1
GATE ECE 2000
Subjective
+8
-0
For the linear, time-invariant system whose block diagram is shown in Fig.
with input x(t) and output y(t),
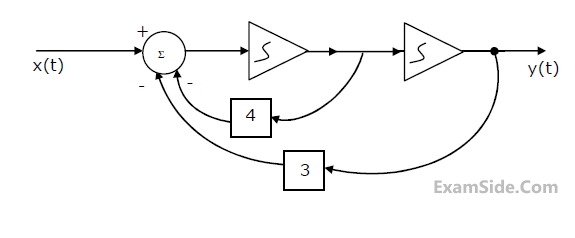
(a) Find the transfer function.
(b) For the step response of the system [i.e. find y(t) when x(t) is a unit step function and the initial conditions are zero]
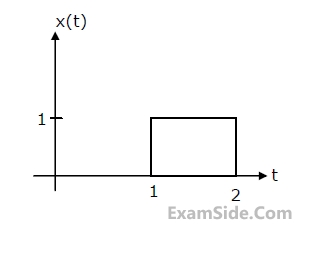
(c) Find y(t), if x(t) is as shown in Fig. and the initial conditions are zero.


(a) Find the transfer function.
(b) For the step response of the system [i.e. find y(t) when x(t) is a unit step function and the initial conditions are zero]
(c) Find y(t), if x(t) is as shown in Fig. and the initial conditions are zero.
2
GATE ECE 1992
Subjective
+8
-0
Block diagram model of a position control system is shown in figure.

(a) In absence of derivative feedback (Kt=0) , determine damping ratio of the system for amplifier gain KA=5. Also find the steady state error to unit ramp input.
(b) Find suitable values of the parameters KA and Kt so that damping ratio of the system is increased to 0.7 without affecting the steady state error as obtained in part (a).

(a) In absence of derivative feedback (Kt=0) , determine damping ratio of the system for amplifier gain KA=5. Also find the steady state error to unit ramp input.
(b) Find suitable values of the parameters KA and Kt so that damping ratio of the system is increased to 0.7 without affecting the steady state error as obtained in part (a).
Questions Asked from Time Response Analysis (Marks 8)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude