1
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A plant transfer function is given as $$$G\left(s\right)=\left(K_p+\frac{K_1}s\right)\left(\frac1{s\left(s+2\right)}\right)$$$
. When the plant operates in a
unity feedback configuration, the condition for the stability of the closed loop system is
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider a transfer function $$G_p\left(s\right)\;=\;\frac{ps^2+3ps\;-2}{s^2+\left(3+p\right)s\;+\left(2-p\right)}$$ with 'p' a positive real parameter.
The maximum value of 'p' until which Gp remains stable is ________.
Your input ____
3
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The feedback system shown below oscillates at 2 rad/s when
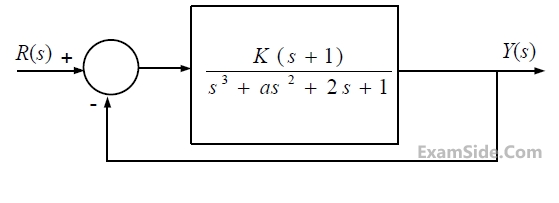
4
GATE ECE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The number of open right half plane poles of $$$G\left(s\right)\;=\;\frac{10}{s^5\;+2s^4\;+3s^3\;+6s^2\;+5s\;+3}\;is$$$
Questions Asked from Stability (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (1)
GATE ECE 2022 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1)
GATE ECE 2012 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (2)
GATE ECE 2006 (1)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (1)
GATE ECE 2002 (2)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 1994 (1)
GATE ECE 1993 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE 1988 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics