1
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
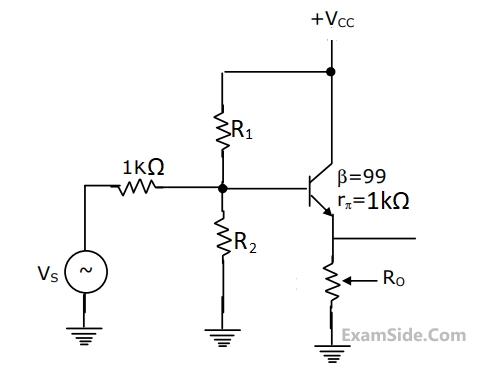
In the circuit of fig. Determine the resistance Ro seen by the output terminals, ignore the effects of R1 and R2.

2
GATE ECE 1997
Subjective
+5
-0
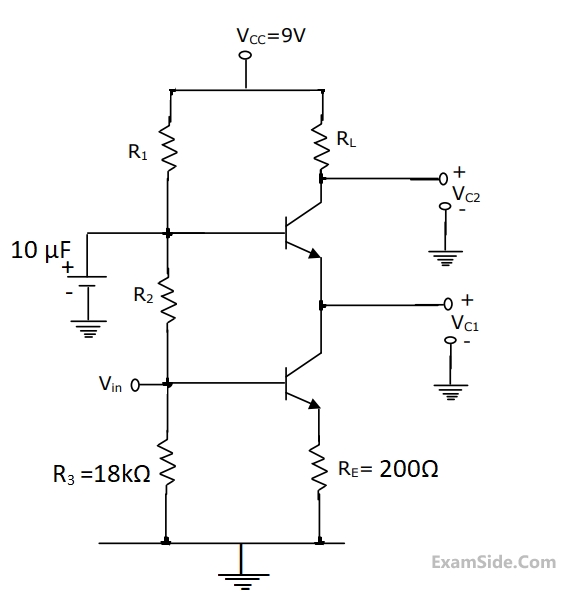
In the cascade amplifier circuit shown below, determine the values of R1, R2 and RL. Such that the quiescent current through the transistors is 1mA and the collector voltage Vc1 = 3V, and Vc2 = 6V. Tke VBE = 0.7V, Transistor $$\beta $$ to be hifgh and base currents to be negligible.

3
GATE ECE 1997
Subjective
+5
-0
The transistor in the circuit shown in the figure. is so biased (dc biasing N/W is not shown) that the dc collector current IC = 1mA. Supply is VCC = 5V.


The N/W components have following values, RC = 2$$k\Omega $$,
RS = $$1.4k\Omega $$,
RE = $$100\Omega $$.
The transistor has specifications, $$\beta \,\, = \,\,100$$
and base spreading resistance $${r_{bb\,}}^1\, = \,100\Omega $$
Evaluate input resistance Ri for two cases. At a frequency of 10 kHz
(a)CE, the bypass capacitor across RE is 25 $$\mu F$$
(b)The bypass capacitor CE is removed leaving RE unbypassed.
Questions Asked from Bipolar Junction Transistor (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics