (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics