1
GATE ECE 2011
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
X(t) is a stationary random process with autocorrelation function Rx$$\left( \tau \right)$$= exp$$\left( { - \pi {\tau ^2}} \right)$$. This process is passed through the system shown below. The power spectral density of the output process Y(t) is


2
GATE ECE 2010
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
X(t) is a stationary process with the power spectral density Sx(f) > 0 for all f. The process is passed through a system shown below.
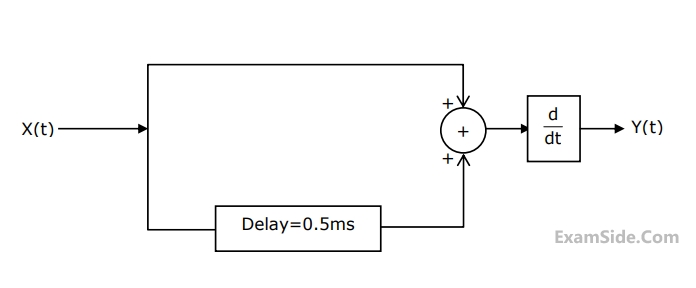

Let Sy(f) be the power spectral density of Y(t). Which one of the following statements is correct?
3
GATE ECE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Noise with double-sided power spectral density of K over all frequencies is passed through a RC low pass filter with 3-dB cut-off frequency of fc. The noise power at the filter output is
4
GATE ECE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A zero-mean white Gaussian noise is passed through an ideal low-pass filter of bandwidth 10 kHz. The output is then uniformly sampled with sampling period ts = 0.03 msec. The samples so obtained would be
Questions Asked from Random Signals and Noise (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (1)
GATE ECE 2024 (2)
GATE ECE 2023 (2)
GATE ECE 2022 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (2)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (3)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (3)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2013 (2)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2010 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2006 (3)
GATE ECE 2005 (2)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2002 (1)
GATE ECE 1992 (1)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (2)
GATE ECE 1987 (2)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics