1
JEE Advanced 2016 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0

Consider an evacuated cylindrical chamber of height h having rigid conducting plates at the ends and an insulating curved surface as shown in the figure. A number of spherical balls made of a light weight and soft material and coated with a conducting material are placed on the bottom plate. The balls have a radius r << h. Now, a high voltage source (HV) connected across the conducting plates such that the bottom plate is at +V0 and the top plate at $$-$$V0. Due to their conducting surface, the balls will get charge, will become equipotential with the plate and are repelled by it. The balls will eventually collide with the top plate, where the coefficient of restitution can be taken to be zero due to the soft nature of the material of the balls. The electric field in the chamber can be considered to be that of a parallel plate capacitor. Assume that there are no collisions between the balls and the interaction between them is negligible. (Ignore gravity)
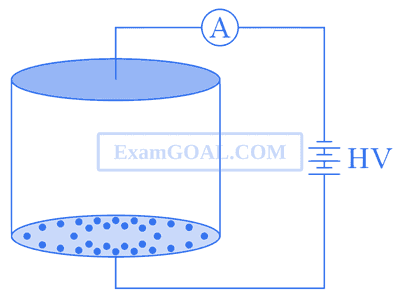
The average current in the steady state registered by the ammeter in the circuit will be

The average current in the steady state registered by the ammeter in the circuit will be
2
JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-1
Charges $$Q,$$ $$2Q$$ and $$4Q$$ are uniformly distributed in three dielectric solid spheres $$1,2$$ and $$3$$ of radii $$R/2,R$$ and $$2R$$ respectively, as shown in figure. If magnitude of the electric fields at point $$P$$ at a distance $$R$$ from the center of sphere $$1,2$$ and $$3$$ are $${E_1}$$, $${E_2}$$ and $${E_3}$$ respectively, then
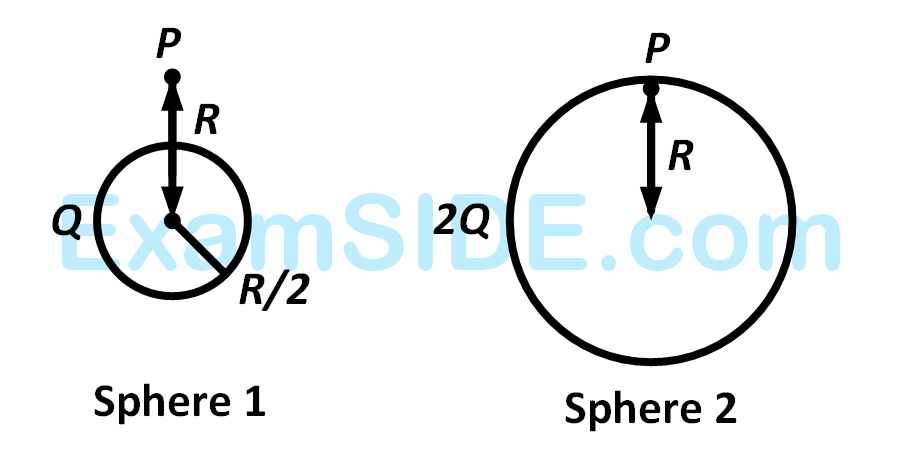
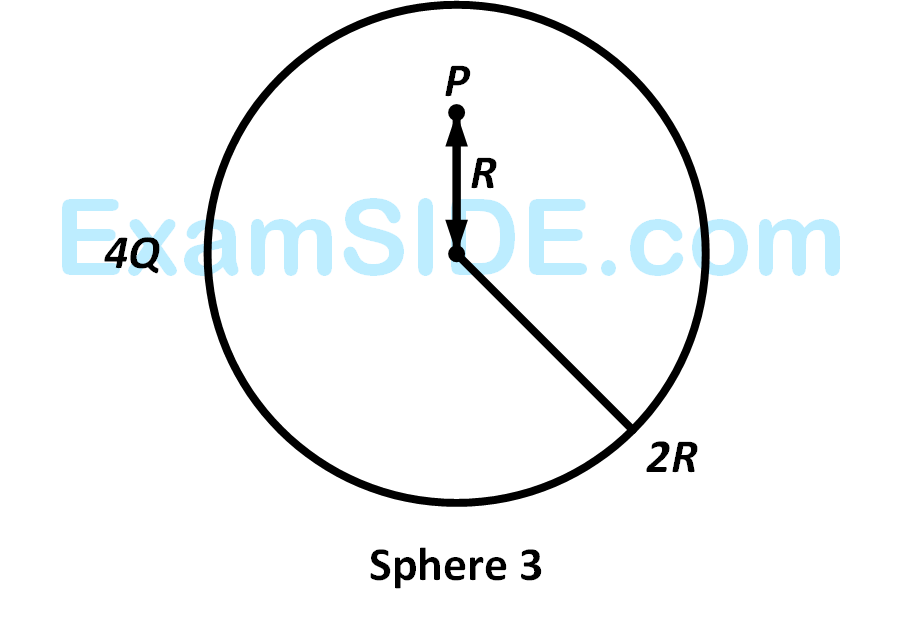


3
JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-1
Four charges Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 of same magnitude are fixed along the x axis at x = $$-$$2a, $$-$$a, +a and +2a, respectively. A positive charge q is placed on the positive y axis at a distance b > 0. Four options of the signs of these charges are given in List I. The direction of the forces on the charge q is given in List II. Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.

| List I | List II | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| P. | Q$$_1$$, Q$$_2$$, Q$$_3$$, Q$$_4$$ all positive | 1. | +x |
| Q. | Q$$_1$$, Q$$_2$$ positive; Q$$_3$$, Q$$_4$$ negative | 2. | $$ - $$x |
| R. | Q$$_1$$, Q$$_4$$ positive; Q$$_2$$, Q$$_3$$ negative | 3. | +y |
| S. | Q$$_1$$, Q$$_3$$ positive; Q$$_2$$, Q$$_4$$ negative | 4. | $$ - $$y |
4
JEE Advanced 2013 Paper 1 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+4
-1
Two non-conducting solid spheres of radii $$R$$ and $$2R,$$ having uniform volume charge densities $${\rho _1}$$ and $${\rho _2}$$ respectively, touch each other. The net electric field at a distance $$2$$ $$R$$ from the center of the smaller sphere, along the line joining the centers of the spheres, is zero. The ratio $${{{\rho _1}} \over {{\rho _2}}}$$ can be
Questions Asked from Electrostatics (MCQ (Single Correct Answer))
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 2 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2025 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2023 Paper 2 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2019 Paper 1 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2018 Paper 2 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2016 Paper 2 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 2 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced 2013 Paper 1 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2012 Paper 1 Offline (2)
IIT-JEE 2011 Paper 1 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2011 Paper 2 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2010 Paper 2 Offline (2)
IIT-JEE 2009 Paper 1 Offline (3)
IIT-JEE 2008 Paper 2 Offline (6)
IIT-JEE 2007 Paper 2 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Units & Measurements Motion Laws of Motion Work Power & Energy Impulse & Momentum Rotational Motion Properties of Matter Heat and Thermodynamics Simple Harmonic Motion Waves Gravitation
Electricity
Electrostatics Current Electricity Capacitor Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Current Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Modern Physics
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Structure of Atom Redox Reactions Gaseous State Chemical Equilibrium Ionic Equilibrium Solutions Thermodynamics Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry Electrochemistry Solid State Surface Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Periodic Table & Periodicity Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Isolation of Elements Hydrogen s-Block Elements p-Block Elements d and f Block Elements Coordination Compounds Salt Analysis
Organic Chemistry
Mathematics
Algebra
Quadratic Equation and Inequalities Sequences and Series Mathematical Induction and Binomial Theorem Matrices and Determinants Permutations and Combinations Probability Vector Algebra 3D Geometry Statistics Complex Numbers
Trigonometry
Coordinate Geometry
Calculus