Waves · Physics · JEE Advanced
Numerical


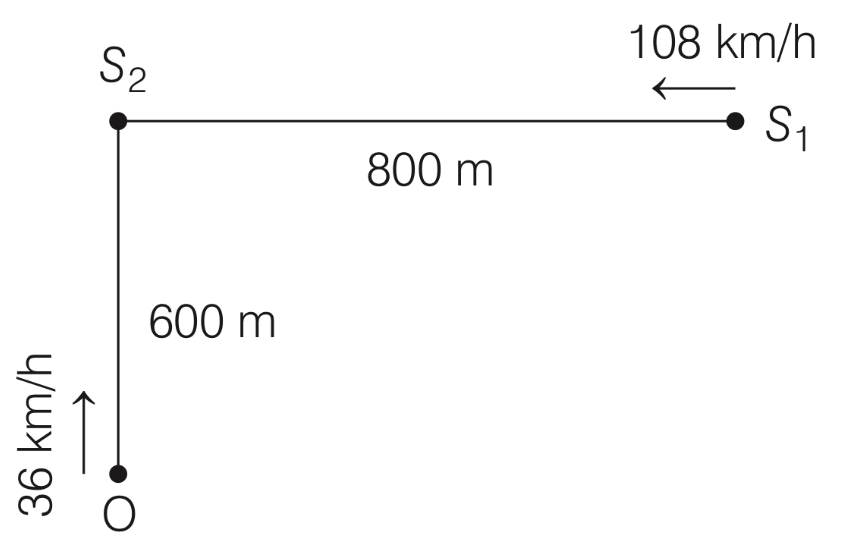
Both the trains are blowing whistles of same frequency 120 Hz. When O is 600 m away from S2 and distance between S1 and S2 is 800 m, the number of beats heard by O is ............ . [Speed of the sound = 330 m/s ............ .]
What will be the beat frequency of the resulting signal in $$Hz$$? (Given that the speed of sound in air is $$330\,m{s^{ - 1}}$$ and the car reflects the sound at the frequency it has received).
A stationary source is emitting sound at a fixed frequency f0, which is reflected by two cars approaching the source. The difference between the frequencies of sound reflected from the cars is 1.2% of f0. What is the difference in the speeds of the cars (in km per hour) to the nearest integer? The cars are moving at constant speeds much smaller than the speed of sound which is 330 ms$$-$$1.
When two progressive waves $${y_1} = 4\sin (2x - 6t)$$ and $${y_2} = 3\sin \left( {2x - 6t - {\pi \over 2}} \right)$$ are superimposed, the amplitude of the resultant wave is __________.
A 20 cm long string, having a mass of 1.0 g, is fixed at both the ends. The tension in the string is 0.5 N. The string is set into vibrations using an external vibrator of frequency 100 Hz. find the separation (in cm) between the successive nodes on the string.
MCQ (More than One Correct Answer)
Two uniform strings of mass per unit length $\mu$ and $4 \mu$, and length $L$ and $2 L$, respectively, are joined at point $\mathrm{O}$, and tied at two fixed ends $\mathrm{P}$ and $\mathrm{Q}$, as shown in the figure. The strings are under a uniform tension $T$. If we define the frequency $v_0=\frac{1}{2 L} \sqrt{\frac{T}{\mu}}$, which of the following statement(s) is(are) correct?

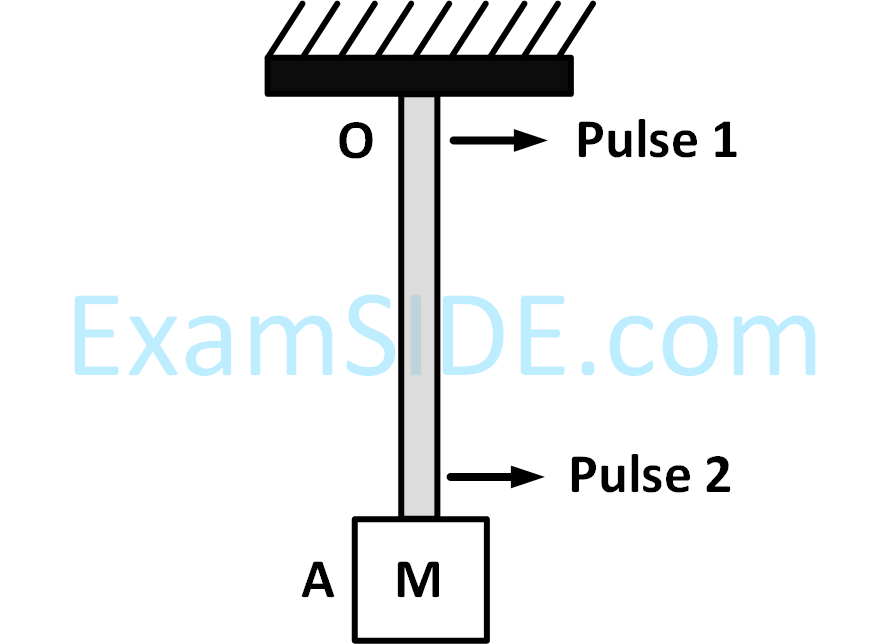
Let v(t) represent the beat frequency measured by a person sitting in the car at time t. Let vP, vQ and vR be the beat frequencies measured at locations P, Q and R respectively. The speed of sound in air is 330 ms$$-$$1. Which of the following statement(s) is (are) true regarding the sound heard by the person?
(Useful information : $$\sqrt {167RT} $$ = 640 J1/2 mol$$-$$1/2; $$\sqrt {140RT} $$ = 590 J1/2 mol$$-$$1/2. The molar mass M in grams is given in the options. Take the values of $$\sqrt {10/M} $$ for each gas as given there.)
Two vehicles, each moving with speed u on the same horizontal straight road, are approaching each other. Wind blows along the road with velocity w. One of these vehicles blows a whistle of frequency f1. An observer in the other vehicle hears the frequency of the whistle to be f2. The speed of sound in still air is V. The correct statement(s) is(are)
A horizontal stretched string, fixed at two ends, is vibrating in its fifth harmonic according to the equation
y(x, t) = (0.01 m) sin[(62.8 m$$-$$1)x] cos[(628 s$$-$$1)t]
Assuming $$\pi$$ = 3.14, the correct statement(s) is(are)
Under the influence of the Coulomb field of charge +Q, a charge $$-$$q is moving around it in an elliptical orbit. Find out the correct statement(s):
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
List-I gives the above four strings while list-II lists the magnitude of some quantity.
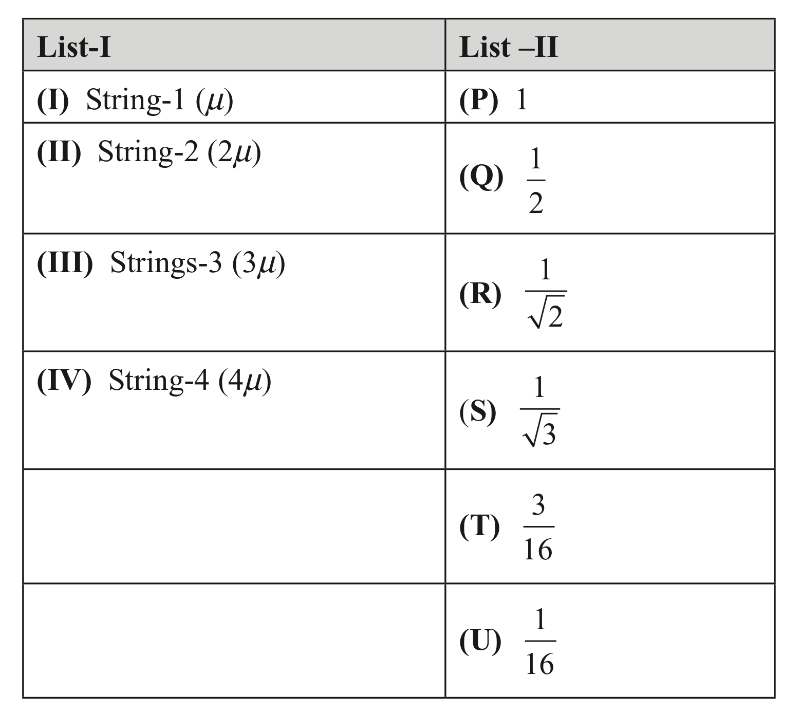
If the tension in each string is T0, the correct match for the highest fundamental frequency in f0 units will be
List-I gives the above four strings while list-II lists the magnitude of some quantity.

The length of the strings 1, 2, 3 and 4 are kept fixed at L0, $${{3{L_0}} \over 2}$$, $${{5{L_0}} \over 4}$$ and $${{7{L_0}} \over 4}$$ respectively. Strings 1, 2, 3 and 4 are vibrated at their 1st, 3rd, 5th and 14th harmonies, respectively such that all the strings have same frequency.
The correct match for the tension in the four strings in the units of T0 will be
Column I shows four systems, each of the same length L, for producing standing waves. The lowest possible natural frequency of a system is called its fundamental frequency, whose wavelength is denoted as $$\lambda$$f. Match each system with statements given in Column II describing the nature and wavelength of the standing waves :

A transverse sinusoidal wave moves along a string in the positive x-direction at a speed of 10 cm/s. The wavelength of the waves is 0.5 m and its amplitude is 10 cm. At a particular time t, the snap-shot of the wave is shown in figure. The velocity of point P when its displacement is 5 cm is :

A vibrating string of certain length 1 under a tension T resonates with a mode corresponding to the first overtone (third harmonic) of an air column of length 75 cm inside a tube closed at one end. The string also generates 4 beats per second when excited along with a tuning fork of frequency n. Now when the tension of the string is slightly increased the number of beats reduces to 2 per second. Assuming the velocity of sound in air to be 340 m/s, the frequency n of the tuning fork in Hz is:
In the experiment to determine the speed of sound using a resonance column,
The speed of sound of the whistle is
The distribution of the sound intensity of the whistle as observed by the passengers in train $$\mathrm{A}$$ is best represented by
The spread of frequency as observed by the passengers in train B is
Column I describe some situations in which a small object moves. Column II describes some characteristics of these motions. Match the situation in Column I with the characteristics in Column II and indicate your answer by darkening appropriate bubbles in the $$4 \times 4$$ matrix given in the ORS.
| Column I | Column II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| (A) | The object moves on the x-axis under a conservative force in such a way that its "speed" and "position" satisfy $$v = {c_1}\sqrt {{c_2} - {x^2}} $$, where $$c_1$$ and $$c_2$$ are positive constants. | (P) | The object executes a simple harmonic motion. |
| (B) | The object moves on the x-axis in such a way that its velocity and its displacement from the origin satisfy $$v=-kx$$, where $$k$$ is a positive constant. | (Q) | The object does not change its direction. |
| (C) | The object is attached to one end of a massless spring of a given spring constant. The other end of the spring is attached to the ceiling of an elevator. Initially everything is at rest. The elevator starts going upwards with a constant acceleration a. The motion of the object is observed from the elevator during the period it maintains this acceleration. | (R) | The kinetic energy of the object keeps on decreasing |
| (D) | The object is projected from the earth's surface vertically upwards with a speed $$2\sqrt {GMe/{\mathop{\rm Re}\nolimits} } $$, where, M$$_e$$ is the mass of the earth and R$$_e$$ is the radius of the earth. Neglect forces from objects other than the earth. | (S) | The object can change its direction only once. |