1
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2
Numerical
+1
-0
Resistor R1 in the circuit below has been adjusted so that I1 = 1 mA. The bipolar transistor Q1 and Q2 are perfectly matched and have very high current gain, so their base currents are negligible. The supply voltage Vcc is 6 V. The thermal voltage kT/q is 26 mV.


The value of R2 (in $$\Omega $$ ) for which I2 = 100 $$\mu {\rm A}$$ is ________.
Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
If the emitter resistance in a common-emitter voltage amplifier is not bypassed, it will
3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3
Numerical
+1
-0
In the circuit shown, the PNP transistor has $$\left|{\mathrm V}_\mathrm{BE}\right|=0.7\;\mathrm V$$ and β = 50. Assume that RB = 100 kΩ.
For V0 to be 5 V, the value of RC ( in kΩ) is _____________.
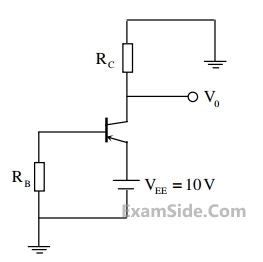

Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
Numerical
+1
-0
A cascade connection of two voltage amplifiers A1 and A2 is shown in the figure. The open-loop
gain Av0, input resistance Rin, and output resistance R0 for A1 and A2 are as follows:
A1: Av0 = 10,Rin = 10 kΩ ,R0 =1 kΩ
A2 : Av0 = 5,Rin = 5 kΩ , R0 = 200 Ω
The approximate overall voltage gain $$\frac{{\mathrm V}_\mathrm{out}}{{\mathrm V}_\mathrm{in}}$$ is ______.
A1: Av0 = 10,Rin = 10 kΩ ,R0 =1 kΩ
A2 : Av0 = 5,Rin = 5 kΩ , R0 = 200 Ω
The approximate overall voltage gain $$\frac{{\mathrm V}_\mathrm{out}}{{\mathrm V}_\mathrm{in}}$$ is ______.

Your input ____
Questions Asked from Bipolar Junction Transistor (Marks 1)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (2)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2012 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2010 (2)
GATE ECE 2006 (1)
GATE ECE 2005 (1)
GATE ECE 2004 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 2000 (1)
GATE ECE 1998 (4)
GATE ECE 1995 (2)
GATE ECE 1994 (2)
GATE ECE 1993 (2)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics