1
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
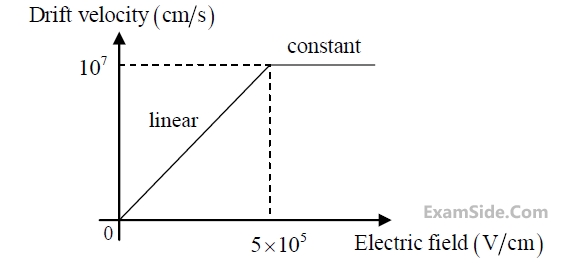
The dependence of drift velocity of electrons on electric field in a semiconductor is shown
below. The semiconductor has a uniform electron concentration of n = 1x1016 $$cm^{-3}$$ and electronic charge q = 1.6x10-19 C. If a bias of 5V is applied across a 1 $$\mu$$m region of this
semiconductor, the resulting current density in this region, in kA/cm2, is _________.

Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
A dc voltage of 10V is applied across an n–type silicon bar having a rectangular cross–section
and a length of 1cm as shown in figure. The donor doping concentration ND and the mobility of electrons $$\mu$$n are $$10^{16}$$ cm-3 and 1000 cm2 V-1s-1, respectively. The average time (in $$\mu$$s)
taken by the electrons to move from one end of the bar to other end is _______________.


Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider a silicon sample doped with ND = 1×1015/cm3 donor atoms. Assume that the
intrinsic carrier concentration ni = 1.5×1010/cm3. If the sample is additionally doped with NA = 1×1018/cm3 acceptor atoms, the approximate number of electrons/cm3 in the sample, at
T=300 K, will be _________________.
Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
An N-type semiconductor having uniform doping is biased as shown in the figure.


If EC is the lowest energy level of the conduction band, EV is the highest energy level of the valance band and EF is the Fermi level, which one of the following represents the energy band diagram for the biased N-type semiconductor?
Questions Asked from Semiconductor Physics (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude



