Electrochemistry · Chemistry · JEE Advanced
Numerical
An electrochemical cell is fueled by the combustion of butane at 1 bar and 298 K . Its cell potential is $\frac{\boldsymbol{X}}{F} \times 10^3$ volts, where $F$ is the Faraday constant. The value of $\boldsymbol{X}$ is _____________.
Use: Standard Gibbs energies of formation at 298 K are: $\Delta_f G_{\mathrm{CO}_2}^o=-394 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} ; \Delta_f G_{\text {water }}^o=$ $-237 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1} ; \Delta_f G_{\text {butane }}^o=-18 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$
In an electrochemical cell, dichromate ions in aqueous acidic medium are reduced to Cr3+. The current (in amperes) that flows through the cell for 48.25 minutes to produce 1 mole of Cr3+ is ______.
Use: 1 Faraday = 96500 C mol−1
Given:
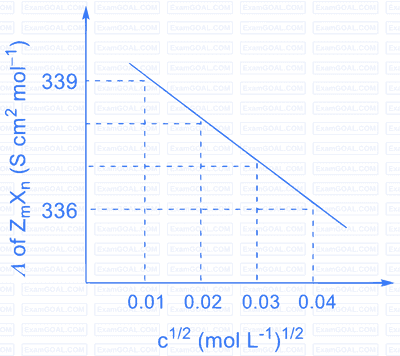
| Ion | $\mathrm{Z}^{\mathrm{n}+}$ | $\mathrm{U}^{\mathrm{p}+}$ | $\mathrm{V}^{\mathrm{n}+}$ | $\mathrm{X}^{\mathrm{m}-}$ | $\mathrm{Y}^{\mathrm{m}-}$ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| $\lambda^{0}\left(\mathrm{~S} \mathrm{~cm}^{2} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\right)$ | $50.0$ | $25.0$ | $100.0$ | $80.0$ | $100.0$ |
$\lambda^{0}$ is the limiting molar conductivity of ions
The plot of molar conductivity ( $\Lambda$ ) of $\mathrm{Z}_{\mathrm{m}} \mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{n}} v s\, \mathrm{c}^{1 / 2}$ is given below.
The reduction potential $\left(E^{0}\right.$, in $\left.\mathrm{V}\right)$ of $\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}(\mathrm{aq}) / \mathrm{Mn}(\mathrm{s})$ is __________.
[Given: $E_{\left(\mathrm{MnO}_{4}^{-}(\mathrm{aq}) / \mathrm{MnO}_{2}(\mathrm{~s})\right)}^{0}=1.68 \mathrm{~V} ; E_{\left(\mathrm{MnO}_{2}(\mathrm{~s}) / \mathrm{Mn}^{2+}(\mathrm{aq})\right)}^{0}=1.21 \mathrm{~V} ; E_{\left(\mathrm{Mn}^{2+}(\mathrm{aq}) / \mathrm{Mn}(\mathrm{s})\right)}^{0}=-1.03 \mathrm{~V}$ ]
The value of $$\alpha$$ is __________.
The value of y is __________.
$${H_2}(g) + {1 \over 2}{O_2}(g)\buildrel {} \over \longrightarrow {H_2}O(l)$$
The work derived from the cell on the consumption of 1.0 $$ \times $$ 10$$-$$3 mole of H2(g) is used to compress 1.00 mole of a monoatomic ideal gas in a thermally insulated container. What is the change in the temperature (in K) of the ideal gas?
The standard reduction potentials for the two half-cells are given below :
$${O_2}(g) + 4{H^ + }(aq) + 4{e^ - }\buildrel {} \over \longrightarrow 2{H_2}O(l),$$
$${E^o} = 1.23V$$
$$2{H^ + }(aq) + 2{e^ - }\buildrel {} \over \longrightarrow {H_2}(g),$$
$${E^o} = 0.00\,V$$
Use, $$F = 96500\,C\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$, $$R = 8.314\,J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}\,{K^{ - 1}}$$.
$$A\left( s \right)\left| {{A^{n + }}\left( {aq,2M} \right)} \right|{B^{2n + }}\left( {aq,1M} \right)\left| {B\left( s \right).} \right.$$
The value of $$\Delta {H^ \circ }$$ for the cell reaction is twice that of $$\Delta {G^ \circ }$$ at $$300$$ $$K.$$ If the $$emf$$ of the cell is zero, the $$\Delta {S^ \circ }$$ (in $$J\,{K^{ - 1}}mo{l^{ - 1}}$$) of the cell reaction per mole of $$B$$ formed at $$300$$ $$K$$ is ___________.
(Given: $$\ln \left( 2 \right) = 0.7,R$$ (universal gas constant) $$ = 8.3J\,{K^{ - 1}}\,mo{l^{ - 1}}.$$ $$H,S$$ and $$G$$ are enthalpy, entropy and Gibbs energy, respectively.)
$$\left. {Mg\left( s \right)} \right|M{g^{2 + }}\left( {aq,1\,M} \right)\left\| {C{u^{2 + }}} \right.\left( {aq,1M} \right)\left| {Cu\left( s \right)} \right.$$
the standard $$emf$$ of the cell is $$2.70$$ $$V$$ at $$300$$ $$K.$$ When the concentration of $$M{g^{2 + }}$$ is changed to $$x$$ $$M,$$ the cell potential changes to $$2.67$$ $$V$$ at $$300$$ $$K.$$ The value of $$x$$ is ___________.
(given, $${F \over R} = 11500\,K{V^{ - 1}},$$ where $$F$$ is the Faraday constant and $$R$$ is the gas constant, In $$(10=2.30)$$
$$X \to Y, \Delta _tG^o $$ = -193 kJ mol-1 is used for oxidizing M+ as M+ $$\to$$ M3+ + 2e-, Eo = -0.25 V
Under standard conditions, the number of moles of M+ oxidized when one mole of X is converted to Y is [F = 96500 C mol–1]
MCQ (More than One Correct Answer)
An aqueous solution of hydrazine $\left(\mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{H}_4\right)$ is electrochemically oxidized by $\mathrm{O}_2$, thereby releasing chemical energy in the form of electrical energy. One of the products generated from the electrochemical reaction is $\mathrm{N}_2(\mathrm{~g})$.
Choose the correct statement(s) about the above process
Pb2+ /Pb = $$- $$0.13 V
Ni2+ /Ni = $$-$$ 0.24 V
Cd2+ /Cd = $$-$$ 0.40 V
Fe2+ /Fe = $$-$$ 0.44 V
To a solution containing 0.001 M of X2+ and 0.1 M of Y2+, the metal rods X and Y are inserted (at 298 K) and connected by a conducting wire. This resulted in dissolution of X. The correct combination(s) of X and Y, respectively, is(are)
(Given : Gas constant, R = 8.314 J K$$-$$ mol$$-$$1, Faraday constant, F = 96500 C mol$$-$$1)
For the reduction of NO$$_3^ - $$ ion in an aqueous solution, E$$^0$$ is + 0.96 V. Values of E$$^0$$ for some metal ions are given below:
$$\matrix{ {{V^{2 + }}(aq.) + 2{e^ - } \to V} & {{E^0} = - 1.19\,V} \cr {F{e^{3 + }}(aq.) + 3{e^ - } \to Fe} & {{E^0} = - 0.04\,V} \cr {A{u^{3 + }}(aq) + 3{e^ - } \to Au} & {{E^0} = + 1.40\,V} \cr {H{g^{2 + }}(aq) + 2{e^ - } \to Hg} & {{E^0} = + 0.86\,V} \cr } $$
The pair(s) of metals that is (are) oxidized by NO$$_3^ - $$ in aqueous solution is(are)
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
In a conductometric titration, small volume of titrant of higher concentration is added stepwise to a larger volume of titrate of much lower concentration, and the conductance is measured after each addition.
The limiting ionic conductivity $\left(\Lambda_0\right)$ values (in $\mathrm{mS} \mathrm{m}{ }^2 \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}$ ) for different ions in aqueous solutions are given below:
$$ \begin{array}{|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline \text { Ions } & \mathrm{Ag}^{+} & \mathrm{K}^{+} & \mathrm{Na}^{+} & \mathrm{H}^{+} & \mathrm{NO}_3^{-} & \mathrm{Cl}^{-} & \mathrm{SO}_4^{2-} & \mathrm{OH}^{-} & \mathrm{CH}_3 \mathrm{COO}^{-} \\ \hline \Lambda_0 & 6.2 & 7.4 & 5.0 & 35.0 & 7.2 & 7.6 & 16.0 & 19.9 & 4.1 \\ \hline \end{array} $$
For different combinations of titrates and titrants given in List-I, the graphs of 'conductance' versus 'volume of titrant' are given in List-II.
Match each entry in List-I with the appropriate entry in List-II and choose the correct option.
| LIST-I | LIST-II |
|---|---|
| (P) Titrate: KCl Titrant: AgNO$_3$ |

|
| (Q) Titrate: AgNO$_3$ Titrant: KCl |

|
| (R) Titrate: NaOH Titrant: HCl |

|
| (S) Titrate: NaOH Titrant: CH$_3$COOH |

|

|
$$ \begin{aligned} & {\left[\Lambda_{\mathrm{m}}=\right.\text { molar conductivity }} \\\\ & \Lambda_{\mathrm{m}}^{\mathrm{o}}=\text { limiting molar conductivity } \\\\ & \mathrm{c}=\text { molar concentration } \\\\ & \left.\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{a}}=\text { dissociation constant of } \mathrm{HX}\right] \end{aligned} $$
(critical micelle concentration (CMC) is marked with an arrow in the figures)
$$Zn\left( s \right)\left| {ZnS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|\left| {CuS{O_4}\left( {aq} \right)} \right|Cu\left( s \right)$$
when the concentration of $$Z{n^{2 + }}$$ is $$10$$ times the concentration of $$C{u^{2 + }},$$ the expression for $$\Delta G$$ (in $$J\,mo{l^{ - 1}}$$) is [$$F$$ is Faraday constant; $$R$$ is gas constant; $$T$$ is temperature; $${E^0}$$ (cell)$$=1.1$$ $$V$$]
Pt(s) | H2 (g, 1 bar) | H+ (aq, 1 M) || M4+ (aq), M2+ (aq) | Pt (s)
Ecell = 0.092 V when $${{\left[ {{M^{2 + }}(aq)} \right]} \over {\left[ {{M^{4 + }}(aq)} \right]}}$$ = 10x
Give, $$E_{{M^{4+}}/{M^{2 + }}}^o$$ = 0.151 V; 2.303 RT/F = 0.059 V
The value of x is
List - I
P. $$\mathop {(C{}_2{H_5}){}_3N}\limits_X $$ + $$\mathop {C{H_3}COOH}\limits_Y $$
Q. $$\mathop {KI(0.1M)}\limits_X $$ + $$\mathop {AgN{O_3}(0.01M)}\limits_Y $$
R. $$\mathop {C{H_3}COOH}\limits_X $$ + $$\mathop {KOH}\limits_Y $$
S. $$\mathop {NaOH}\limits_X $$ + $$\mathop {HI}\limits_Y $$
List - II
1. Conductivity decreases then increases
2. Conductivity decreases then does not change much
3. Conductivity increases then does not change much
4. Conductivity does not change much then increases
Eo (Fe3+ , Fe2+) = +0.77V;
Eo (Fe2+ , Fe) = -0.44V;
Eo (Cu2+ , Cu) = +0.34V;
Eo (Cu+ , Cu) = +0.52V;
Eo [O2(g) + 4H+ + 4e- $$\to$$ 2H2O] = +1.23V;
Eo [O2(g) + 2H2O + 4e- $$\to$$ 4OH-] = +0.40 V
Eo (Cr3+ , Cr) = -0.74V;
Eo (Cr2+ , Cr) = -0.91V;
Match Eo of the redox pair in List – I with the values given in List – II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists:
List - I
P. Eo (Fe3+ , Fe)
Q. Eo (4H2O $$\leftrightharpoons$$ 4H+ + 4OH-)
R. Eo (Cu2+ + Cu $$\to$$ 2Cu+)
S. Eo (Cr3+, Cr2+)
List - II
1. -0.18 V
2. -0.4 V
3. -0.04 V
4. -0.83 V
The solubility product (Ksp; mol3 dm–9) of MX2 at 298 K based on the information available for the given concentration cell is (take 2.303 $$\times$$ R $$\times$$ 298/F = 0.059 V)
The value of ∆G (kJ mol–1) for the given cell is (take 1F = 96500 C mol–1)
AgNO3(aq.) was added to an aqueous KCl solution gradually and the conductivity of the solution was measured. The plot of conductance ($$\Lambda $$) versus the volume of AgNO3 is

2Fe(s) + O2(g) + 4H+(aq) $$\to$$ 2Fe2+ (aq) + 2H2O (l); Eo = 1.67 V
At [Fe2+] = 10-3 M, P(O2) = 0.1 atm and pH = 3, the cell potential at 25oC is
M(s) | M+ (aq ; 0.05 molar) || M+ (aq ; 1 molar) | M(s)
For the above electrolytic cell the magnitude of the cell potential | Ecell | = 70 mV.
For the above cell :
M(s) | M+ (aq ; 0.05 molar) || M+ (aq ; 1 molar) | M(s)
For the above electrolytic cell the magnitude of the cell potential | Ecell | = 70 mV.
If the 0.05 molar solution of M+ is replaced by a 0.0025 molar M+ solution, then the magnitude of the cell potential would be :
Electrolysis of dilute aqueous NaCl solution was carried out by passing 10 milli ampere current. The time required to liberate 0.01 mol of H$$_2$$ gas at the cathode is (1 Faraday = 96500 C mol$$^{-1}$$].
Subjective
Ag+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) $$\leftrightharpoons$$ AgCl (s)
Given:
| Species | $$\Delta G_f^o$$ (kJ/mol) |
|---|---|
| Ag+ (aq) | +77 |
| Cl- (aq) | -129 |
| AgCl (s) | -109 |
Write the cell representation of above reaction and calculate $$E_{cell}^o$$ at 298 K. Also find the solubility product if AgCl.
(b) If 6.539 $$\times$$ 10-2 g of metallic zinc is added to 100 ml saturated solution of AgCl. Find the value of $${\log _{10}}{{\left[ {Z{n^{2 + }}} \right]} \over {{{\left[ {A{g^ + }} \right]}^2}}}$$. How many moles of Ag will be precipitated in the above reaction. Given that
Ag+ + e- $$\to$$ Ag; Eo = 0.80 V;
Zn2+ + 2e- $$\to$$ Zn; Eo = -0.76 V;
(It was given that atomic mass of Zn = 65.39)
In2+ + Cu2+ $$\to$$ In3+ + Cu+ at 298 K
given
$$E_{C{u^{2 + }}/C{u^ + }}^o$$ = 0.15 V; $$E_{l{n^{2 + }}/l{n^ + }}^o$$ = -0.40 V; $$E_{l{n^{3 + }}/l{n^ + }}^o$$ = -0.42 V;
Pt | H2 (g) | HCl (aq) | AgCl (s) | Ag (s)
(i) Write the cell reaction.
(ii) Calculate $$\Delta H^o$$ and $$\Delta S^o$$m for the cell reaction by assuming that these quantities remain unchanged in the range 15oC to 35oC.
(iii) Calculate the solubility of AgCl in water at 25oC
Given : The standard reduction potential of the Ag+ (aq) / Ag (s) couple is 0.80 V at 25oC
Pt(1) | Fe3+, Fe2+ (a = 1) | Ce4+, Ce3+ (a=1) | Pt(2)
Eo (Fe3+, Fe2+) = 0.77 V; Eo (Ce4+, Ce3+) = 1.61 V
If an ammeter is connected between the two platinum electrodes, predict the direction of flow of current. Will the current increase or decrease with time?
2Fe3+ + 3I- $$\leftrightharpoons$$ 2Fe2+ + $$I_3^-$$. The standard reduction potentials in acidic conditions are 0.78 V and 0.54 V respectively for Fe3+ | Fe2+ and $$I_3^-$$ | I- couples.
Fe2+ + Ce4+ $$\leftrightharpoons$$ Fe3+ + Ce3+
(given $$E_{C{e^{4 + }}/C{e^{3 + }}}^o$$ = 1.44 V; $$E_{F{e^{3 + }}/F{e^{2 + }}}^o$$ = 0.68 V)
2Hg + 2Fe3+ $$\to$$ $$Hg_2^{2+}$$ + 2Fe2+
(Given $$E_{F{e^{3 + }}|\,F{e^{2 + }}}^o$$ = 0.77 V)
Fe(s) | FeO(s) | KOH (aq) | Ni2O3(s) | Ni(s)
The half-cell reactions are:
Ni2O3 + H2O (l) + 2e- $$\leftrightharpoons$$ 2NiO(s) + 2OH-; Eo = +0.40V
FeO(s) + H2O(l) + 2e- $$\leftrightharpoons$$ Fe(s) + 2OH-; Eo = -0.87V
(i) What is the cell reaction?
(ii) What is the cell e.m.f? How does it depend on the concentration of KOH?
(iii) What is the maximum amount of electrical energy that can be obtained from one mole of Ni2O3?
CrO3 (aq) + 6H+ (aq) + 6e- $$\to$$ Cr(s) + 3H2O
Calculate (i) how many grams of chromium will be plated out by 24,000 coulombs and (ii) how long will it take to plate out 1.5 g of chromium by using 12.5 amp current.
$$NO_3^-$$ + 2H+ (aq) + e $$\to$$ NO2 (g) + H2O is 0.78 V
(i) Calculate the reduction potential in 8 M H+
(ii) What will be the reduction potential of the half-cell in a neutral solution? Assume all the other species to be at unit concentration.
2Cl- (aq) + 2H2O = 2OH- (aq) + H2 (g) + Cl2 (g)
A direct current of 25 amperes with a current efficiency of 62 % is passed through 20 litres of NaCl solution (20% by weight). Write down the reactions taking place at the anode and cathode. How long will it take to produce 1kg of Cl2? What will be the molarity of the solution with respect to hydroxide ion? (Assume no loss due to evaporation)
Ag | AgCl(s), KCl (0.2M) || KBr (0.001M), AgBr(s) | Ag
Calculate the EMF generated and assign correct polarity to each electrode for a spontaneous process after taking into account the cell reaction at 25oC.
[Ksp(AgCl) = 2.8 $$times$$ 10-10; Ksp(AgBr) = 3.3 $$times$$ 10-13]
$$BrO_3^- + 6H^+ + 6e^- \to $$ $$Br^- + 3H_2O$$
(ii) What would be the weight as well as molarity if the half-cell reaction is:
$$2BrO_3^- + 12H^+ + 10e^- \to$$ $$Br_2 \,+ 6H_2O$$