1
GATE ECE 2012
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The Fourier transform of a signal h(t) is $$H(j\omega )$$ =(2 cos $$\omega $$) (sin 2$$\omega $$) / $$\omega $$. The value of h(0) is
2
GATE ECE 2008
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
The signal x(t) is described by $$x\left( t \right) = \left\{ {\matrix{
{1\,\,\,for\,\, - 1 \le t \le + 1} \cr
{0\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,otherwise} \cr
} } \right.$$
Two of the angular frequencies at which its Fourier transform becomes zero are
3
GATE ECE 2005
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
For a signal x(t) the Fourier transform is X(f). Then the inverse Fourier transform of X(3f+2) is given by
4
GATE ECE 2004
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
Let x(t) and y(t) (with Fourier transforms X(f) and Y(f) respectively) be related as shown in Fig.(1) & (2).
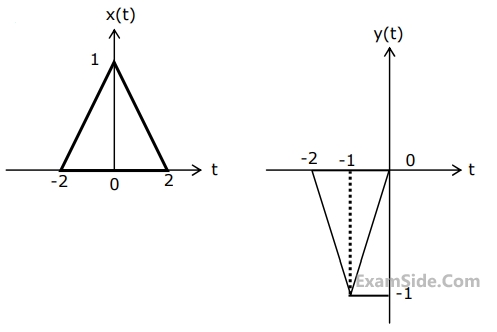

Then Y(f) is
Questions Asked from Fourier Transform (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE ECE Subjects
Signals and Systems
Representation of Continuous Time Signal Fourier Series Discrete Time Signal Fourier Series Fourier Transform Discrete Time Signal Z Transform Continuous Time Linear Invariant System Transmission of Signal Through Continuous Time LTI Systems Discrete Time Linear Time Invariant Systems Sampling Continuous Time Signal Laplace Transform Discrete Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform Transmission of Signal Through Discrete Time Lti Systems Miscellaneous Fourier Transform
Network Theory
Control Systems
Digital Circuits
General Aptitude
Electronic Devices and VLSI
Analog Circuits
Engineering Mathematics
Microprocessors
Communications
Electromagnetics