1
GATE ECE 2003
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
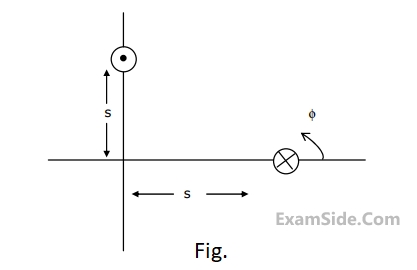
Two identical antennas are placed in the $$\theta = \pi /2$$
plane as shown in figure. The
elements have equal amplitude excitation with 180° polarity difference, operating
at wavelength λ. The correct value of the magnitude of the far zone resultant
electric field strength normalized with that of a single element, both computed for $$\phi = 0$$ is

2
GATE ECE 2002
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A person with a receiver is 5 Km away from the transmitter. What is the distance that this person must move further to detect a 3-dB decrease in signal strength?
3
GATE ECE 2001
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
In a uniform linear array, four isotropic radiating elements are spaced $$\lambda /4$$ apart. The progressive phase shift between the elements required for forming the main beam at 60° off the end-fire is
4
GATE ECE 2001
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A medium wave radio transmitter operating at a wavelength of 492 m has a tower antenna of height 124m. What is the radiation resistance of the antenna?
Questions Asked from Antennas (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE 2017 Set 1 (1)
GATE ECE 2016 Set 1 (3)
GATE ECE 2015 Set 2 (1)
GATE ECE 2008 (1)
GATE ECE 2007 (1)
GATE ECE 2006 (1)
GATE ECE 2005 (1)
GATE ECE 2003 (1)
GATE ECE 2002 (1)
GATE ECE 2001 (2)
GATE ECE 2000 (2)
GATE ECE 1999 (1)
GATE ECE 1997 (1)
GATE ECE 1996 (2)
GATE ECE 1992 (2)
GATE ECE 1991 (1)
GATE ECE 1990 (1)
GATE ECE 1989 (1)
GATE ECE 1988 (1)
GATE ECE Subjects
Network Theory
Control Systems
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Digital Circuits
Microprocessors
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Communications
Electromagnetics
General Aptitude