1
GATE ECE 2001
Subjective
+5
-0
A rectangular hollow metal waveguide has dimensions a = 2.29 cm and b = 1.02 cm. Microwave power at 10 GHz is transmitted through the waveguide in the $$T{E_{10}}$$ mode.
(a) Calculate the cut-off wavelength and the guide wavelength for this mode.
(b) What are the other (TE or TM) modes that can propagate through the waveguide?
(c) If a = b = 2.29 cm, what are the modes which can propagate through the waveguide?
(a) Calculate the cut-off wavelength and the guide wavelength for this mode.
(b) What are the other (TE or TM) modes that can propagate through the waveguide?
(c) If a = b = 2.29 cm, what are the modes which can propagate through the waveguide?
2
GATE ECE 1999
Subjective
+5
-0
A 100 m section of an air-filled rectangular wave-guide operating in the $$T{E_{10}}$$ mode has a cross-sectional dimension of 1.071 cm $$ \times $$ 0.5 cm. Two pulses carriers of 21 GHz and 28 GHz are simultaneously launched at one end of the wave-guide section. What is the time delay difference between the two pulses at the other end of the waveguide?
3
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
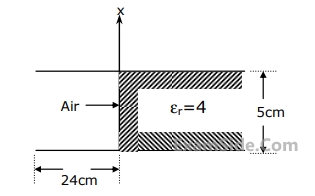
The region between a pair of parallel perfectly conducting planes of infinite extent in the y and z directions is partially filled with a dielectric as shown in Figure. A 30 GHz $$T{E_{10}}$$ wave is incident on the air dielectric interface as shown. Find the
VSWR at the interface.

4
GATE ECE 1998
Subjective
+5
-0
A rectangular waveguide with inner dimensions 6 cm $$ \times $$ 3 cm has been designed for a single mode operation. Find the possible frequency range of operation such that the lowest frequency is 5% above the cut off and the highest frequency is 5% below the cut off of the next higher mode.
Questions Asked from Waveguides (Marks 5)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Sampling Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics