1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
Numerical
+2
-0
The electric field (assumed to be one-dimensional) between two points A and B is shown. Let
$$\psi_A$$ and $$\psi_B$$ be the electrostatic potentials at A and B, respectively. The value of $$\psi_A$$ − $$\psi_B$$ in
Volts is ________.
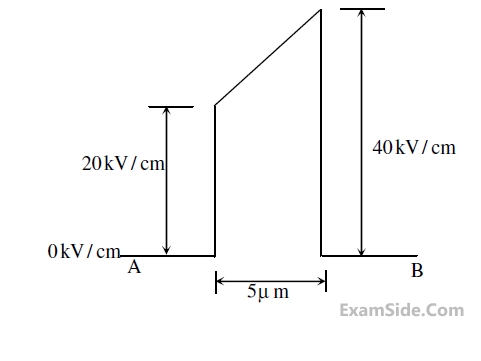

Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
If $$\overrightarrow{\mathrm E}=-\left(2\mathrm y^2\;-3\mathrm{yz}^2\right)\widehat{\mathrm x}\;-\left(6\mathrm{xy}^2-3\mathrm{xz}^2\right)\widehat{\mathrm y}+\left(6\mathrm{xyz}\right)\widehat{\mathrm z}$$
is the electric field in a source free region, a valid expression for the electrostatic potential is
3
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3
Numerical
+2
-0
Given the vector $$$\mathrm A=\left(\cos\;\mathrm x\right)\left(\sin\;\mathrm y\right)\;{\widehat{\mathrm a}}_\mathrm x\;+\;\left(\sin\;\mathrm x\right)\left(\cos\;\mathrm y\right){\widehat{\mathrm a}}_\mathrm y$$$ where $${\widehat{\mathrm a}}_\mathrm x$$ , $${\widehat{\mathrm a}}_\mathrm y$$ denote unit vectors
along x, y directions, respectively. The magnitude of curl of A is ________
Your input ____
4
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
An infinitely long uniform solid wire of radius a carries a uniform dc current of density $$\widehat{\mathrm j}$$.

A hole of radius b (b < a) is now drilled along the length of the wire at a distance d from the center of the wire as shown below.

The magnetic field inside the hole is
Questions Asked from Maxwell Equations (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (2)
GATE ECE 2022 (1)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2012 (2)
GATE ECE 2010 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 1993 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (2)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE 1988 (2)
GATE ECE 1987 (2)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude