1
GATE ECE 2000
Subjective
+5
-0
The network $$N$$ in Fig. consists only of two elements: a resistor of $$1\Omega $$ and an inductor of L Henry. $$A$$ $$5$$ $$V$$ source is connected at the input at $$t\, = \,0$$ seconds. The inductor current is zero at $$t\, = \,0$$. The output voltage is found to be $$5{e^{ - 3t}}\,\,V,$$ for $$t\, = \,0$$.
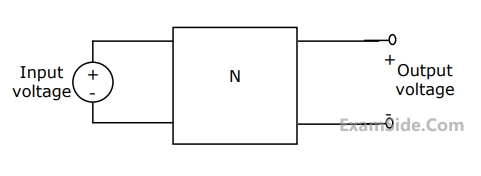

(a) Find the voltage transfer function of the network.
(b) Find L, and draw the configuration of the network.
(c) Find the impulse response of the network.
2
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
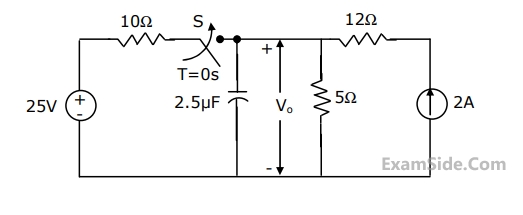
In the circuit of figure, the switch $$'S'$$ has remained open for a long time. The switch closes instantaneously at $$ t = 0$$.
 n
n
 n
n
(a) Find $${V_0}$$ for $$t \le 0$$ and as $$t \to \infty $$.
(b) Write an expression for $${V_0}$$ as a function of time for $$0 \le t \le \infty $$.
(c) Evaluate $${V_0}$$ at $$t = 25\,\,\mu $$sec.
3
GATE ECE 1994
Subjective
+5
-0
The circuit shown in the figure, is initially in its steady state. Switch is opened at
t = 0.
(1) Determine the initial voltage, VC(0-), across the capacitor, and the initial current, iL(0-) , through the indicator.
(2) Calculate the voltage, VL(t) , across the inductance for t > 0.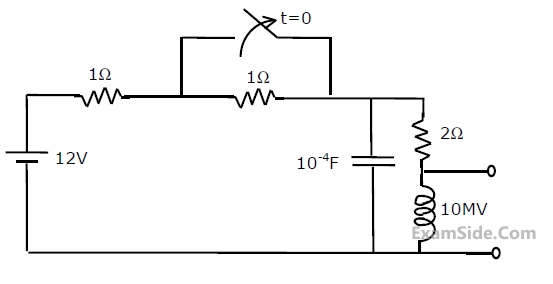
(1) Determine the initial voltage, VC(0-), across the capacitor, and the initial current, iL(0-) , through the indicator.
(2) Calculate the voltage, VL(t) , across the inductance for t > 0.

4
GATE ECE 1993
Subjective
+5
-0
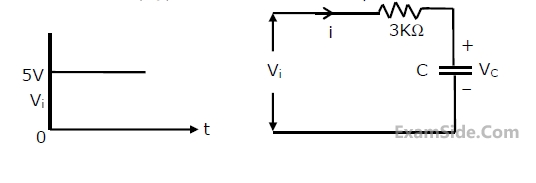
In the following circuit the capacitance varies as C = KQ, where K is a constant
equal to 0.5 Farads/Coulomb and Q, the charge on the capacitor in Coulombs.
Determine the current through the circuit and sketch the voltage waveform
across the capacitor (VC) for a step input Vi as shown in figure.

Questions Asked from Transient Response (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics