1
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
A plane wave with $$\overrightarrow E = 10\,{e^{j\left( {\omega t - \beta z} \right)\,}}\,\,{\overrightarrow a _{_y}}$$ is incident normally on a thick plane conductor lying in the $$X - Y$$ plane. Its conductivity is $$6 \times {10^6}\,\,\,S/m\,\,\,$$ and surface impedance is $$5 \times {0^{ - 4}}\,\angle {45^0}\Omega $$. Determine the propagation constant and the skin depth in the conductor.
2
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
The electric field vector of a wave is given as
$$$\vec E = {E_0}{\mkern 1mu} {e^{j\left( {\omega t + 3x - 4y} \right)}}{\mkern 1mu} {{8{{\vec a}_x} + 6{{\vec a}_y} + 5{{\vec a}_z}} \over {\sqrt {125} }}\,\,V/m$$$
Its frequency is 10 GHz.
(i) Investigate if this wave is a plane wave.
(ii) Determine its propagation constant, and
(iii) Calculate the phase velocity in $$y$$-direction.
3
GATE ECE 1997
Subjective
+5
-0
A uniform plane wave is normally incident from air on an infinitely thick magnetic material with relative permeability 100 and relative permittivity 4 (sec in Fig.). The wave has an electric field of 1 V/meter (rms). Find the average Poynting vector inside the material.


4
GATE ECE 1996
Subjective
+5
-0
A uniform plane wave having parallel polarization is obliquely incident on an air - dielectric interface as shown in Fig. If the wave has an electric field $$E = 10\,\,V/m$$, find
(i) The angle of incidence $${\theta _i}$$ for which there is no reflection of the wave.
(ii) The surface charge density at the interface.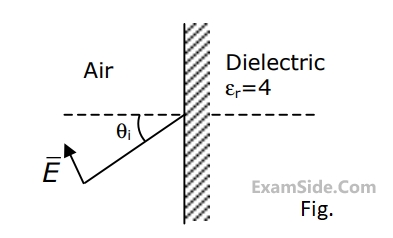
(i) The angle of incidence $${\theta _i}$$ for which there is no reflection of the wave.
(ii) The surface charge density at the interface.

Questions Asked from Uniform Plane Waves (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics