Match the additive manufacturing technique in Column I with its corresponding input material in Column II.
|
Additive manufacturing technique (Column I) |
Input Material (Column II) |
||
|
P. |
Fused deposition modeling |
1. |
Photosensitive liquid resin |
|
Q. |
Laminated object Manufacturing |
2. |
Heat fusible power |
|
R. |
Selective laser sintering |
3. |
Filament of polymer |
|
|
|
4. |
Sheet of thermoplastic or green compacted metal sheet |
A square plate is supported in four different ways (configurations (P) to (S) as shown in the figure). A couple moment C is applied on the plate. Assume all the members to be rigid and mass-less, and all joints to be frictionless. All support links of the plate are identical.
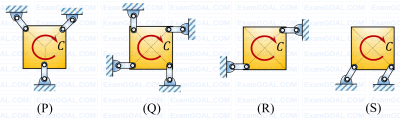
The square plate can remain in equilibrium in its initial state for which one or more of the following support configurations?
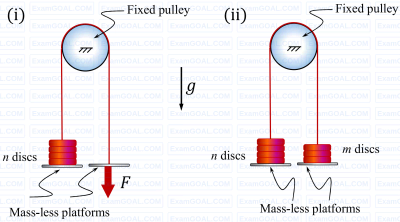
A rope with two mass-less platforms at its two ends passes over a fixed pulley as shown in the figure. Discs with narrow slots and having equal weight of 20 N each can be placed on the platforms. The number of discs placed on the left side platform is n and that on the right side platform is m.
It is found that for n = 5 and m = 0, a force F= 200 N (refer to part (i) of the figure) is just sufficient to initiate upward motion of the left side platform. If the force F is removed then the minimum value of m (refer to part (ii) of the figure) required to prevent downward motion of the left side platform is (in integer).
The plane of the figure represents a horizontal plane. A thin rigid rod at rest is pivoted without friction about a fixed vertical axis passing through O. Its mass moment of inertia is equal to 0.1 kg∙cm2 about O. A point mass of 0.001 kg hits it normally at 200 cm/s at the location shown, and sticks to it. Immediately after the impact, the angular velocity of the rod is ___________ rad/s (in integer).
