1
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
The switch S in the circuit shown has been closed for a long time. It is opened at time t = 0 and
remains open after that. Assume that the diode has zero reverse current and zero forward
voltage drop.
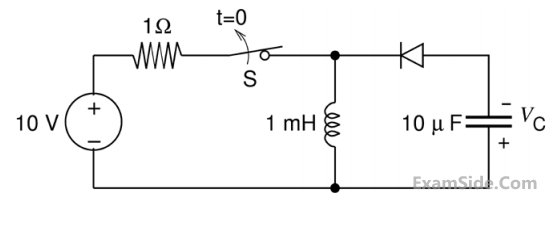 The steady state magnitude of the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) is ____________.
The steady state magnitude of the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) is ____________.
 The steady state magnitude of the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) is ____________.
The steady state magnitude of the capacitor voltage VC (in volts) is ____________.Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3
Numerical
+2
-0
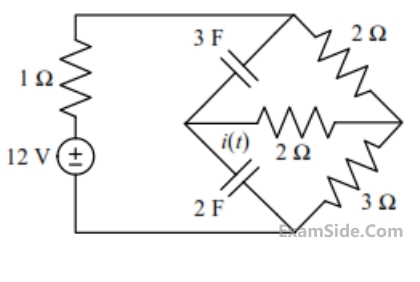
Assume that the circuit in the figure has reached the steady state before time t = 0 when the
3 Ω
resistor suddenly burns out, resulting in an open circuit. The current i(t) (in ampere) at t = 0+ is ____________.

Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2
Numerical
+2
-0
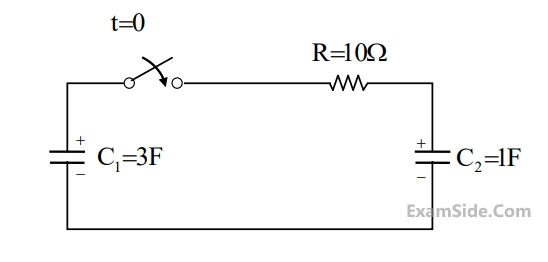
In the circuit shown, the initial voltages across the capacitors
C1 and C2
are 1 V and 3 V,
respectively. The switch is closed at time t = 0. The total energy dissipated (in Joules) in the
resistor R until steady state is reached is _______________.

Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1
Numerical
+2
-0
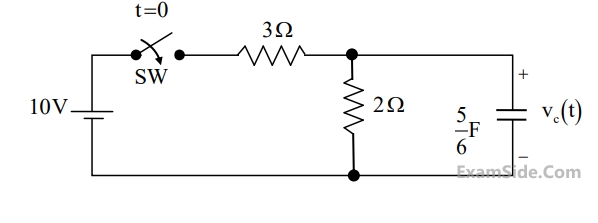
In the circuit shown, switch SW is closed at t = 0. Assuming zero initial conditions, the value
of vc(t) (in Volts) at t= 1 sec is ___________.

Your input ____
Questions Asked from Transient Response (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2023 (1)
GATE ECE 2018 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2010 (1)
GATE ECE 2009 (2)
GATE ECE 2008 (3)
GATE ECE 2007 (1)
GATE ECE 2006 (2)
GATE ECE 2005 (1)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (2)
GATE ECE 1996 (1)
GATE ECE 1992 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics