1
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1 Online
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-1

Four identical thin, square metal sheets, $S_1, S_2, S_3$ and $S_4$, each of side $a$ are kept parallel to each other with equal distance $d(\ll a)$ between them, as shown in the figure. Let $${C_0} = {{{\varepsilon _0}{a^2}} \over d}$$, where $\varepsilon_0$ is the permittivity of free space.
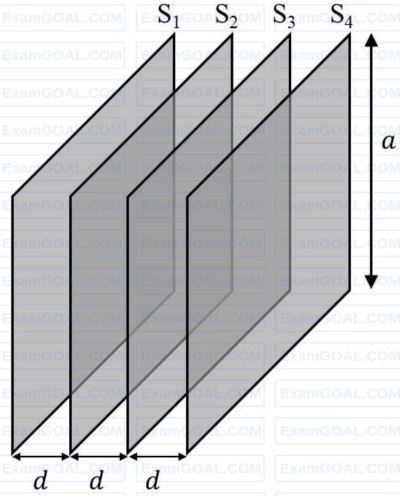
Match the quantities mentioned in List-I with their values in List-II and choose the correct option.
| List-I | List-II |
|---|---|
| (P) The capacitance between $S_1$ and $S_4$, with $S_2$ and $S_3$ not connected, is | (1) $3C_0$ |
| (Q) The capacitance between $S_1$ and $S_4$, with $S_2$ shorted to $S_3$, is | (2) $\frac{C_0}{2}$ |
| (R) The capacitance between $S_1$ and $S_3$, with $S_2$ shorted to $S_4$, is | (3) $\frac{C_0}{3}$ |
| (S) The capacitance between $S_1$ and $S_2$, with $S_3$ shorted to $S_1$, and $S_2$ shorted to $S_4$, is | (4) $\frac{2C_0}{3}$ |
| (5) $2C_0$ |
2
JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 1 Online
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-1

A container has a base of $50 \mathrm{~cm} \times 5 \mathrm{~cm}$ and height $50 \mathrm{~cm}$, as shown in the figure. It has two parallel electrically conducting walls each of area $50 \mathrm{~cm} \times 50 \mathrm{~cm}$. The remaining walls of the container are thin and non-conducting. The container is being filled with a liquid of dielectric constant 3 at a uniform rate of $250 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$. What is the value of the capacitance of the container after 10 seconds?
[Given: Permittivity of free space $\epsilon_0=9 \times 10^{-12} \mathrm{C}^2 \mathrm{~N}^{-1} \mathrm{~m}^{-2}$, the effects of the non-conducting walls on the capacitance are negligible]

[Given: Permittivity of free space $\epsilon_0=9 \times 10^{-12} \mathrm{C}^2 \mathrm{~N}^{-1} \mathrm{~m}^{-2}$, the effects of the non-conducting walls on the capacitance are negligible]

3
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0

Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in Figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e. charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to $${{{V_0}} \over 3}$$ and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then, the voltage is raised to $${{2{V_0}} \over 3}$$ without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.
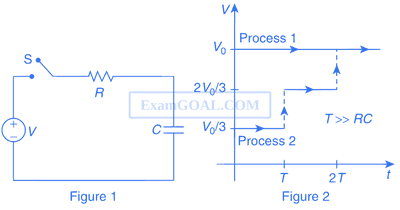
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e. charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to $${{{V_0}} \over 3}$$ and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then, the voltage is raised to $${{2{V_0}} \over 3}$$ without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.

In Process 1, the energy stored in the capacitor EC and heat dissipated across resistance ED are related by
4
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0

Consider a simple RC circuit as shown in Figure 1.
Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e. charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to $${{{V_0}} \over 3}$$ and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then, the voltage is raised to $${{2{V_0}} \over 3}$$ without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.

Process 1 : In the circuit the switch S is closed at t = 0 and the capacitor is fully charged to voltage V0 (i.e. charging continues for time T >> RC). In the process some dissipation (ED) occurs across the resistance R. The amount of energy finally stored in the fully charged capacitor is EC.
Process 2 : In a different process the voltage is first set to $${{{V_0}} \over 3}$$ and maintained for a charging time T >> RC. Then, the voltage is raised to $${{2{V_0}} \over 3}$$ without discharging the capacitor and again maintained for a time T >> RC. The process is repeated one more time by raising the voltage to V0 and the capacitor is charged to the same final voltage V0 as in Process 1.
These two processes are depicted in Figure 2.

In Process 2, total energy dissipated across the resistance ED is
Questions Asked from Capacitor (MCQ (Single Correct Answer))
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
JEE Advanced Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Units & Measurements Motion Laws of Motion Work Power & Energy Impulse & Momentum Rotational Motion Properties of Matter Heat and Thermodynamics Simple Harmonic Motion Waves Gravitation
Electricity
Electrostatics Current Electricity Capacitor Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Current Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Modern Physics
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Structure of Atom Redox Reactions Gaseous State Chemical Equilibrium Ionic Equilibrium Solutions Thermodynamics Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry Electrochemistry Solid State Surface Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Periodic Table & Periodicity Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Isolation of Elements Hydrogen s-Block Elements p-Block Elements d and f Block Elements Coordination Compounds Salt Analysis
Organic Chemistry
Mathematics
Algebra
Quadratic Equation and Inequalities Sequences and Series Mathematical Induction and Binomial Theorem Matrices and Determinants Permutations and Combinations Probability Vector Algebra 3D Geometry Statistics Complex Numbers
Trigonometry
Coordinate Geometry
Calculus