Engineering Mechanics Static and Dynamics · Engineering Mechanics · GATE ME
Marks 1
A truss structure is loaded as shown in the figure below. Among the options given, which member in the truss is a zero-force member?

A ram in the form of a rectangular body of size $l = 9 \text{ m}$ and $b = 2 \text{ m}$ is suspended by two parallel ropes of lengths $7 \text{ m}$. Assume the center-of-mass of the body is at its geometric center and $g = 9.81 \text{ m/s}^2$. For striking the object P with a horizontal velocity of $5 \text{ m/s}$, what is the angle $\theta$ with the vertical from which the ram should be released from rest?

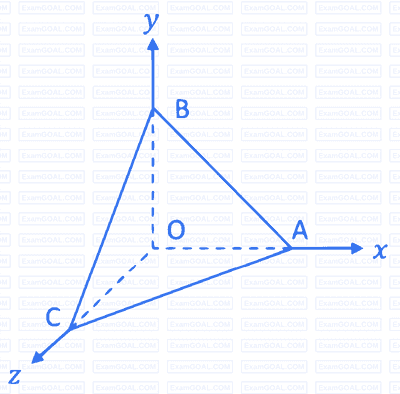
A rigid massless tetrahedron is placed such that vertex O is at the origin and the other three vertices A, B, and C lie on the coordinate axes as shown in the figure. The body is acted on by three point loads, of which one is acting at A along x-axis and another at point B along y-axis. For the body to be in equilibrium, the third point load acting at point O must be
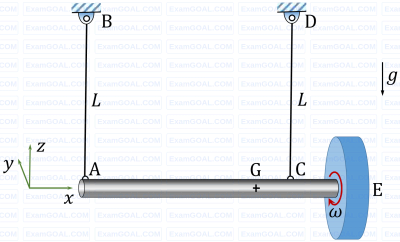
A massive uniform rigid circular disc is mounted on a frictionless bearing at the end E of a massive uniform rigid shaft AE which is suspended horizontally in a uniform gravitational field by two identical light inextensible strings AB and CD as shown, where G is the center of mass of the shaft-disc assembly and g is the acceleration due to gravity. The disc is then given a rapid spin w about its axis in the positive xaxis direction as shown, while the shaft remains at rest. The direction of rotation is defined by using the right-hand thumb rule. If the string AB is suddenly cut, assuming negligible energy dissipation, the shaft AE will
Match the additive manufacturing technique in Column I with its corresponding input material in Column II.
|
Additive manufacturing technique (Column I) |
Input Material (Column II) |
||
|
P. |
Fused deposition modeling |
1. |
Photosensitive liquid resin |
|
Q. |
Laminated object Manufacturing |
2. |
Heat fusible power |
|
R. |
Selective laser sintering |
3. |
Filament of polymer |
|
|
|
4. |
Sheet of thermoplastic or green compacted metal sheet |
A square plate is supported in four different ways (configurations (P) to (S) as shown in the figure). A couple moment C is applied on the plate. Assume all the members to be rigid and mass-less, and all joints to be frictionless. All support links of the plate are identical.
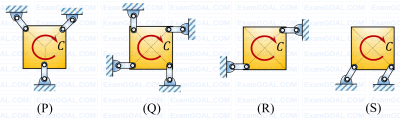
The square plate can remain in equilibrium in its initial state for which one or more of the following support configurations?
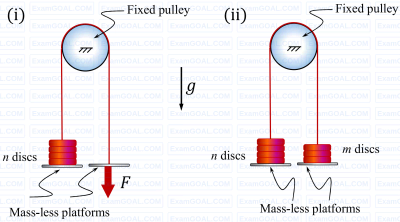
A rope with two mass-less platforms at its two ends passes over a fixed pulley as shown in the figure. Discs with narrow slots and having equal weight of 20 N each can be placed on the platforms. The number of discs placed on the left side platform is n and that on the right side platform is m.
It is found that for n = 5 and m = 0, a force F= 200 N (refer to part (i) of the figure) is just sufficient to initiate upward motion of the left side platform. If the force F is removed then the minimum value of m (refer to part (ii) of the figure) required to prevent downward motion of the left side platform is (in integer).
The plane of the figure represents a horizontal plane. A thin rigid rod at rest is pivoted without friction about a fixed vertical axis passing through O. Its mass moment of inertia is equal to 0.1 kg∙cm2 about O. A point mass of 0.001 kg hits it normally at 200 cm/s at the location shown, and sticks to it. Immediately after the impact, the angular velocity of the rod is ___________ rad/s (in integer).

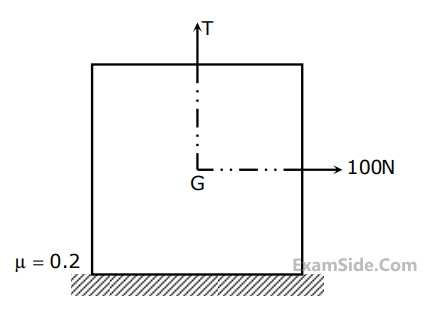
 The CORRECT free body diagram is
The CORRECT free body diagram is 



 v
v


Marks 2
A three-hinge arch ABC in the form of a semi-circle is shown in the figure. The arch is in static equilibrium under vertical loads of $P = 100$ kN and $Q = 50$ kN. Neglect friction at all the hinges. The magnitude of the horizontal reaction at B is _________ kN (rounded off to 1 decimal place).

A spherical ball weighing 2 kg is dropped from a height of 4.9 m onto an immovable rigid block as shown in the figure. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the momentum vector of the ball (in kg m/s) just after impact?
Take the acceleration due to gravity to be 𝑔 = 9.8 m/s2. Options have been rounded off to one decimal place.

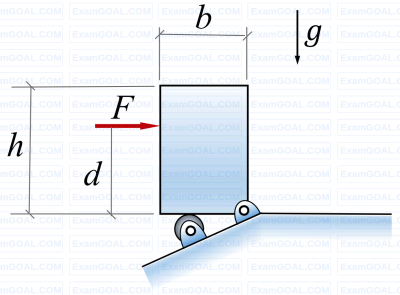
A rigid homogeneous uniform block of mass 1 kg, height h = 0.4 m and width b = 0.3 m is pinned at one corner and placed upright in a uniform gravitational field (g = 9.81 m/s2), supported by a roller in the configuration shown in the figure. A short duration (impulsive) force F, producing an impulse IF is applied at a height of d = 0.3 m from the bottom as shown. Assume all joints to be frictionless. The minimum value of IF required to topple the block is
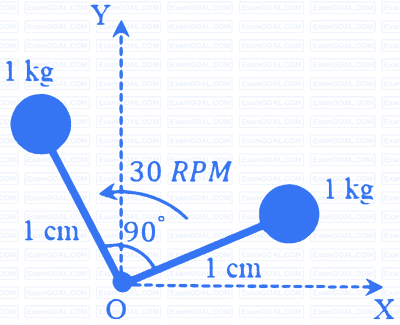
A rigid body in the X-Y plane consists of two point masses (1 kg each) attached to the ends of two massless rods, each of 1 cm length, as shown in the figure. It rotates at 30 RPM counter-clockwise about the Z-axis passing through point O. A point mass of √2 kg, attached to one end of a third massless rod, is used for balancing the body by attaching the free end of the rod to point O. The length of the third rod is ______ cm.
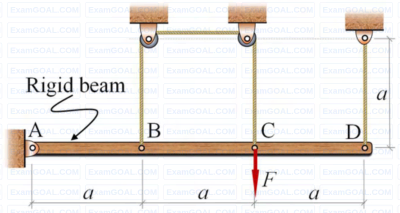
A rigid beam AD of length 3a = 6 m is hinged at frictionless pin joint A and supported by two strings as shown in the figure. String BC passes over two small frictionless pulleys of negligible radius. All the strings are made of the same material and have equal cross-sectional area. A force F = 9 KN is applied at C and the resulting stresses in the strings are within linear elastic limit. The self-weight of the beam is negligible with respect to the applied load. Assuming small deflections, the tension developed in the string at C is KN (round off to 2 decimal places).
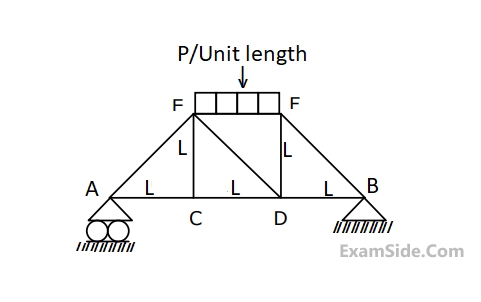
The lengths of members BC and CE in the frame shown in the figure are equal. All the members are rigid and lightweight, and the friction at the joints is negligible. Two forces of magnitude Q > 0 are applied as shown, each at the mid-length of the respective member on which it acts.

Which one or more of the following members do not carry any load (force)?
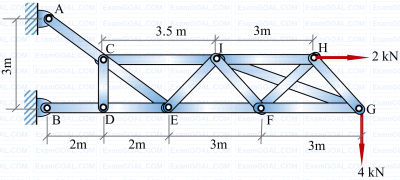
A structure, along with the loads applied on it, is shown in the figure. Self-weight of all the members is negligible and all the pin joints are friction-less. AE is a single member that contains pin C. Likewise, BE is a single member that contains pin D. Members GI and FH are overlapping rigid members. The magnitude of the force carried by member CI is ________ kN (in integer).
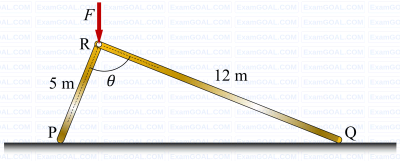
Two rigid massless rods PR and RQ are joined at frictionless pin-joint R and are resting on ground at P and Q, respectively, as shown in the figure. A vertical force F acts on the pin R as shown. When the included angle 𝜃 < 90°, the rods remain in static equilibrium due to Coulomb friction between the rods and ground at locations P and Q. At 𝜃 = 90°, impending slip occurs simultaneously at points P and Q. Then the ratio of the coefficient of friction at Q to that at P (μQ /μP) is _________ (round off to two decimal places).
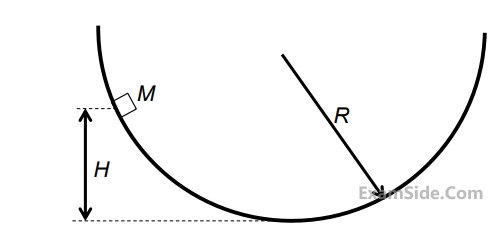
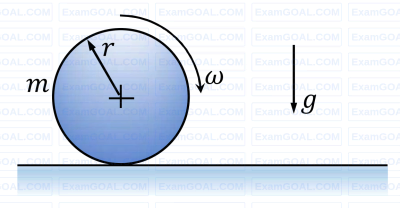
A cylindrical disc of mass m = 1 kg and radius r = 0.15 m was spinning at 𝜔 = 5 rad/s when it was placed on a flat horizontal surface and released (refer to the figure). Gravity g acts vertically downwards as shown in the figure. The coefficient of friction between the disc and the surface is finite and positive. Disregarding any other dissipation except that due to friction between the disc and the surface, the horizontal velocity of the center of the disc, when it starts rolling without slipping, will be _________ m/s (round off to 2 decimal places).

Take $$\cos \theta = 0.8$$ and $$\sin \theta = 0.6$$. Acceleration due to gravity g $$=$$ $$10$$ m/s2
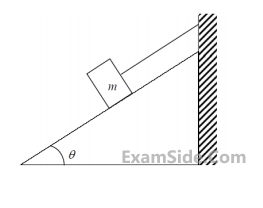
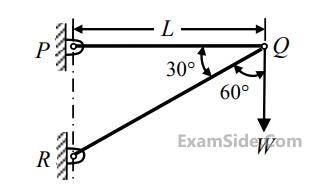
Acceleration due to gravity g = 10 m/s2



The magnitude of the velocity $${V_2}$$ (in $$m/s$$) at the end $$B$ is __________


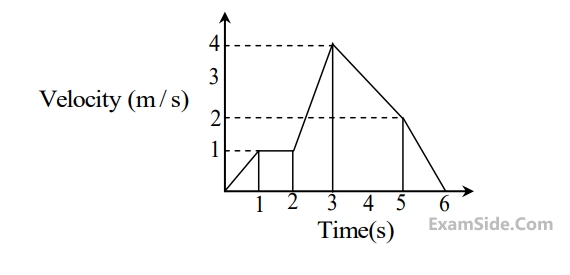
Where v is the instantaneous velocity of the object. The velocity of the object after $$3$$ seconds will be _______

Helical slots are such that one turn of helix is completed over a distance of 0.5m. If velocity of bullet when it exits the barrel is 20m/s, its spinning speed (in rad/s) is ________





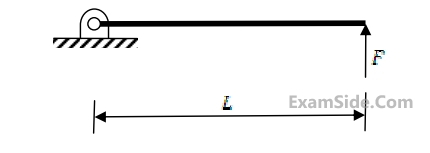

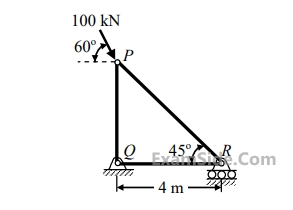
The maximum force F in kN that can be applied at C such that the axial stress in any of the truss members DOES NOT exceed 100MPa is

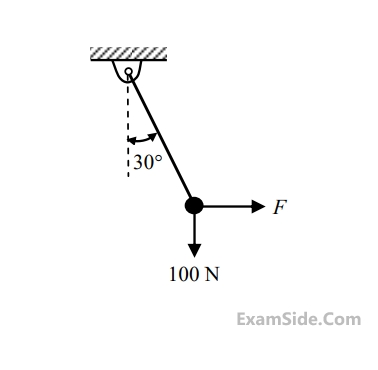
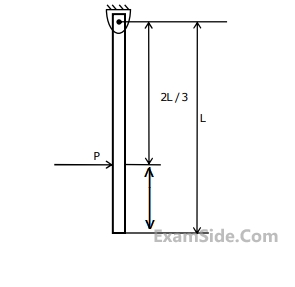
If F = 1 kN, the magnitude of the vertical reaction force developed at the point B in kN is




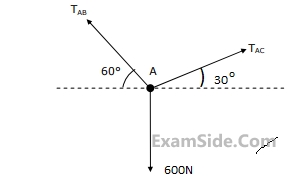






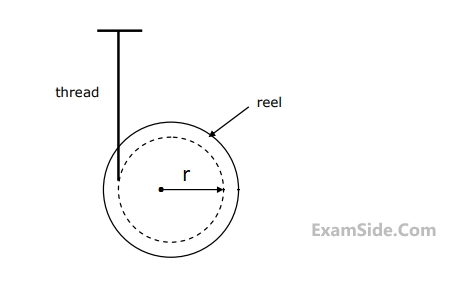
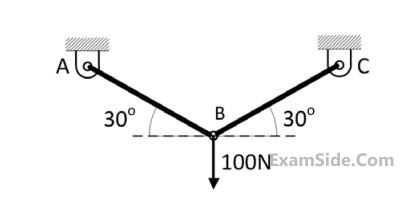
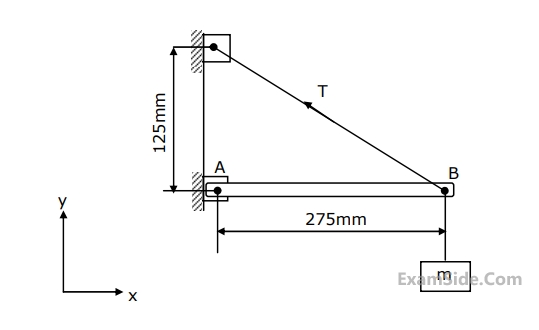
The tension in thread is

The linear acceletation of the reel is:



List $$I$$
(a) Collision of particles
(b) Stability
(C) Satellite motion
(D) Spinning top
List $$II$$
(1) Euler’s equation of motion
(2) Minimum kinetic energy
(3) Minimum potential energy
(4) Impulse-momentum principle
(5) Conservation of moment of momentum
