1
GATE ECE 2022
Numerical
+1
-0
An ideal MOS capacitor (p-type semiconductor) is shown in the figure. The MOS capacitor is under strong inversion with VG = 2V. The corresponding inversion charge density (QIN) is 2.2 $$\mu$$C/cm2. Assume oxide capacitance per unit area as Cox = 1.7 $$\mu$$F/cm2. For VG = 4V, the value of QIN is __________ $$\mu$$C/cm2 (rounded off to one decimal place).

Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2
Numerical
+1
-0
Consider the circuit shown in the figure. Assume base-to-emitter voltage VBE=0.8 V and common base current gain $$\left(\alpha\right)$$ of the transistor is unity.
 The value of the collector-to–emitter voltage VCE (in volt) is _______.
The value of the collector-to–emitter voltage VCE (in volt) is _______.
 The value of the collector-to–emitter voltage VCE (in volt) is _______.
The value of the collector-to–emitter voltage VCE (in volt) is _______.Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
An npn bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is operating in the active region. If the reverse bias
across the base-collector junction is increased, then
4
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
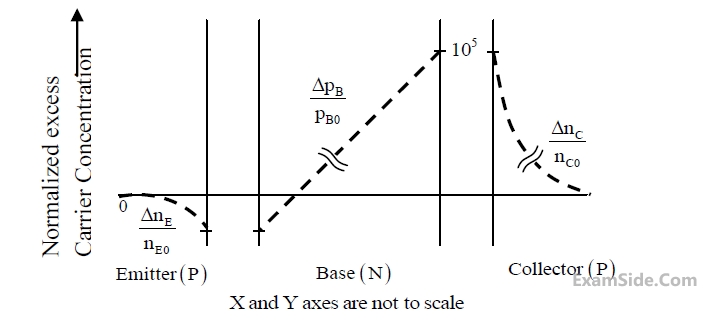
For a narrow base PNP BJT, the excess minority carrier concentration ($$\bigtriangleup n_E$$ for emitter,
$$\bigtriangleup p_B$$ for base, $$\bigtriangleup n_E$$ for collector) normalized to equilibrium minority carrier concentration
($$\bigtriangleup n_{E0}$$ for emitter, $$\bigtriangleup p_{B0}$$ for base, $$\bigtriangleup n_{C0}$$ for collector) in the quasi-neutral emitter, base and collector
regions are shown below. Which one of the following biasing modes is the transistor operating in?

Questions Asked from BJT and FET (Marks 1)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics