Simple Stress and Strain · Strength of Materials · GATE ME
Marks 1


Marks 2
Cylindrical bars P and Q have identical lengths and radii, but are composed of different linear elastic materials. The Young’s modulus and coefficient of thermal expansion of Q are twice the corresponding values of P. Assume the bars to be perfectly bonded at the interface, and their weights to be negligible.
The bars are held between rigid supports as shown in the figure and the temperature is raised by Δ𝑇. Assume that the stress in each bar is homogeneous and uniaxial. Denote the magnitudes of stress in P and Q by σ1 and σ2, respectively.
Which of the statement(s) given is/are CORRECT?

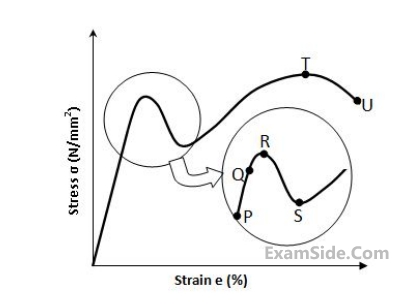
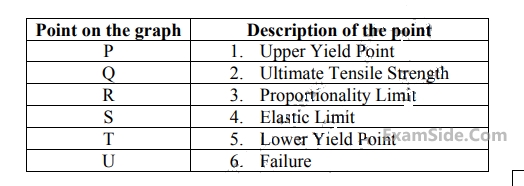
Ignoring the small elastic region, the true stress (𝜎) – true strain (𝜀) variation of a material beyond yielding follows the equation 𝜎 = 400𝜀0.3 MPa. The engineering ultimate tensile strength value of this material is ________ MPa.
(Rounded off to one decimal place)
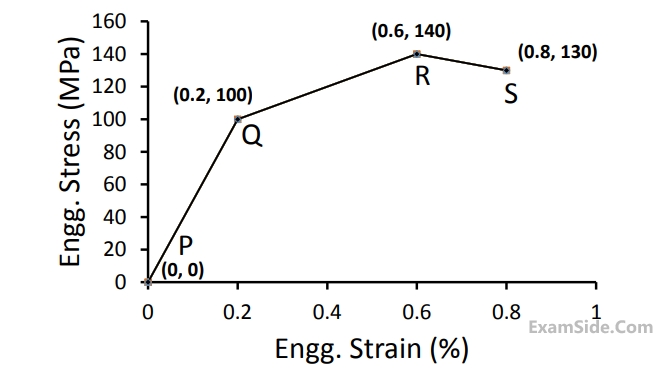
The tougness of the material (in MJ/m3) is __________.
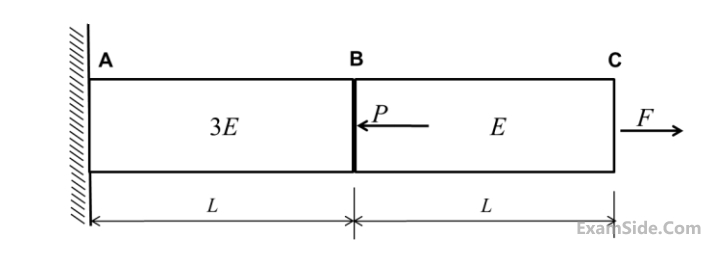
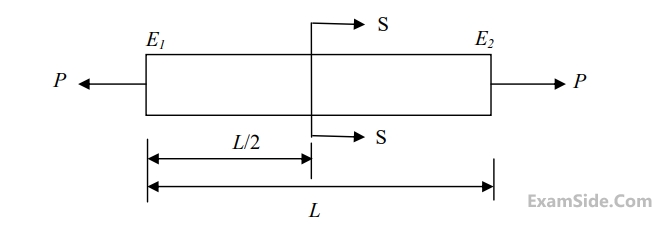
For the deflection at C to be zero, the ratio P/F is ________.

The deformed shape is a square of dimension 𝐿 − 2$$\delta .$$ If 𝐿 = 2 m and $$\delta $$ = 0.001 m, the Poisson’s ratio of the plate material is __________ .

Young’s modulus of the material of the rod is 200 GPa and the coefficient of thermal expansion is 10−5 per oC.

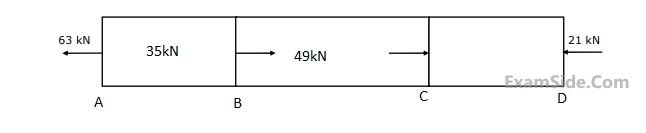
The stress (in Pa) in the link AB is _______.
$$(Indicate\,\,compressive\,\,stress\,\,by\,\,a\,\,negative\,$$
$$\,sign\,\,and\,\,tensile\,\,stress\,\,by\,\,a\,\,positive\,\,sign)$$