A spherical ball weighing 2 kg is dropped from a height of 4.9 m onto an immovable rigid block as shown in the figure. If the collision is perfectly elastic, what is the momentum vector of the ball (in kg m/s) just after impact?
Take the acceleration due to gravity to be 𝑔 = 9.8 m/s2. Options have been rounded off to one decimal place.

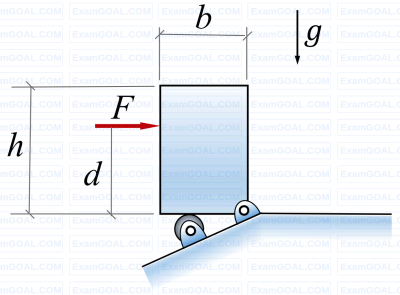
A rigid homogeneous uniform block of mass 1 kg, height h = 0.4 m and width b = 0.3 m is pinned at one corner and placed upright in a uniform gravitational field (g = 9.81 m/s2), supported by a roller in the configuration shown in the figure. A short duration (impulsive) force F, producing an impulse IF is applied at a height of d = 0.3 m from the bottom as shown. Assume all joints to be frictionless. The minimum value of IF required to topple the block is
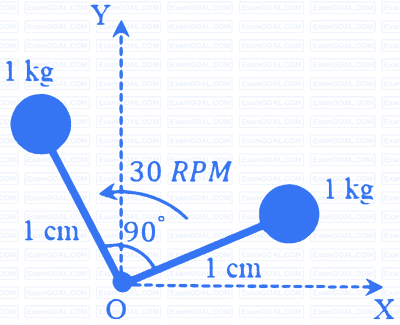
A rigid body in the X-Y plane consists of two point masses (1 kg each) attached to the ends of two massless rods, each of 1 cm length, as shown in the figure. It rotates at 30 RPM counter-clockwise about the Z-axis passing through point O. A point mass of √2 kg, attached to one end of a third massless rod, is used for balancing the body by attaching the free end of the rod to point O. The length of the third rod is ______ cm.
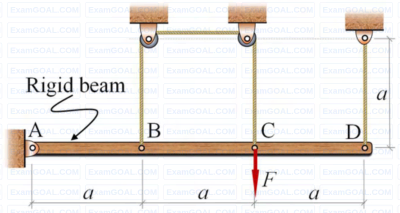
A rigid beam AD of length 3a = 6 m is hinged at frictionless pin joint A and supported by two strings as shown in the figure. String BC passes over two small frictionless pulleys of negligible radius. All the strings are made of the same material and have equal cross-sectional area. A force F = 9 KN is applied at C and the resulting stresses in the strings are within linear elastic limit. The self-weight of the beam is negligible with respect to the applied load. Assuming small deflections, the tension developed in the string at C is KN (round off to 2 decimal places).