Rankine Cycle · Thermodynamics · GATE ME
Marks 1
Which one of the following statements regarding a Rankine cycle is FALSE?
(i) increase in average temperature of heat addition
(ii) reduction in thermal efficiency
(iii) drier steam at the turbine exit
Marks 2
A thermal power plant is running with no reheat or regeneration. The specific enthalpy and specific entropy of steam at the turbine inlet are $3344 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}$ and $6.5 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}$, respectively. The turbine isentropic efficiency is 0.9 , and the mass flow rate of steam at the turbine inlet is $102 \mathrm{~kg} \mathrm{~s}^{-1}$. The turbine power output is ________ MW (rounded off to 1 decimal place). Properties of saturated liquid and saturated vapor at turbine exit pressure
| $$ \text { Saturated liquid water } $$ |
$$ \text { Saturated liquid vapor } $$ |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| $$ \begin{aligned} &\text { Specific entropy }\\ &\left(\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}\right) \end{aligned} $$ |
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { Specific entropy }\\ &\left(\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1} / \mathrm{K}^{-1}\right) \end{aligned} $$ |
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { Specific enthalpy }\\ &\left(\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1}\right) \end{aligned} $$ |
$$ \begin{aligned} &\text { Specific entroopy }\\ &\left(\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{~kg}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1}\right) \end{aligned} $$ |
| 341 | 1.1 | 2645 | 7.6 |
Given data:
For saturated liquid, at $$P=75$$ $$kPa,$$
$$\eqalign{
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{h_f} = 384.39\,\,kJ/kg, \cr
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{v_f} = 0.001037\,\,{m^3}/kg, \cr
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{s_f} = 1.213\,\,kJ/kg K \cr} $$
At $$75$$ $$kPa,$$ $${h_{fg}} = 2278.6\,\,kJ/kg,$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{s_{fg}} = 6.2434\,\,kJ/kg$$-$$K$$
At $$P=3$$ $$MPa$$ and
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,T = {350^ \circ }C\,\,\,$$ (Superheated steam),
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,h = 3115.3\,\,kJ/kg,$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,s = 6.7428\,\,kJ/kg$$-$$K$$
Intermediate stage: $$h=2776$$ $$kJ/kg$$
Exit of turbine : $$P=9kPa,$$ $${h_f} = 174\,\,kJ/kg,$$
$$\eqalign{
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{h_g} = 2574\,\,kJ/kg,\,\,\,{s_f} = 0.6kJ/\left( {kg.K} \right); \cr
& \,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,{s_g} = 8.1\,\,kJ/(kg.K) \cr} $$
If the flow rate of steam entering the turbine is $$100$$ $$kg/s,$$ then the work output (in $$MW$$) is __________.

Disregarding the pump work, the cycle efficiency (in percentage ) is ________________

$$h$$ is specific enthalpy, $$s$$ is specific entropy and $$v$$ the specific volume; subscripts $$f$$ and $$g$$ denote saturated liquid state and saturated vapour state.
The net work output $$(kJ/kg)$$ of the cycle is

$$h$$ is specific enthalpy, $$s$$ is specific entropy and $$v$$ the specific volume; subscripts $$f$$ and $$g$$ denote saturated liquid state and saturated vapour state.
Heat supplied $$(kJ/kg)$$ to the cycle is

If mass flow rate of steam through the turbine is $$20kg/s,$$ the power output of the turbine (in $$MW$$) is

Assume the above turbine to be part of a simple Rankine cycle. The density of water at the inlet to the pump is $$1000$$ $$kg/{m^3}.$$ Ignoring kinetic and potential energy effects, the specific work (in $$kJ/kg$$) supplied to the pump is

The incorporation of re-heater in a steam power plant.
$$P:$$ always increases the thermal efficiency of the plant.
$$Q:$$ always increases the dryness function of steam at condenser inlet.
$$R:$$ always increases the mean temperature of heat addition
$$S:$$ always increases the specific work output.
Assertion(A): In a power plant working on a Rankine cycle, the regenerative feed water heating improves the efficiency of the steam turbine.
Reason(R): The regenerative feed water heating raises the average temperature of heat addition in the Rankine cycle.
Reason(R): For the same mass flow rate and the same pressure rise, a water pump requires substantially less power than a steam compressor.


The thermal efficiency of the plant neglecting pump work is

The enthalpy at the pump discharge $$({h_2})$$ is
Nozzle angle $$=$$ $${20^ \circ };$$
Blade velocity $$= 200$$ $$m/s;$$
Relative steam velocity at entry $$= 350$$ $$m/s;$$
Blade inlet $$30;$$
Blade exit angle $$ = {25^ \circ }.$$
If blade friction is neglected, the work done per $$kg$$ steam is
Marks 5





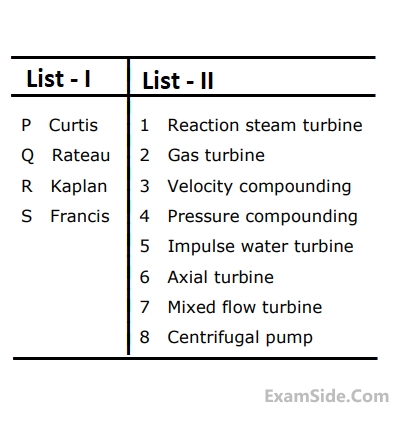
Boiler $$-$$ $$B$$
Feed water heater $$-R$$
Pump $$-P$$