1
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 2 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0.75

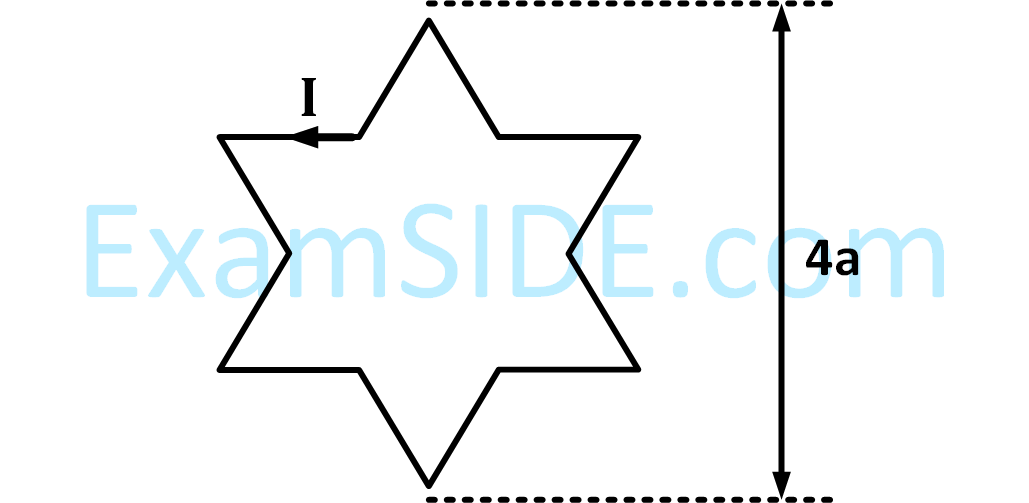
A symmetric star shaped conducting wire loop is carrying a steady state current $${\rm I}$$ as shown in the figure. The distance between the diametrically opposite vertices of the star is $$4a.$$ The magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the loop is

2
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 1 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0.75

A charged particle (electron or proton) is introduced at the origin (x=0,y=0,z=0) with a given initial velocity $$\overrightarrow v .$$ A uniform electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and a uniform magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ exist everywhere. The velocity $$\overrightarrow v ,$$ electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ are given in column $$1,2$$ and $$3,$$ respectively. The quantities $${E_0},{B_0}$$ are positive in magnitude.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (i) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat z$$ | (P) | $$\overrightarrow B = - {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (II) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = {{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat y$$ | (ii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat y$$ | (Q) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (III) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 0$$ | (iii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (R) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat y$$ |
| (IV) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (iv) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (S) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat z$$ |
In which case will the particle move in a straight line with constant velocity?
3
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 1 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0.75

A charged particle (electron or proton) is introduced at the origin (x=0,y=0,z=0) with a given initial velocity $$\overrightarrow v .$$ A uniform electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and a uniform magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ exist everywhere. The velocity $$\overrightarrow v ,$$ electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ are given in column $$1,2$$ and $$3,$$ respectively. The quantities $${E_0},{B_0}$$ are positive in magnitude.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (i) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat z$$ | (P) | $$\overrightarrow B = - {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (II) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = {{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat y$$ | (ii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat y$$ | (Q) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (III) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 0$$ | (iii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (R) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat y$$ |
| (IV) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (iv) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (S) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat z$$ |
In which case will the particle describe a helical path with axis along the positive $$z$$ direction?
4
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 1 Offline
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+3
-0.75

A charged particle (electron or proton) is introduced at the origin (x=0,y=0,z=0) with a given initial velocity $$\overrightarrow v .$$ A uniform electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and a uniform magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ exist everywhere. The velocity $$\overrightarrow v ,$$ electric field $$\overrightarrow E $$ and magnetic field $$\overrightarrow B $$ are given in column $$1,2$$ and $$3,$$ respectively. The quantities $${E_0},{B_0}$$ are positive in magnitude.
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (I) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (i) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat z$$ | (P) | $$\overrightarrow B = - {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (II) | Electron with $$\overrightarrow v = {{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat y$$ | (ii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat y$$ | (Q) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat x$$ |
| (III) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 0$$ | (iii) | $$\overrightarrow E = - {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (R) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat y$$ |
| (IV) | Proton with $$\overrightarrow v = 2{{{E_0}} \over {{B_0}}}\widehat x$$ | (iv) | $$\overrightarrow E = {E_0}\widehat x$$ | (S) | $$\overrightarrow B = {B_0}\widehat z$$ |
In which case would the particle move in a straight line along the negative direction of $$y$$-axis (i.e., move along $$ - \widehat y$$)?
Questions Asked from Magnetism (MCQ (Single Correct Answer))
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 2 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2024 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 2 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2022 Paper 1 Online (1)
JEE Advanced 2021 Paper 2 Online (2)
JEE Advanced 2020 Paper 1 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 2 Offline (1)
JEE Advanced 2017 Paper 1 Offline (3)
JEE Advanced 2014 Paper 2 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced 2013 Paper 2 Offline (2)
IIT-JEE 2012 Paper 2 Offline (2)
IIT-JEE 2011 Paper 1 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2011 Paper 2 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2010 Paper 1 Offline (3)
IIT-JEE 2008 Paper 2 Offline (1)
IIT-JEE 2007 Paper 2 Offline (2)
JEE Advanced Subjects
Physics
Mechanics
Units & Measurements Motion Laws of Motion Work Power & Energy Impulse & Momentum Rotational Motion Properties of Matter Heat and Thermodynamics Simple Harmonic Motion Waves Gravitation
Electricity
Electrostatics Current Electricity Capacitor Magnetism Electromagnetic Induction Alternating Current Electromagnetic Waves
Optics
Modern Physics
Chemistry
Physical Chemistry
Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Structure of Atom Redox Reactions Gaseous State Chemical Equilibrium Ionic Equilibrium Solutions Thermodynamics Chemical Kinetics and Nuclear Chemistry Electrochemistry Solid State Surface Chemistry
Inorganic Chemistry
Periodic Table & Periodicity Chemical Bonding & Molecular Structure Isolation of Elements Hydrogen s-Block Elements p-Block Elements d and f Block Elements Coordination Compounds Salt Analysis
Organic Chemistry
Mathematics
Algebra
Quadratic Equation and Inequalities Sequences and Series Mathematical Induction and Binomial Theorem Matrices and Determinants Permutations and Combinations Probability Vector Algebra 3D Geometry Statistics Complex Numbers
Trigonometry
Coordinate Geometry
Calculus