Marks 1
The Z-transform of a discrete signal $$x[n]$$ is
$$X(z) = {{4z} \over {(z - {1 \over 5})(z - {2 \over 3})(z - 3)}}$$ with $$ROC = R$$.
Which one of the following statements is true?
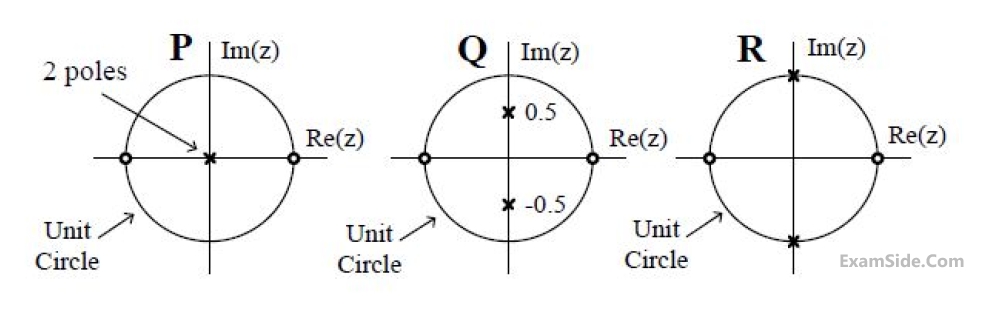 Which one of the following is TRUE about the frequency selectivity of these systems?
Which one of the following is TRUE about the frequency selectivity of these systems?Marks 2
If the Z-transform of a finite-duration discrete-time signal $x[n]$ is $X(z)$, then the Z-transform of the signal $y[n] = x[2n]$ is
The discrete-time Fourier transform of a signal $$x[n]$$ is $$X(\Omega ) = (1 + \cos \Omega ){e^{ - j\Omega }}$$. Consider that $${x_p}[n]$$ is a periodic signal of period N = 5 such that
$${x_p}[n] = x[n]$$, for $$n = 0,1,2$$
= 0, for $$n = 3,4$$
Note that $${x_p}[n] = \sum\nolimits\limits_{k = 0}^{n - 1} {{a_k}{e^{j{{2\pi } \over N}kn}}} $$. The magnitude of the Fourier series coeffiient $$a_3$$ is __________ (Round off to 3 decimal places).
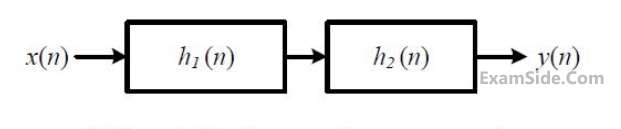 The input sequence x(n) for which the cascade system produces an output sequence
$$$\begin{array}{l}y\left(n\right)=\left\{1,\;2,\;1,\;-1,\;-2,\;-1\right\}\;\;is\\\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow\end{array}$$$
The input sequence x(n) for which the cascade system produces an output sequence
$$$\begin{array}{l}y\left(n\right)=\left\{1,\;2,\;1,\;-1,\;-2,\;-1\right\}\;\;is\\\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\uparrow\end{array}$$$
x[n]=(-0.25)nu[n]+(0.5)nu[-n-1]
The region of convergence of its Z-transform would be