1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
For the second order closed-loop system shown in the figure, the natural frequency (in rad/s)
is
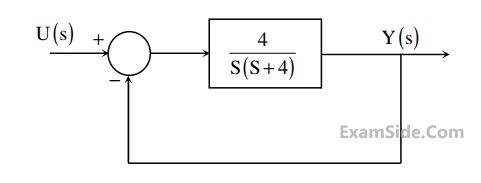

2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3
Numerical
+1
-0
The input $$-3\mathrm e^{2\mathrm t}\;\mathrm u\left(\mathrm t\right)$$, where u(t) is the unit step function, is applied to a system with transfer
function $$\frac{s-2}{s+3}$$. If the initial value of the output is -2, then the value of the output at steady
state is __________.
Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
Numerical
+1
-0
The natural frequency of an undamped second-order system is 40 rad/s. If the system is
damped with a damping ratio 0.3, the damped natural frequency in rad/s is ________.
Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2011
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
The differential equation
$$$100\frac{\mathrm d^2\mathrm y}{\mathrm{dt}^2}-20\frac{\mathrm{dy}}{\mathrm{dt}}+\mathrm y=\mathrm x\left(\mathrm t\right)$$$ describes a system with an
input x(t) and an output y(t). The system, which is initially relaxed, is excited by
a unit step input. The output y(t) can be represented by the waveform
Questions Asked from Time Response Analysis (Marks 1)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2024 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2007 (1)
GATE ECE 2002 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 1999 (1)
GATE ECE 1998 (3)
GATE ECE 1995 (4)
GATE ECE 1994 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude



