1
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2 Online
Numerical
+2
-0

A soft plastic bottle, filled with water of density 1 gm/cc, carries an inverted glass test-tube with some air (ideal gas) trapped as shown in the figure. The test-tube has a mass of 5 gm, and it is made of a thick glass of density 2.5 gm/cc. Initially the bottle is sealed at atmosphere pressure p0 = 105 Pa so that the volume of the trapped air is v0 = 3.3 cc. When the bottle is squeezed from outside at constant temperature, the pressure inside rises and the volume of the trapped air reduces. It is found that the test tube begins to sink at pressure p0 + $$\Delta$$p without changing its orientation. At this pressure, the volume of the trapped air is v0 $$-$$ $$\Delta$$v. Let $$\Delta$$v = X cc and $$\Delta$$p = Y $$\times$$ 103 Pa.
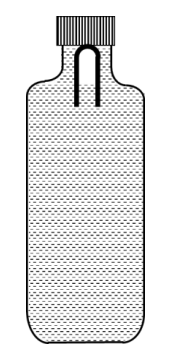
The value of X is _______________.

The value of X is _______________.
Your input ____
2
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2 Online
Numerical
+2
-0

A soft plastic bottle, filled with water of density 1 gm/cc, carries an inverted glass test-tube with some air (ideal gas) trapped as shown in the figure. The test-tube has a mass of 5 gm, and it is made of a thick glass of density 2.5 gm/cc. Initially the bottle is sealed at atmosphere pressure p0 = 105 Pa so that the volume of the trapped air is v0 = 3.3 cc. When the bottle is squeezed from outside at constant temperature, the pressure inside rises and the volume of the trapped air reduces. It is found that the test tube begins to sink at pressure p0 + $$\Delta$$p without changing its orientation. At this pressure, the volume of the trapped air is v0 $$-$$ $$\Delta$$v. Let $$\Delta$$v = X cc and $$\Delta$$p = Y $$\times$$ 103 Pa.

The value of Y is _______________.

The value of Y is _______________.
Your input ____
3
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 1 Online
Numerical
+4
-0

A small object is placed at the center of a large evacuated hollow spherical container. Assume that the container is maintained at 0 K. At time t = 0, the temperature of the object is 200 K. The temperature of the object becomes 100 K at t = t1 and 50 K at t = t2. Assume the object and the container to be ideal black bodies. The heat capacity of the object does not depend on temperature. The ratio (t2/t1) is ____________.
Your input ____
4
JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2 Offline
Numerical
+3
-1

A thermally isolated cylindrical closed vessel of height 8 m is kept vertically. It is divided into two
equal parts by a diathermic (perfect thermal conductor) frictionless partition of mass 8.3 kg. Thus the
partition is held initially at a distance of 4 m from the top, as shown in the schematic figure below.
Each of the two parts of the vessel contains 0.1 mole of an ideal gas at temperature 300 K. The
partition is now released and moves without any gas leaking from one part of the vessel to the other.
When equilibrium is reached, the distance of the partition from the top (in m) will be _______.
(take the acceleration due to gravity = 10 ms−2 and the universal gas constant = 8.3 J mol−1K−1).

(take the acceleration due to gravity = 10 ms−2 and the universal gas constant = 8.3 J mol−1K−1).

Your input ____
Questions Asked from Heat and Thermodynamics (Numerical)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 2 Online (2)
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2 Online (3)
JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2 Online (2)
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 2 Offline (3)
JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2016 Paper 1 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2015 Paper 1 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 1 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2011 Paper 1 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2010 Paper 1 Offline (2)
IIT-JEE 2010 Paper 2 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2009 Paper 2 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Units & Measurements Motion Laws of Motion Work Power & Energy Impulse & Momentum Rotational Motion Properties of Matter Heat and Thermodynamics Simple Harmonic Motion Waves Gravitation
Electricity
Electrostatics Current Electricity Capacitor Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Current Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Modern Physics
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Structure of Atom Redox Reactions Gaseous State Chemical Equilibrium Ionic Equilibrium Solutions Thermodynamics Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry Electrochemistry Solid State Surface Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Periodic Table & Periodicity Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Isolation of Elements Hydrogen s-Block Elements p-Block Elements d and f Block Elements Coordination Compounds Salt Analysis
Organic Chemistry
Mathematics
Algebra
Quadratic Equation and Inequalities Sequences and Series Mathematical Induction and Binomial Theorem Matrices and Determinants Permutations and Combinations Probability Vector Algebra 3D Geometry Statistics Complex Numbers
Trigonometry
Coordinate Geometry
Calculus