1
GATE ECE 1994
Subjective
+5
-0
A wave traveling in the $$+Z$$-direction, is the resultant of two linearly polarized components, $${E_x}\,\,\, = \,\,\,\,\,\,3$$ $$\,\,\,\,\cos \omega t$$ and $$\,{E_y}\,\,\,\, = \,\,\,2\,\cos \,\left( {\omega t + {{45}^ \circ }} \right)$$
Determine
(1) The axial ratio
(2) The angle between the major axis of the polarization ellipse and the $$+x$$-axis.
2
GATE ECE 1993
Subjective
+5
-0
Match the following descriptions with each of the diagrams given in Fig. Fields are near the interface, but on opposite sides of the boundary. Vectors are drawn to scale.
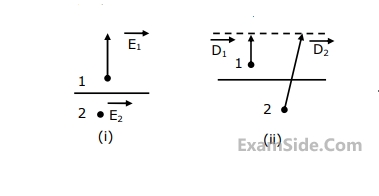
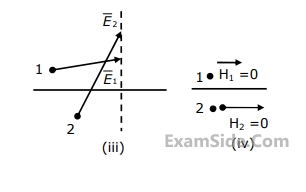
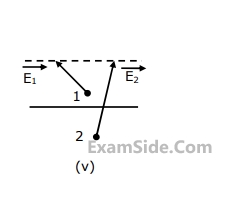
(a) Medium $$1$$ and medium $$2$$ are dielectrics with $${\varepsilon _1} > {\varepsilon _2}$$
(b) Medium $$1$$ and medium $$2$$ are dielectrics with $${\varepsilon _1} < {\varepsilon _2}$$
(c) Medium $$2$$ is a perfect conductor
(d) Impossible
(e) Medium $$1$$ is a perfect conduct



Questions Asked from Uniform Plane Waves (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics