Calculus · Engineering Mathematics · GATE ME
Marks 1
Let $f(.)$ be a twice differentiable function from $ \mathbb{R}^{2} \rightarrow \mathbb{R}$. If $P, \mathbf{x}_{0} \in \mathbb{R}^{2}$ where $\vert \vert P\vert \vert$ is sufficiently small (here $\vert \vert . \vert \vert$ is the Euclidean norm or distance function), then $f (\mathbf{x}_{0} + p) = f(\mathbf{x}_{0}) + \nabla f(\mathbf{x}_{0})^{T}p + \dfrac{1}{2} p^{T} \nabla^{2}f(\psi)p$ where $\psi \in \mathbb{R}^{2}$ is a point on the line segment joining $\mathbf{x}_{0}$ and $\mathbf{x}_{0} + p$. If $\mathbf{x}_{0}$ is a strict local minimum of $f (\mathbf{x})$, then which one of the following statements is TRUE?
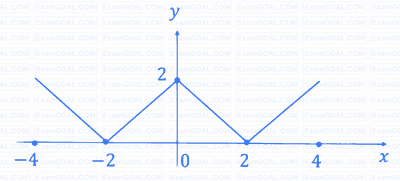
The figure shows the plot of a function over the interval [-4, 4]. Which one of the options given CORRECTLY identifies the function?
Given $\int^{\infty}_{-\infty}e^{-x^2}dx=\sqrt{\pi}$
If a and b are positive integers, the value of $\int^{\infty}_{-\infty}e^{-a(x+b)^2}dx$ is _________.
The limit
$\rm p = \displaystyle\lim_{x \rightarrow \pi} \left( \frac{x^2 + α x + 2 \pi^2}{x - \pi + 2 \sin x} \right)$
has a finite value for a real α. The value of α and the corresponding limit p are
$${\rm I} = \int\limits_0^8 {\int\limits_{{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle x$} \kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em \lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 4$}}}^2 {f\left( {x,\,y} \right)dy\,dx} } $$ leads to $$\,{\rm I} = \int\limits_r^s {\int\limits_p^q {f\left( {x,\,y} \right)dy\,dx} } .$$ What is $$q$$?
Marks 2
In the closed interval $[0,3]$, the minimum value of the function $f$ given below is $f(x)=2 x^3-9 x^2+12 x$
If the value of the double integral
$\int_{x=3}^{4} \int_{y=1}^{2} \frac{dydx}{(x + y)^2}$
is $\log_e(\frac{a}{24})$, then $a$ is __________ (answer in integer).

$$V = \int\limits_0^{2\pi } {\int\limits_0^{{\raise0.5ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle \pi $} \kern-0.1em/\kern-0.15em \lower0.25ex\hbox{$\scriptstyle 3$}}} {\int\limits_0^1 {{r^2}} \,Sin\phi \,drd\phi \,d\theta .} } $$ The value of the integral