1
GATE EE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
$$x\left[ n \right] = 0;\,n < - 1,\,n > 0,\,x\left[ { - 1} \right] = - 1,\,x\left[ 0 \right]$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, = 2$$ is the input and
$$y\left[ n \right] = 0;\,n < - 1,\,n > 2,\,y\left[ { - 1} \right] = - 1,\, = y\left[ 1 \right],\,y\left[ 0 \right] = 3,\,y\left[ 2 \right]$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, =- 2$$ is the output of a discrete-time $$LTI$$ system. The system impulse response $$h\left[ n \right]$$ will be
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, = 2$$ is the input and
$$y\left[ n \right] = 0;\,n < - 1,\,n > 2,\,y\left[ { - 1} \right] = - 1,\, = y\left[ 1 \right],\,y\left[ 0 \right] = 3,\,y\left[ 2 \right]$$
$$\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, =- 2$$ is the output of a discrete-time $$LTI$$ system. The system impulse response $$h\left[ n \right]$$ will be
2
GATE EE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
$$y\left[ n \right]$$ denotes the output and $$x\left[ n \right]$$ denotes the input of a discrete-time system given by the difference equation $$y\left[ n \right] - 0.8y\left[ {n - 1} \right] = x\left[ n \right] + 1.25\,x\left[ {n + 1} \right].$$ Its right-sided impulse response is
3
GATE EE 2006
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
A discrete real all pass system has a pole at $$z = 2\angle {30^ \circ };\,$$ it, therefore,
4
GATE EE 2004
MCQ (Single Correct Answer)
+2
-0.6
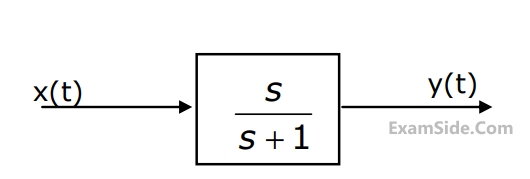
In the system shown in Fig. the input $$x\left( t \right) = \sin t.$$ In the steady-state, the response $$y(t)$$ will be

Questions Asked from Linear Time Invariant Systems (Marks 2)
Number in Brackets after Paper Indicates No. of Questions
GATE EE Subjects
Electromagnetic Fields
Signals and Systems
Engineering Mathematics
General Aptitude
Power Electronics
Power System Analysis
Analog Electronics
Control Systems
Digital Electronics
Electrical Machines
Electric Circuits