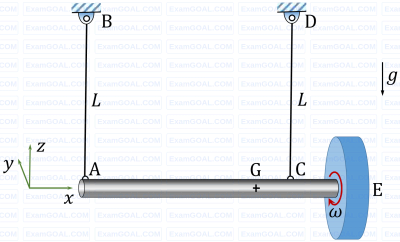
A massive uniform rigid circular disc is mounted on a frictionless bearing at the end E of a massive uniform rigid shaft AE which is suspended horizontally in a uniform gravitational field by two identical light inextensible strings AB and CD as shown, where G is the center of mass of the shaft-disc assembly and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The disc is then given a rapid spin w about its axis in the positive xaxis direction as shown, while the shaft remains at rest. The direction of rotation is defined by using the right-hand thumb rule. If the string AB is suddenly cut, assuming negligible energy dissipation, the shaft AE will
Match the additive manufacturing technique in Column I with its corresponding input material in Column II.
|
Additive manufacturing technique (Column I) |
Input Material (Column II) |
||
|
P. |
Fused deposition modeling |
1. |
Photosensitive liquid resin |
|
Q. |
Laminated object Manufacturing |
2. |
Heat fusible power |
|
R. |
Selective laser sintering |
3. |
Filament of polymer |
|
|
|
4. |
Sheet of thermoplastic or green compacted metal sheet |
A square plate is supported in four different ways (configurations (P) to (S) as shown in the figure). A couple moment C is applied on the plate. Assume all the members to be rigid and mass-less, and all joints to be frictionless. All support links of the plate are identical.
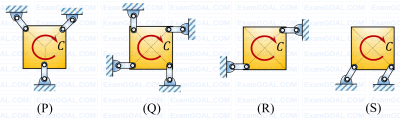
The square plate can remain in equilibrium in its initial state for which one or more of the following support configurations?



