1
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1
Numerical
+1
-0
A continuous-time sinusoid of frequency 33 Hz is multiplied with a periodic Dirac impulse train of frequency 46 Hz. The resulting signal is passed through an ideal analog low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 23Hz. The fundamental frequency (in Hz) of the output is _____________________.
Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
A real - values signal x(t) limited to the frequency band $$\left| f \right| \le {W \over 2}$$ is passed through a linear time invariant system whose frequency response is
$$H(f) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{e^{ - j4\pi f}},} & {\left| f \right| \le \,{W \over 2}} \cr {0,} & {\left| f \right| > \,{W \over 2}} \cr } } \right.$$
$$H(f) = \left\{ {\matrix{ {{e^{ - j4\pi f}},} & {\left| f \right| \le \,{W \over 2}} \cr {0,} & {\left| f \right| > \,{W \over 2}} \cr } } \right.$$
The output of the system is
3
GATE ECE 2013
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
Let g(t) = $${e^{ - \pi {t^2}}}$$, and h(t) is a filter matched to g(t). If g(t) is applied as input to h(t), then the Fourier transform of the output is
4
GATE ECE 2013
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+1
-0.3
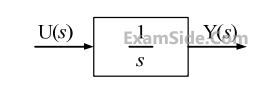
Assuming zero initial condition, the response y (t) of the system given below to a unit step input u(t) is

Questions Asked from Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems (Marks 1)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude