1
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
The circuit diagram of a synchronous counter is shown in the figure. Determine the
sequence of states of the counter assuming that the initial state is ‘000’. Give
your answer in a tabulor form showing the present state QA(n), QB(n), QC(n), J-K inputs ( JA, KA, JB, KB, JC, K,) and the next state $${Q_{A\left( {n + 1} \right)}},\,{Q_{B\left( {n + 1} \right)}},{Q_{C\left( {n + 1} \right)}}$$ From the table, determine the modulus of the counter.
2
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
The mod-5 counter shown in figure counts through states Q2 Q1 Q0 = 000, 001, 010, 011 and 100.
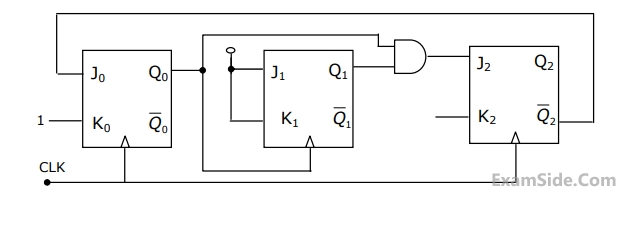

(a) Will the counter lockout if it happens to be in any one of the unused states?
(b) Find the maximum rate at which the counter will operate satisfactorily. Assume the propagation delays of flip-flop and AND gate to be tF and tA
3
GATE ECE 1997
Subjective
+5
-0
A sequence generator is shown in figure. The counter status (Q0 Q1 Q3) is intialized to 010 using preset/clear inputs.
The Clock has a period of 50ns and transitions take place at the rising clock edge.
(a) Give the sequence generated at Q0 till it repeats.
(b) What is the repetition rate for the generated sequence?
The Clock has a period of 50ns and transitions take place at the rising clock edge.
(a) Give the sequence generated at Q0 till it repeats.
(b) What is the repetition rate for the generated sequence?

4
GATE ECE 1996
Subjective
+5
-0
A 4-bit shift register, which shifts 1 bit to the right at every clock pulse, is intialized to values (1000) for (Q0Q1Q2Q3). The D input is derived from Q0, Q2 and Q3 through two XOR gates as shown in figure.


(a) Write the 4-bit values (Q0Q1Q2Q3) after each clock pulse till the pattern (1000) reappears on (Q0Q1Q2Q3).
(b) To what values should the shift register be intialized so that the pattern (1001) occurs after the first clock pulse?
Questions Asked from Sequential Circuits (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics