Let $\mathbb{R}$ denote the set of all real numbers. For a real number $x$, let [ x ] denote the greatest integer less than or equal to $x$. Let $n$ denote a natural number.
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II and choose the correct option.
| List–I | List–II |
|---|---|
| (P) The minimum value of $n$ for which the function $$ f(x)=\left[\frac{10 x^3-45 x^2+60 x+35}{n}\right] $$ is continuous on the interval $[1,2]$, is | (1) 8 |
| (Q) The minimum value of $n$ for which $g(x)=\left(2 n^2-13 n-15\right)\left(x^3+3 x\right)$, $x \in \mathbb{R}$, is an increasing function on $\mathbb{R}$, is | (2) 9 |
| (R) The smallest natural number $n$ which is greater than 5 , such that $x=3$ is a point of local minima of $$ h(x)=\left(x^2-9\right)^n\left(x^2+2 x+3\right) $$ is | (3) 5 |
| (S) Number of $x_0 \in \mathbb{R}$ such that
$$ l(x)=\sum\limits_{k=0}^4\left(\sin |x-k|+\cos \left|x-k+\frac{1}{2}\right|\right) $$ $x \in \mathbb{R}$, is NOT differentiable at $x_0$, is |
(4) 6 |
| (5) 10 |

Let $\vec{w} = \hat{i} + \hat{j} - 2\hat{k}$, and $\vec{u}$ and $\vec{v}$ be two vectors, such that $\vec{u} \times \vec{v} = \vec{w}$ and $\vec{v} \times \vec{w} = \vec{u}$. Let $\alpha, \beta, \gamma$, and $t$ be real numbers such that
$\vec{u} = \alpha \hat{i} + \beta \hat{j} + \gamma \hat{k},\ \ \ - t \alpha + \beta + \gamma = 0,\ \ \ \alpha - t \beta + \gamma = 0,\ \ \ \alpha + \beta - t \gamma = 0.$
Match each entry in List-I to the correct entry in List-II and choose the correct option.
| List – I | List – II |
|---|---|
| (P) $\lvert \vec{v} \rvert^2$ is equal to | (1) 0 |
| (Q) If $\alpha = \sqrt{3}$, then $\gamma^2$ is equal to | (2) 1 |
| (R) If $\alpha = \sqrt{3}$, then $(\beta + \gamma)^2$ is equal to | (3) 2 |
| (S) If $\alpha = \sqrt{2}$, then $t + 3$ is equal to | (4) 3 |
| (5) 5 |

The center of a disk of radius $r$ and mass $m$ is attached to a spring of spring constant $k$, inside a ring of radius $R>r$ as shown in the figure. The other end of the spring is attached on the periphery of the ring. Both the ring and the disk are in the same vertical plane. The disk can only roll along the inside periphery of the ring, without slipping. The spring can only be stretched or compressed along the periphery of the ring, following the Hooke's law. In equilibrium, the disk is at the bottom of the ring. Assuming small displacement of the disc, the time period of oscillation of center of mass of the disk is written as $T=\frac{2 \pi}{\omega}$. The correct expression for $\omega$ is ( $g$ is the acceleration due to gravity):


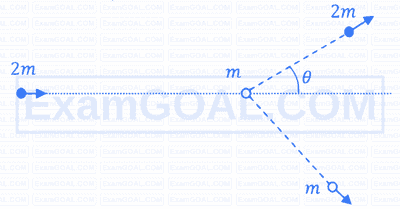
In a scattering experiment, a particle of mass 2m collides with another particle of mass m, which is initially at rest. Assuming the collision to be perfectly elastic, the maximum angular deviation θ of the heavier particle, as shown in the figure, in radians is: