1
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4
Numerical
+2
-0
Consider the Z- channel given in the figure. The input is 0 or 1 with equal probability.
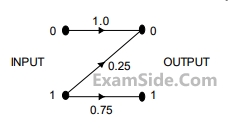 If the output is 0, the probability that the input is also 0 equals____________________________________
If the output is 0, the probability that the input is also 0 equals____________________________________
 If the output is 0, the probability that the input is also 0 equals____________________________________
If the output is 0, the probability that the input is also 0 equals____________________________________Your input ____
2
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The capacity of band-limited additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channel is given by $$C = \,W\,\,{\log _2}\left( {1 + {P \over {{\sigma ^2}\,W}}} \right)$$ bits per second (bps), where W is the channel bandwidth, P is the average power received and $${{\sigma ^2}}$$ is the one-sided power spectral density of the AWGN.
For a Fixed $${{P \over {{\sigma ^2}\,}} = 1000}$$, the channel capacity (in kbps) with infinite band width $$(W \to \infty )$$ is approximately
For a Fixed $${{P \over {{\sigma ^2}\,}} = 1000}$$, the channel capacity (in kbps) with infinite band width $$(W \to \infty )$$ is approximately
3
GATE ECE 2009
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A communication channel with AWGN operating at a signal to noise ratio SNR > > 1 and band width B has capacity $${{C_1}}$$ . If the SNR is doubled keeping B constant, the resulting capacity $${{C_2}}$$ is given
4
GATE ECE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A memory less source emits n symbols each with a probability p. The entropy of the source as a function of n
Questions Asked from Fundamentals of Information Theory (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2025 (2)
GATE ECE 2023 (1)
GATE ECE 2022 (2)
GATE ECE 2017 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 3 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 4 (1)
GATE ECE 2014 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2009 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2006 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (1)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude