1
GATE ECE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A uniform plane wave in the free space is normally incident on an infinitely thick dielectric slab (dielectric constant $${\varepsilon _r} = 9$$ ). The magnitude of the reflection coefficient is
2
GATE ECE 2007
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The $$\overrightarrow H $$ field (in A/m) of a plane wave propagating in free space is given by
$$$\overrightarrow H = \widehat x{{5\sqrt 3 } \over {{\eta _0}}}\cos \left( {\omega \,t - \beta \,z} \right) + \widehat y{5 \over {{\eta _0}}}\sin \left( {\omega \,t - \beta \,z + {\pi \over 2}} \right)$$$
The time average power flow density in Watts is
3
GATE ECE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A medium of relative permittivityb $${\varepsilon _r} = 2$$ forms an interface with free-space. A point source of electromagnetic energy is located in the medium at a depth of $$1$$ meter from the interface. Due to the total internal reflection, the transmitted beam has a circular cross-section over the interface. The area of the beam cross-section
at the interface is given by
4
GATE ECE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
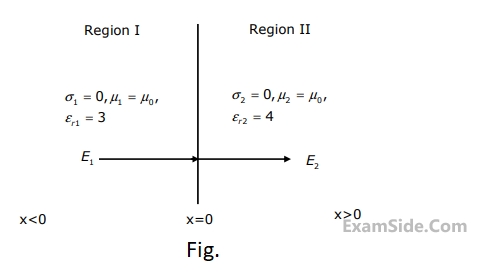
A medium is divided into regions $${\rm I}$$ and $${\rm I}$$$${\rm I}$$ about $$x = 0$$ plane, as shown in the Fig. below. An electromagnetic wave with electric field $${\overrightarrow E _1} = 4{\widehat a_x} + 3{\widehat a_y} + 5{\widehat a_z}$$ is incident normally on the interface form region-$${\rm I}$$ . The electric field $${E_2}$$ in region-$${\rm I}$$$${\rm I}$$
at the interface is

Questions Asked from Uniform Plane Waves (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2024 (1)
GATE ECE 2023 (2)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2013 (2)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2010 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2007 (1)
GATE ECE 2006 (3)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (3)
GATE ECE 2002 (2)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 2000 (1)
GATE ECE 1996 (2)
GATE ECE 1993 (2)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE 1988 (1)
GATE ECE 1987 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude