1
GATE ECE 2022
Numerical
+2
-0
A linear 2-port network is shown in Fig. (a). An ideal DC voltage source of 10 V is connected across Port 1. A variable resistance R is connected across Port 2. As R is varied, the measured voltage and current at Port 2 is shown in Fig. (b) as a V2 versus $$-$$I2 plot. Note that for V2 = 5 V, I2 = 0 mA, and for V2 = 4 V, I2 = $$-$$4 mA. When the variable resistance R at Port 2 is replaced by the load shown in Fig. (c), the current I2 is ________ mA (rounded off to one decimal place).



Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The z-parameter matrix $$\begin{bmatrix}z_{11}&z_{12}\\z_{21}&z_{22}\end{bmatrix}$$ for the two-port network shown is


3
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The ABCD parameters of the following 2-port network are


4
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
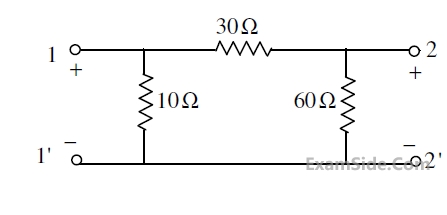
For the two-port network shown in the figure, the impedance (Z) matrix (in Ω) is

Questions Asked from Two Port Networks (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (1)
GATE ECE 2024 (1)
GATE ECE 2023 (2)
GATE ECE 2022 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (2)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2011 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (3)
GATE ECE 2006 (2)
GATE ECE 2005 (2)
GATE ECE 2004 (2)
GATE ECE 2003 (2)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 1999 (1)
GATE ECE 1997 (1)
GATE ECE 1995 (1)
GATE ECE 1992 (1)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (3)
GATE ECE 1988 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics